People's Liberation Army Ground Force
The People's Liberation Army Ground Force (PLAGF) (simplified Chinese: 中国人民解放军陆军; traditional Chinese: 中國人民解放軍陸軍; pinyin: Zhōngguó Rénmín Jiěfàngjūn Lùjūn) is the land-based service branch of the People's Liberation Army and it is the largest and oldest branch of the entire Chinese armed forces. The PLAGF can trace its lineage from 1927; however, it was not officially established until 1948.

History
In February 1949 the existing large number of armies and divisions were regularised into up to seventy armies of three divisions each. While some, such as the 1st Army, survived for over fifty years, a number were quickly amalgamated and disestablished in the early 1950s. It appears that twenty per cent or even more of the seventy new armies were disestablished up to 1953; in 1952 alone, the 3rd, 4th, 10th, 17th, 18th, and 19th Armies were disbanded.[3]
The PLA ground forces consist of conventionally armed main and regional units, which in 1987 made up over 70 percent of the PLA. It provided a good conventional defense, but in 1987 had only limited offensive potential and was poorly equipped for nuclear, biological, or chemical warfare. Main forces included about 35 group armies, comprising 118 infantry divisions, 13 armored divisions, and 33 artillery and antiaircraft artillery divisions, plus 71 independent regiments and 21 independent battalions of mostly support troops.[4] Regional forces consisted of 73 divisions of border defense and garrison troops plus 140 independent regiments.
Under the old system, a field army consisted of three partially motorized infantry divisions and two regiments of artillery and anti-aircraft artillery.[4] Each field army division had over 12,000 personnel in three infantry regiments, one artillery regiment, one armored regiment, and one anti-aircraft artillery battalion. Organization was flexible, the higher echelons being free to tailor forces for combat around any number of infantry divisions. At least theoretically, each division had its own armor and artillery — actual equipment levels were not revealed and probably varied — and the assets at army level and within the independent units could be apportioned as needed.
In 1987 the new, main-force group armies typically included 46,300 soldiers in up to four divisions, believed to include infantry, armor, artillery, air defense, airborne, and air support elements.[4] Although the new group armies were supposed to reflect a move to combined-arms operations, because of a lack of mechanization they continued to consist of infantry supported by armor, artillery, and other units. The 13 armored divisions each had 3 regiments and 240 main battle tanks (MBT) but lacked adequate mechanized infantry support. There was little evidence of the use of armored personnel carriers during the Sino-Vietnamese border conflict in 1979, and tanks were used as mobile artillery and as support for dismounted infantry. Artillery forces emphasized towed guns, howitzers, and truck-mounted multiple rocket launchers. In the 1980s some self-propelled artillery entered service, but the PLA also produced rocket launchers as a cheaper but not totally effective alternative to self-propelled guns. There was a variety of construction equipment, mobile bridging, trucks, and prime movers. A new multiple rocket launcher for scattering antitank mines appeared in 1979, but mine-laying and mine-clearing equipment remained scarce.
Regional forces consisted of full-time PLA troops organized as independent divisions for garrison missions.[4] Garrison divisions were static, artillery-heavy units deployed along the coastline and borders in areas of likely attack. Regional forces were armed less heavily than their main-force counterparts, and they were involved in training the militia. They were the PLA units commonly used to restore order during the Cultural Revolution. When chairman Mao proclaimed the People's Republic of China on October 1, 1949, PLA ground force was 4.9 million-strong peasant army. After some time, demobilization of ill-trained and politically unreliable troops began, resulting in the reduction of army strength.
While the size of the PLA Ground Force has been reduced over the past few decades, technology-intensive elements such as special operations forces (SOF), army aviation (helicopters), surface-to-air missiles (SAMs), and electronic warfare units have all been rapidly expanded. The latest operational doctrine of the PLA ground forces highlights the importance of information technology, electronic and information warfare, and long-range precision strikes in future warfare. The older generation telephone/radio-based command, control, and communications (C3) systems are being replaced by an integrated battlefield information networks featuring local/wide-area networks (LAN/WAN), satellite communications, unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-based surveillance and reconnaissance systems, and mobile command and control centers.[5]
 Soldiers of the People's Liberation Army Ground Force in 2011
Soldiers of the People's Liberation Army Ground Force in 2011.jpg.webp) Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff Peter Pace shakes hands with Chinese tankers at Shenyang in 2007
Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff Peter Pace shakes hands with Chinese tankers at Shenyang in 2007.jpg.webp) PLAGF and Oregon National Guard work alongside during a disaster response exercise in 2017
PLAGF and Oregon National Guard work alongside during a disaster response exercise in 2017
Structure

Operational structure
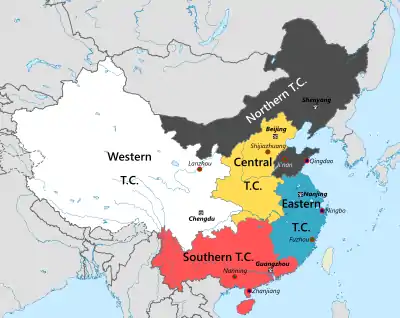
There are 13 corps sized Army groups of China since the end of April 2017, divided among five Theater commands — Eastern, Southern, Northern, Western and Central. Within the Theater Commands, starting 2011, the divisions are being downsized into full brigades (Chinese: 旅; pinyin: Lǚ) - armored, mechanized infantry, field artillery, air defense artillery, engineering and logistics brigades. Many are now full combined arms brigades under these commands, which serve as a Chinese adaptation of the American brigade combat team concept.
The International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) currently attributes the PLA Ground Force with nine active armored divisions consisting of a number of armored brigades and 25 infantry divisions (mechanized or motorized), organized into a number of infantry brigades. Dennis Blasko wrote in 2000[6] that the traditional structure of PLA divisions (armored and mechanized) consisted roughly of three regiments – tuan (Chinese: 团; pinyin: Tuán) (later on brigades) – of the main service arm, each of three battalions (Chinese: 营; pinyin: yíng) plus support units, a fourth regiment/brigade of infantry (in an armored division) or armor (in an infantry division), a field artillery regiment, an anti-aircraft defense regiment or battalion, and signals, engineer, reconnaissance, and chemical defense battalions or companies, plus combat service support units.
A typical PLAGF armored brigade has the brigade HQ, 4 tank battalions (124 main battle tanks) – each tank battalion has 3 tank companies (30 + 1 tank for the battalion commander), 1 mechanized infantry battalion (40 armored personnel carriers), 1 field artillery battalion (18 self-propelled howitzers) – 3 batteries of 6 guns each and 1 air defense artillery battalion plus a support battalion. In a mechanized/motorized infantry brigade, the organization is 4 mechanized/motorized infantry battalions, each wth 40 APCs or infantry fighting vehicles, 1 tank battalion and the rest as in the armored brigades but with either self-propelled or towed guns, together with mortars, in the field artillery battalion.
There are 8 active artillery divisions consisting of a number of artillery brigades. A typical PLAGF artillery brigade has 4 field artillery battalions each with 18 guns in 3 batteries and 1 self-propelled anti-tank gun battalion (18 vehicles).
Brigades are a relatively new formation for the PLAGF. Introduced in the 1990s, the PLAGF plans to expand their number and rid itself of the massive, rigid formations of the Soviet model. As a step towards modernizing its army, this new system allows for smaller, cross-service arm battle groups of battalion size within a brigade to operate independently, increasing the PLA's ability to respond to a rapidly changing battle situation. By the 2000s, the PLAGF had yet to fully take advantage of this new formation, but has been taking steps to successfully integrate it in its force structure, since 2011 the PLAGF has been mostly organized into brigades.
In the 1980s, regional forces consisted of full-time PLA troops organized as independent divisions for garrison missions. An example of such a formation was the 1st Garrison Division of Lanzhou Military Region. Garrison divisions were static, artillery-heavy units deployed along the coastline and borders in areas of likely attack. Regional forces were armed less heavily than their main-force counterparts, and they were involved in training the militia. They were the PLA units commonly used to restore order during the Cultural Revolution.
Special operations forces
The PLA first became interested in modern special warfare in the mid-1980s when it was shifting from the "people's war" to "fighting a local war under hi-tech conditions." The PLA planners believed that the next war would be a short, fast-pace conflict on the periphery rather than a total war on Chinese territories, and conventional infantry-orientated ground forces in their mass numbers could no longer meet the requirements. It specialises in rapid reaction combat in a limited regional war under high-tech conditions, commando operations, counter-terrorism, and intelligence gathering. The size of the Special Operations Forces is estimated at 7,000 ~ 14,000 troops.
 U.S. Defense Secretary Robert Gates greets Chinese Defense Minister Cao Gangchuan in Beijing, China
U.S. Defense Secretary Robert Gates greets Chinese Defense Minister Cao Gangchuan in Beijing, China.jpg.webp) Military guard of the PLAGF in 2012
Military guard of the PLAGF in 2012 PLAGF infantrymen at the 2015 China Victory Day Parade
PLAGF infantrymen at the 2015 China Victory Day Parade
Equipment
In 1987 the PLA ground forces, which relied upon obsolescent but serviceable equipment, were most anxious to improve defenses against armored vehicles and aircraft.[4] Most equipment was produced from Soviet designs of the 1950s, but weapons were being incrementally upgraded, some with Western technology. One example of upgraded, Soviet-design equipment was the Type 69 MBT, an improved version of the Type 59 MBT, itself based on the Soviet T-54. The Type 69 had improved armor, a gun stabilizer, a fire control system including a laser rangefinder, infrared searchlights, and a 105 mm smooth-bore gun. In 1987 the existence of a new, Type 80 MBT was revealed in the Western press. The tank had a new chassis, a 105 mm gun, and a fire control system. The PLA was believed to have atomic demolition munitions, and there were unconfirmed reports that it also had tactical nuclear weapons. In any case, nuclear bombs and missiles in the Chinese inventory could be used in a theater role. The PLA had a scarcity of antitank guided missiles, tactical surface-to-air missiles, and electronics to improve communications, fire control, and sensors. China began production of the Soviet Sagger antitank missile in 1979 but lacked a more powerful, longer range, semiautomatic antitank guided missile. The PLA required a mobile surface-to-air missile and an infantry shoulder-fired missile for use against helicopters and certain other aircraft.
The PLA Ground Forces continue to undergo significant modernisation and re-structuring to deal with potential threats and enhance their capabilities. Front line troops such as special forces, marines and paratroopers are given priority in receiving modern weapon systems and equipment. Other areas of improvement are its battlefield C4ISR capabilities, with the introduction of satellite communications, wireless networks, and digital radios, army commanders are now able to maintain constant communications with their front-line units while on the move. The bulk of the ground forces have been regularly asked to operate under severe electronic countermeasures conditions in exercises. Also a network-centric warfare capability connecting different combat, intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance elements to form an integrated network is being developed.[7]
Approximately 40% of the ground force divisions and brigades are either armoured or mechanized to deal with potential large scale conventional threats. Mechanized infantry are soldiers carried by Infantry Fighting Vehicles or Armored Personnel Carriers. A mechanized infantry squad consists of nine men; six armed with QBZ-95 assault rifles, one machine gunner and crewman, and one RPG gunner. Non-mechanized infantry are soldiers moved by truck. A non-mechanized squad consists of 12 men; the original nine men plus one extra machine gun crew and RPG. Troops wear green-patterned camouflage uniforms, combat helmets, and flak jackets (ballistic vests with ceramic plates are only issued in rare cases). The dismounted squad has two walkie-talkie radios, while the vehicle has a longer range radio and intercom system.[8]
The standard sidearm of PLA ground forces is the QSZ-92, with soldiers and special forces having it chambered in 9×19mm, and commanders and officers in 5.8×21mm DAP92. Vehicle crew are equipped with QBZ-95B short-barreled carbine. The QCW-05 is a 5.8 mm submachine gun used by special forces and non-combat personnel. Sharpshooting is provided by the QBU-88 marksman rifle. The QJB-95 serves as the squad automatic weapon with its 75-round drum magazine.[9] The QJY-88 is a general-purpose machine gun that sometimes used in squads by a two-man crew.[10]
At platoon and company levels, the QJZ-89 and PF-89 is used for fire support.[11] Also at those levels are the QLZ-87 35 mm automatic grenade launcher and the QLU-11 sniper grenade launcher. At company and battalion levels, weapons include the QLZ-04 automatic grenade launcher and the PF-98 anti-tank rocket launcher. The PP-87 82mm mortar is fielded at the battalion level.[10]
Chinese infantry were equipped with Type 07 uniforms and camouflage since 2007. In 2014, the cost to equip a single Chinese soldier is about 9,400 yuan (US$1,523). The standard kit includes the helmet, tactical vest, gas mask, backpack, first-aid kit, Type 95 Rifle, woven belt, rain cap, camouflaged uniform, kettle, and combat boots. However, regular infantrymen rarely use the issued body armor that stored in the armory.[12][13] Prior to 2015, only special operation detachment and soldiers in active mission were equipped with body armor.[14] The infantry equipments such as heavy body armor, personal radio, knee pads has been seen in standard kit in 2015 when PLA are deployed into high risk areas, as observed for units participating in UN Peacekeeping and counter-piracy operations.[15] PLA started to procure body armors for soldiers in large scale since March 2020, with 1.4 millions of body armor on order, which includes 930,000 units of plates for universal bulletproof vests and 467,000 units of plates for enhanced bulletproof vest.[16]
As of 2017, the PLAGF fielded the largest active force of main battle tanks in the world, comprising roughly 3,390 third-generation, 400-500 second-generation, and 2,850 first-generation tanks. First-generation tanks are ZTZ-59-I/II/D license-built variants of the T-54, remaining in service with a significant proportion of the PLA despite even the latest version (upgraded in the 1980s) being obsolete. Second-generation tanks consist of the ZTZ-79 (though sometimes considered first-gen) and ZTZ-88/B; both had limited production runs in the 1980s and 1990s respectively and are now only in the inventory of units in northern and western China, with ZTZ-79s largely being exported. The bulk of China's third-generation tank force is made up of some 2,500 ZTZ-96/A/B tanks, as well as more than 600 ZTZ-99/A tanks, though due to high cost they were produced in relatively small numbers and issued to strategic-reserve units near Beijing. China also has designed the new ZTQ-15 light tank for service in high-altitude regions.[17]
Equipment Summary
The PLAGF inventory maintains an array of military vehicles. All figures below are provided by the Centre for Land Warfare Studies.[18]
| Type | Active |
|---|---|
| Main battle tanks | 7,950[18] |
| Light tanks | 1,200[18] |
| Infantry fighting vehicles | 1,490[18] |
| Armoured personnel carriers | 3,298[18] |
| Towed artillery | 6,246[18] |
| Self-propelled artillery | 1,710[18] |
| Rocket artillery | 1,770[18] |
| SAM systems | 1,531[18] |





.jpg.webp) Infantrymen with QBZ-95
Infantrymen with QBZ-95
Relationship with other Organizations

The People's Liberation Army Ground Force maintains close relationships with several paramilitary organizations within China, primarily the People's Armed Police (PAP) and the Militia (also known as the China Militia). Both of these paramilitary organisations act as a reserve force for the PLAGF during a time of national emergency such as war or natural disaster. The PAP consists of approximately 1.5 million personnel. Their primary mission during peacetime is internal security and counter-terrorism.[19][20] The Militia is a mass force engaged in daily production under the leadership of the Communist Party of China (CPC), and forms part of the Chinese armed forces. Under the command of the military organs, it undertakes such jobs as war preparation services, security and defense operation tasks and assistance in maintaining social order and public security. The Militia numbers some 3 million service men and women.[21][22]
See also
References
Citations
- International Institute for Strategic Studies: The Military Balance 2018, p. 251.
- "Chinese army soldiers conduct first mission as peacekeepers in Mali 1612131 - Army Recognition". Armyrecognition.com. Retrieved 2014-02-11.
- "陆军军史:中国解放军第三军". www.360doc.com. Archived from the original on 2018-03-10. Retrieved 2017-07-21.
- Warden, Robert L.; Savada, Andrea; Dolan, Ronald; Library of Congress, Federal Research Division (1988). "China: A Country Study". pp. 582–3. Retrieved 2017-07-21.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- "Chinese Ground Forces". SinoDefence.com. Archived from the original on 2013-11-04. Retrieved 2010-02-12.
- Chapter 8, PLA Ground Forces, by Dennis J Blasko, in The People's Liberation Army as Organisation, RAND, CF182
- "World's Largest Army, Largest Army in the World". World's Largest Army, Largest Army in the World. Archived from the original on 2008-10-17. Retrieved 2008-11-07.
- Chinese squad – Strategypage.com, September 1, 2012
- "QBZ-95 family". Gun’s World.
- PLA Infantry Weapons: Small Arms of the World’s Largest Army - SAdefensejournal.com, 29 April 2014
- Indigenous Machine Guns of China - SAdefensejournal.com, 20 March 2014
- "Cost of PLA infantry".
- The Minuscule Cost of Equipping a Chinese Soldier - WSJ.com, 8 December 2014
- "Chinese peacekeeping force equipment questioned".
- "How much does PLA soldier's individual equipment cost?". www.iiss.com. China Military Online. 8 December 2014. Retrieved 18 January 2015.
- "Chinese to procure body armor".
- China Now Has the World's Largest Active Service Tank Force - TheDiplomat.com, 15 February 2018
- People’s Liberation Army Ground Forces Modernisation Archived 2013-01-23 at the Wayback Machine 2012, Page 48- 52
- Top legislature passes armed police law. China Daily. August 27, 2009.
- Wines, Michael (August 27, 2009). China Approves Law Governing Armed Police Force . The New York Times.
- The Components of the Armed Forces Archived 2012-08-09 at the Wayback Machine, PRC's official website
- "China's Armed Forces, CSIS (Page 24)" (PDF). 2006-07-25.
Sources
- International Institute for Strategic Studies (2018). The Military Balance 2018. Routledge. ISBN 978-1857439557.
- Sinodefence.com – Chinese military information website
- Global Defence Forum
 This article incorporates public domain material from the Library of Congress Country Studies website http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/cntoc.html.
This article incorporates public domain material from the Library of Congress Country Studies website http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/cntoc.html.