Paucipodia
Paucipodia inermis is a lobopod known from the Lower Cambrian Chengjiang lagerstätte.[1] Its gut is puzzling; in some places, it is preserved in three dimensions, infilled with sediment; whereas in others it may be flat. These cannot result from phosphatisation, which is usually responsible for three-dimensional gut preservation,[2] for the phosphate content of the guts is under 1% – the contents comprise quartz and muscovite.[1] Its fossils do not suggest it had any sclerites, especially when compared with the related Hallucigenia.[1]
| Paucipodia inermis | |
|---|---|
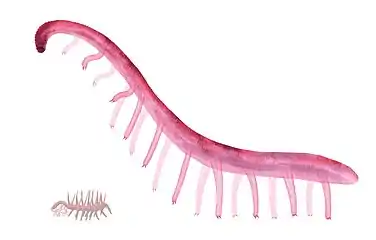 | |
| reconstruction of P. inermis (right), and Hallucigenia sparsa (left) for scale. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| (unranked): | Panarthropoda |
| Phylum: | †"Lobopodia" |
| Class: | †Xenusia |
| Order: | †Archonychophora |
| Family: | †Paucipodiidae Hou et al., 2004 |
| Genus: | †Paucipodia Chen, Zhou & Ramsköld, 1995 |
| Species: | †P. inermis |
| Binomial name | |
| †Paucipodia inermis Chen, Zhou & Ramsköld, 1995 | |
See also
References
- Xian-Guang Hou; Xiao-Ya Ma; Jie Zhao; Jan Bergström (2004). "The lobopodian Paucipodia inermis from the Lower Cambrian Chengjiang fauna, Yunnan, China". Lethaia. 37 (3): 235–244. doi:10.1080/00241160410006555.
- Nicholas J. Butterfield (2002). "Leanchoilia guts and the interpretation of three-dimensional structures in Burgess Shale-type fossils". Paleobiology. 28 (1): 155–171. doi:10.1666/0094-8373(2002)028<0155:LGATIO>2.0.CO;2.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.