Ox (zodiac)
The Ox (牛) is the second of the 12-year periodic sequence (cycle) of animals which appear in the Chinese zodiac related to the Chinese calendar, and also appears in related calendar systems. The Chinese term translated here as ox is in Chinese niú (牛), a word generally referring to cows, bulls, or neutered types of the bovine family, such as common cattle or water buffalo. The zodiacal ox may be construed as male, female, neuter, and either singular or plural. The Year of the Ox is also denoted by the Earthly Branch symbol chǒu (丑). The term "zodiac" ultimately derives from an Ancient Greek term referring to a "circle of little animals". There are also a yearly month of the ox and a daily hour of the ox (Chinese double hour, 1:00 a.m. to 3:00 a.m.). Years of the oxen (cows) are cyclically differentiated by correlation to the Heavenly Stems cycle, resulting in a repeating cycle of five years of the ox/cow (over a sixty-year period), each ox/cow year also being associated with one of the Chinese wǔxíng, also known as the "five elements", or "phases": the "Five Phases" being Fire (火 huǒ), Water (水 shuǐ), Wood (木 mù), Metal (金 jīn), and Earth (土 tǔ). The Year of the Ox follows after the Year of the Rat (the first year of the zodiacal cycle) and it is followed by the Year of the Tiger.


Zodiac
The meaning of zodiacal in the case of the Zodiacal Ox derives from Ancient Greek. There are similarities and differences with the concept of zodiac in Western Astrology.
Meaning
The meaning of zodiac derives from zōdiacus, the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek zōdiakòs kýklos (ζῳδιακός κύκλος), meaning "cycle/circle of little animals". The term "zodiacal" refers to the classification scheme based on the lunar calendar that assigns an animal and its reputed attributes to each year in a repeating 12-year cycle. The 12 year cycle is an approximation to the 11.85-year orbital period of Jupiter.[1] Originating from China, this form of the zodiac (with some variations) have been popular for a long time in many East Asian countries, such as Japan,[2] South Korea,[3] Vietnam,[3] Cambodia,[4] and Thailand.[5]
Differences with Western Astrology
The term "zodiac" reflects similarities and differences with the Western zodiac. Both similarly have cycles divided into twelve parts, with at least the majority of those parts with named for animals, and each is widely associated with an ascription of a person's personality or events in their life to a supposed influence of the person's particular relationship to the cycle. A major difference between the two is that the animals of the Chinese zodiac are not associated with constellations spanned by the ecliptic plane (that is, the part of the sky through which the Sun appears to move from the perspective of Earth). The Chinese/East Asian 12-part cycle corresponds to years, rather than months.
Mythological ox
The ox of the Chinese zodiac has a long history. In Chinese mythology, the many myths about the oxen or ox-like beings include both celestial and earthly types of oxen, as well as other entities. The myths range from ones which include oxen or composite beings with ox characteristics as major actors to ones which focus on human or divine actors, in which the role of the oxen are more subsidiary. In some cases, Chinese myths focus on oxen-related subjects, such as plowing and agriculture or ox-powered carriage. Another important role for beef cattle is in the religious capacity of sacrificial offerings. Chinese mythology intersects with the idea of the zodiacal ox.
Great race
According to some old mythological traditions there was a race held by a great deity to determine which creatures, in which order, would be the namesakes of the twelve-year cycle. The race was run, and swum, the finishing line being across a great river. The Rat and the Ox crossed easily enough, the Ox due to being large, powerful, and adept both on land and in water: the Rat asked the good-natured Ox for a ride on its back, but then ungratefully jumped off at the last minute to cross the finish line first.
Years and the Five Elements
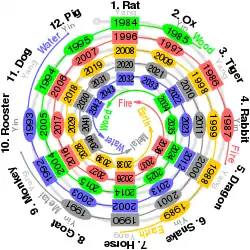
People born within these date ranges can be said to have been born in the "Year of the Ox", while bearing the following elemental phase sign:[6][7]
| Start date | End date | Heavenly branch |
|---|---|---|
| 31 January 1805 | 17 February 1806 | Wood Ox |
| 17 January 1817 | 4 February 1818 | Fire Ox |
| 4 February 1829 | 24 January 1830 | Earth Ox |
| 23 January 1841 | 9 February 1842 | Metal Ox |
| 8 February 1853 | 28 January 1854 | Water Ox |
| 27 January 1865 | 14 February 1866 | Wood Ox |
| 13 February 1877 | 1 February 1878 | Fire Ox |
| 31 January 1889 | 20 January 1890 | Earth Ox |
| 19 February 1901 | 7 February 1902 | Metal Ox |
| 6 February 1913 | 25 January 1914 | Water Ox |
| 24 January 1925 | 12 February 1926 | Wood Ox |
| 11 February 1937 | 30 January 1938 | Fire Ox |
| 29 January 1949 | 16 February 1950 | Earth Ox |
| 15 February 1961 | 4 February 1962 | Metal Ox |
| 3 February 1973 | 22 January 1974 | Water Ox |
| 20 February 1985 | 8 February 1986 | Wood Ox |
| 7 February 1997 | 27 January 1998 | Fire Ox |
| 26 January 2009 | 13 February 2010 | Earth Ox |
| 12 February 2021 | 31 January 2022 | Metal Ox |
| 31 January 2033 | 18 February 2034 | Water Ox |
| 17 February 2045 | 05 February 2046 | Wood Ox |
| 4 February 2057 | 23 January 2058 | Fire Ox |
| 23 January 2069 | 10 February 2070 | Earth Ox |
| 9 February 2081 | 28 January 2083 | Metal Ox |
| 27 January 2093 | 14 February 2094 | Water Ox |
Lunar Mansion
In traditional Chinese astrology as well as traditional Chinese astronomy the sky was mapped into various asterisms or what are sometimes referred to as Chinese constellations. This is actually more similar to the zodiac of Western astrology than is the 12 animal cycle. The stars along the plane of the ecliptic divide into groups known as the Twenty-Eight Mansions. Because the moon during its monthly cycle could be observed to appear to move from one mansion (or "camp") into the next each night in turn, they are also known as Lunar Mansions. Traditionally, these mansions were divided into four groups of seven each, and associated with one of four spiritual entities. This is applicable to the Year of the Ox, Chǒu (丑), a sign linked to the celestial region of the Black Warrior, or Xuánwǔ,[8] linked to the stars of Beta Capricorni, in modern astronomy.
Hour of the Ox
Main Chinese tradition divided the hours of a day-night period into 12 double-hours. Each of these double-hours corresponds with one of the twelve signs of the Chinese zodiac, with similar symbolic motif and astrological significance. The first of the twelve double hours is midnight (at the middle of the double-hour), corresponding with 11:00 p.m. to 1:00 a.m.: this is the Hour of the Rat. The second and next double-hour is the Hour of the Ox: 1:00 a.m. to 3:00 a.m.; that is the double-hour chǒu (丑). [9]
Basic astrology elements
| Earthly Branches of Birth Year: | 丑 Chǒu |
| The Five Elements: | Earth |
| Cardinal Point: | North-Northeast (NNE) |
| Yin/ Yang: | Yin |
| Lunar Month: | Twelfth |
| Season: | Winter |
| Closest Western Zodiac: | Capricorn |
| Earthly Branch Ruling Hours: | 01:00 to 02:59 |
| Twelve Heavenly Generals: | Sanskrit: Caundhula (Hanzi: 招杜羅) |
| Lucky Flowers: | tulip, evergreen, peach blossom, rose |
| Lucky Numbers: | 8, 9, 3; Avoid: 6 |
| Lucky Colors: | blue, red, purple; Avoid: white, green |
Around the world

In the Vietnamese zodiac, the water buffalo occupies the position of the Ox. In Nepal, the Tamu/Gurung people celebrate the year of the cow.[10]
2021–2022
The Year of the Ox does not exactly correspond with years of the commonly used Gregorian calendar. For the 2021–2022 Gregorian time period, the Year of the Ox begins on 12 February 2021 and ends 31 January 2022. This is a year of the Metal Ox.
See also
References
- Dr Zai, J. Taoism and Science: Cosmology, Evolution, Morality, Health and more. Ultravisum, 2015.
- teacher, Namiko Abe Namiko Abe is a Japanese language; translator. "The Twelve Japanese Zodiac Signs". ThoughtCo. Retrieved 16 July 2019.
- "Chinese Zodiac and Chinese Year Animals". astroica.com. Retrieved 16 July 2019.
- "Khmer Calendar". cam-cc.org. Retrieved 19 July 2019.
- "Animals of the Thai Zodiac and the Twelve Year Cycle". Thaizer. 8 September 2011. Retrieved 16 July 2019.
- "When is Chinese New Year?". pinyin.info. Retrieved 13 March 2018.
- "Year of the Ox, Cow: Love Compatibility, Horoscope, Personality – Chinese Zodiac Sign". Your Chinese Astrology. Retrieved 13 March 2018.
- Wu, Zhonxian and Karin Wu (2014, 2016). Heavenly Stems and Earthly Branches:TianGan DiZhi. London and Philadelphia: Singing Dragon, ISBN 978-1-84819-208-9, 28 and 98
- Palmer, Martin, editor, et al, (1986). T'ung Shu: The Ancient Chinese Almanac. Boston: Shambala. ISBN 0-394-74221-4, 34
- Arina Sherchan (11 July 2010). "Tamu (Gurung) Losar Festival". Archived from the original on 29 July 2017. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
Further reading
- Somerville, Neil (2008). Your Chinese Horoscope 2009: What the Year of the Ox Holds in Store for You. HarperCollins. pp. I–VIII. ISBN 9780007283750.
External links
 Media related to Ox (zodiac) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Ox (zodiac) at Wikimedia Commons
