Molotschna
Molotschna Colony or Molochna Colony was a Russian Mennonite settlement in what is now Zaporizhia Oblast in Ukraine. Today the central village is called Molochansk and it has a population of under 10,000. The settlement is named after the Molochna River which forms its western boundary. Today the land falls mostly within the Tokmatskyi and Chernihivskyi Raions. The nearest large city is Melitopol to the southwest of Molochansk.
The colony of Molotschna was founded in 1804 by Mennonite settlers from West Prussia and consisted of 57 villages. The city initially was called Halbstadt (Half-city). Known as the New Colony, it was the second and largest settlement of Mennonites in the Russian Empire. In the late 19th century, hundreds of people left this colony to settle in North America. Colonies there had groups that later relocated to Latin America, where Mennonites settled in several countries. After many ethnic Germans left or were deported during and after the last days of World War II, this area became populated largely by Ukrainians.
History
After the first Mennonite colony within the Russian Empire, Chortitza, was founded in 1789, Mennonite visitors found the freedoms and free land of Southern Ukraine an attractive alternative in view of restrictions placed on them in West Prussia. The imperial Russian government wanted more settlers with the valuable agricultural and craft skills of the Mennonites. In 1800 Paul I of Russia enacted a Privilegium (official privileges) for Mennonites, granting them exemption from military service "for all time". In West Prussia King Frederick William III was making it difficult for Mennonites to acquire land, because of their refusal to serve in the military due to their pacifist religious beliefs. Another reason to immigrate was fear of the changes brought about by the French Revolution. Refuge in Russia was seen as a more secure alternative.
The first settlers, 162 families, emigrated in 1803 to the existing Chortitza settlement and spent the winter there. They founded the first new villages near the Molochna River in 1804. The central Russian government set aside a 1,200 km2 (297,000 acres) tract of land for the settlers along the Molochna River in the Taurida Governorate.[1] The next year an additional group of about the same size arrived. Each family received 0.7 km2 (170 acres) of land.[2] In contrast to the settlement of Chortitza, wealthy Mennonites also immigrated to Molotschna. They sold their farms in Germany, paid a 10% emigration tax, and brought the remainder into the Russian Empire. Arriving with superior farming skills and more wealth, they developed new farms and businesses more easily than had been the case for early settlers in Chortitza. The seaport city of Taganrog provided a convenient market for their dairy products in the early years. Wheat later became the predominant commodity crop.
Between 1803 and 1806, 365 families came to Molotschna. Further immigration was prevented during the Napoleonic Wars. Another 254 families came from 1819-20. After 1835 immigration to Molotschna ended, with about 1200 families, totaling some 6000 people, having moved from Prussia. The settlement consisted of 1,750 km2 (432,000 acres) of land with 46 villages and total population of about 10,000.[1] A part of this was not divided but reserved for future generations, to care for the growing number of families. As the population outgrew the available land, daughter colonies such as Neu Samara Colony were formed.
The settlement was located near the Russian Empire's southern frontier. It was subject to raids by nomadic Crimean Tatars, who had been deported from the Molotschna Valley by the Russian government. After four Mennonites were killed by a raiding party, the imperial government banned the Tatars' spiked and weighted pole weapon which they frequently used on hunting expeditions.[3] Later Mennonites and their neighbors coexisted peacefully.
Local government
Mennonite colonies were self-governing with little intervention from the central authorities in Moscow. The village, the basic unit of government, was headed by an elected magistrate who oversaw village affairs. Each village controlled its own school, roads and cared for the poor. Male landowners decided local matters at village assemblies.
Villages were grouped into districts. Molotschna was divided into two districts: Halbstadt and Gnadenfeld. A district superintendent headed a regional bureau that could administer corporal punishment and handle other matters affecting the villages in common. Insurance and fire protection were handled at the regional level, as well as dealing with delinquents and other social problems. The Mennonite colonies functioned as a democratic state, enjoying freedoms beyond those of ordinary Ukrainian peasants living in Southern Ukraine.[4]
Education
At a time when compulsory education was unknown in Europe, the Mennonite colonies formed an elementary school in each village. Students learned practical skills such as reading and writing German (Plautdietsch dialect), and arithmetic. Religion was included, as was singing in many schools. The teacher was typically a craftsperson or herder, untrained in teaching, who fit class time around his main work.
In 1820 the Molotschna colony started a secondary school at Ohrloff, bringing a trained teacher from Prussia. A school of commerce was started in Halbstadt, employing a faculty with full graduate education. Those who wanted to pursue post-secondary education attended universities in Switzerland, Germany, as well as the Russian Empire.
Johann Cornies
Johann Cornies was perhaps Molotschna's most noted resident. His large estate, Jushanlee, was considered a model farm and showplace of Southern Ukraine. Crown princes of Russia, Alexander I and Alexander II, as well as other government officials visited the estate. His holdings were expanded by gifts from the government for his services and totaled 100 km2 (25,000 acres) at his death. He owned a large herd of thoroughbred cattle, 8000 merino sheep and four hundred horses.[5]
Daughter colonies
As the population of the colony grew and land became scarce, new areas for resettlement were sought. Starting in 1862 settlers from Molotschna formed daughter settlements in the peninsula of Crimea. By 1926 this colony had 25 villages with a total population of 5000.[6] In 1871 the Molotschna colony purchased 240 km2 (59,000 acres) to form the Zagradovka colony in Kherson Oblast.[7] By 1918 Zagradovka was made up of 16 villages with 6000 residents.[6]
In the 1870s the population pressure was eased somewhat when a significant portion of the colony migrated to North America, with many settling in Saskatchewan, Canada. The next daughter colony was formed at Memrik in the Dnipropetrovsk region in 1885. By 1926 this settlement had a population of about 3500, occupying 100 km2 (25,000 acres).[6][8]
Selbstschutz self protection units
Through influence of the short German occupation of Ukraine in 1918, the young men of Molotschna formed a self-defense group (Selbstschutz) for protection of the villages. German soldiers provided training and left weapons and ammunition behind when they retreated. Together with a neighboring Lutheran colony, the Mennonites formed twenty companies totaling 2700 infantry and 300 cavalry, which held back the forces of the Ukrainian anarchist-communist leader Makhno until March 1919. When the Russian communist Red Army combined with Makhno, the self-defense group was forced to retreat to Halbstadt and disband. This attempt to defend the villages departed from the Mennonites' traditional teaching of nonresistance and was disapproved of by many colonists. However, in the absence of effective governmental authority and when faced with the horrific atrocities committed by anarchist partisans, many others came to believe in the necessity of self-defence. Later church conferences and delegations officially condemned this action as a "grave mistake".[9][10]
Famine
Mennonites of Molotschna sent a commission to North America in the summer of 1920 to alert American Mennonites of the dire conditions of war-torn Ukraine. Their plight succeeded in uniting various branches of Mennonites to form the Mennonite Central Committee in an effort to coordinate aid.
The new organization planned to provide aid to Mennonites in Ukraine via existing Mennonite relief work in Istanbul. The Istanbul group, mainly Goshen College graduates, produced three volunteers, who at great risk entered Ukraine during the ongoing Ukrainian Civil War. They arrived in the Mennonite village of Halbstadt just as General Wrangel of the Russian Imperial White Army was retreating. Two of the volunteers withdrew with the Wrangel army, while Clayton Kratz, who remained in Halbstadt as it was overrun by the Red Army, was never heard from again.
A year passed before the Soviet government gave official permission for the international Mennonites to conduct relief work among the villages of Ukraine. Kitchens provided 25,000 people a day with rations over a period of three years beginning in 1922, with a peak of 40,000 servings during August of that year. Fifty Fordson tractor and plow combinations were sent to Mennonite villages to replace horses that had been stolen and confiscated during the war. The cost of this relief effort was $1.2 million.[11]
Evacuation
The residents of Molotschna shared the fate of the Chortitza settlers. They were evacuated to Nazi Reichsgau Wartheland in 1943, and from there marched into Germany, under its national government plans to reunite ethnic Germans. When the Red Army entered Germany, it forcibly repatriated these people to the Soviet Union. They were considered politically suspect and exiled to primitive camps in Siberia and Kazakhstan.
Villages
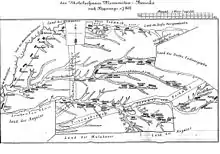
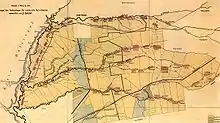
About 57 villages were founded:
| Name | Local name | Founded |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Halbstadt[12] | Molochansk | 1804 |
| 2. Neu-Halbstadt | 1841 | |
| 3. Muntau | 1804 | |
| 4. Schönau | 1804 | |
| 5. Fischau | 1804 | |
| 6. Lindenau | 1804 | |
| 7. Lichtenau | 1804 | |
| 8. Blumstein | 1804 | |
| 9. Münsterberg | 1804 | |
| 10. Altona | 1804 | |
| 11. Ladekopp | 1805 | |
| 12. Schönsee | 1805 | |
| 13. Petershagen | 1805 | |
| 14. Tiegenhagen | 1805 | |
| 15. Ohrloff | 1805 | |
| 16. Tiege | 1805 | |
| 17. Blumenort | 1805 | |
| 18. Rosenort | 1805 | |
| 19. Fürstenau | 1806 | |
| 20. Rückenau | 1811 | |
| 21. Margenau | 1819 | |
| 22. Lichtfelde | Jasna | 1819 |
| 23. Neukirch | 1819 | |
| 24. Alexandertal | 1820 | |
| 25. Schardau | 1820 | |
| 26. Pordenau | 1820 | |
| 27. Mariental | 1820 | |
| 28. Rudnerweide | 1820 | |
| 29. Grossweide | 1820 | |
| 30. Franztal | 1820 | |
| 31. Pastwa | 1820 | |
| 32. Alexanderwohl | 1820[1] | |
| 33. Fürstenwerder | 1821 | |
| 34. Gnadenheim | 1821 | |
| 35. Tiegerweide | 1822 | |
| 36. Liebenau | 1823 | |
| 37. Elisabethtal | 1823 | |
| 38. Wernersdorf | 1824 | |
| 39. Friedensdorf | 1824 | |
| 40. Prangenau | 1824 | |
| 41. Sparrau | 1838 | |
| 42. Konteniusfeld | 1832 | |
| 43. Gnadenfeld | 1835[1] | |
| 44. Waldheim | 1836 | |
| 45. Landskrone | 1839 | |
| 46. Hierschau | 1848 | |
| 47. Nikolajdorf | 1848 | |
| 48. Paulsheim | 1852 | |
| 49. Kleefeld | 1854 | |
| 50. Alexanderkrone | 1857 | |
| 51. Mariawohl | 1857 | |
| 52. Friedensruh | 1857 | |
| 53. Steinfeld | 1857 | |
| 54. Gnadental | 1862 | |
| 55. Hamburg | 1863 | |
| 56. Klippenfeld | 1863 | |
| 57. Fabrikerwiese | 1863 |
Notable residents
- Helmut Oberlander (born 1924), Ukrainian former Canadian who was a member of the Einsatzgruppen death squads of Nazi Germany in the occupied Soviet Union during World War II
- Jakob (Jack) Reimer (1918–2005), Trawniki camp guard born in Friedensdorf, who later emigrated to the United States
See also
- Askania Nova
- Baptists in Ukraine
- History of Christianity in Ukraine
- Protestantism in Ukraine
- Goessel, Kansas (first known as Gnadenfeld village
- Alexanderwohl Mennonite Church near Goessel, Kansas
Notes
- Smith, p. 258.
- Smith, p. 262.
- Smith, p. 259.
- Smith, p. 268.
- Smith, p. 264
- Smith, p. 304.
- Lohrenz, Gerhard (1959). "Zagradovka Mennonite Settlement (Kherson Oblast, Ukraine)". Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. Retrieved 2010-10-06.
- Krahn, Cornelius (1957). "Memrik Mennonite Settlement (Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, Ukraine)". Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. Retrieved 2010-10-06.
- Smith, p. 316.
- Krahn, Cornelius and Al Reimer (1989). "Selbstschutz". Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. Retrieved 2010-10-06.
- Smith, p. 320.
- The center of the Molotschna settlement.
References
- Smith, C. Henry (1981). Smith's Story of the Mennonites. Revised and expanded by Cornelius Krahn. Newton, Kansas: Faith and Life Press. pp. 249–356. ISBN 0-87303-069-9.
External links
- Molotschna Mennonite Settlement (Zaporizhia Oblast, Ukraine) in Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online
- Russian Mennonite Genealogical Resources