Red River Rebellion
The Red River Rebellion (or the Red River Resistance, Red River uprising, or First Riel Rebellion) was the sequence of events that led up to the 1869 establishment of a provisional government by the Métis leader Louis Riel and his followers at the Red River Colony, in what is now the Canadian province of Manitoba. For a period it had been a territory called Rupert's Land under control of the Hudson's Bay Company.
| Red River Rebellion Résistance de la rivière Rouge (French) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 The Métis provisional government | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
| |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| None | 1 (Thomas Scott) | ||||||
The Resistance was the first crisis the new federal government faced following Canadian Confederation in 1867. The Canadian government had bought Rupert's Land from the Hudson's Bay Company in 1869 and appointed an English-speaking governor, William McDougall. He was opposed by the French-speaking, mostly Métis inhabitants of the settlement. Before the land was officially transferred to Canada, McDougall sent out surveyors to plot the land according to the square township system used in the Public Land Survey System. The Métis, led by Riel, prevented McDougall from entering the territory. McDougall declared that the Hudson's Bay Company was no longer in control of the territory and that Canada had asked for the transfer of sovereignty to be postponed. The Métis created a provisional government, to which they invited an equal number of Anglophone representatives. Riel negotiated directly with the Canadian government to establish Manitoba as a province.
Meanwhile, Riel's men arrested members of a pro-Canadian faction who had resisted the provisional government. They included an Orangeman named Thomas Scott. Riel's government tried and convicted Scott, and executed him for threatening to murder Louis Riel.[1] Canada and the Assiniboia provisional government soon negotiated an agreement. In 1870, the Parliament of Canada passed the Manitoba Act, allowing the Red River Colony to enter Confederation as the province of Manitoba. The Act also incorporated some of Riel's demands, such as the provision of separate French schools for Métis children and protection for the practice of Catholicism.
After reaching an agreement, Canada sent a military expedition to Manitoba to enforce federal authority. Now known as the Wolseley Expedition (or Red River Expedition), it consisted of Canadian militia and British regular soldiers led by Colonel Garnet Wolseley. Outrage grew in Ontario over Scott's execution, and many eastern folks demanded that Wolseley's expedition arrest Riel for murder and suppress what they considered to be rebellion.[1] Riel peacefully withdrew from Fort Garry the day the troops arrived. Warned by many that the soldiers would harm him, and denied amnesty for his political leadership of the rebellion, Riel fled to the United States. The arrival of troops marked the end of the Rebellion.
Background

During the late 1860s, the Red River Colony of Rupert's Land was changing rapidly. It had developed under the aegis of the Hudson's Bay Company, which had a continent-wide trading and commercial network. They had been confirmed on this territory by Queen Anne, who had evicted from it Louis XIV and his subjects through the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht.[2] Further notice was given when in 1763 George III dispossessed Louis XV of nearly all his North American colonies in the Treaty of Paris.
Historically, the population had been composed mainly of Francophone Métis, who developed an ethnicity of mixed First Nations-French descent and a unique culture during the decades of the fur trade. During the 18th and 19th centuries, they married among themselves, establishing a tradition of the men working as trappers, guides and interpreters to fur traders, as well as developing farms. Métis women also were sometimes active in the trade, as among several influential families in Sault Ste. Marie in the early 19th century in which the husbands were European. The Métis culture was based on the French language and Roman Catholic religion.
From the later 18th century, as English and Scots men entered the fur trade, they too married into the Ojibwe people and other First Nations in this region. Their mixed-race descendants were generally English-speaking and were sometimes known as the "country born" (also as Anglo-Métis). The third group of settlers to the region were a small number of Presbyterian Scottish settlers. More Anglophone Protestants began to settle there from Ontario in the 19th century.[3]
The newer settlers were generally insensitive to Métis culture and hostile to Roman Catholicism, and many advocated Canadian expansionism. At the same time, many Americans migrated there, some of whom favored annexation of the territory by the United States. Against this backdrop of religious, nationalistic, and ethnic tensions, political uncertainty was high. To forestall United States expansionism and bring law and order to the wild, the British and Canadian governments had been for some time negotiating the transfer of Rupert's Land from the Hudson's Bay Company to Canada. The Rupert's Land Act 1868 authorized the transfer.[4] On December 1, 1869, Canada purchased the territory.
In anticipation of the transfer, the minister of public works, William McDougall, who along with George-Étienne Cartier had been instrumental in securing Rupert's Land for Canada, ordered a survey party to the Red River Colony.[5] Catholic Bishop Taché, the Anglican bishop of Rupert's land Robert Machray, and the HBC governor of Assiniboia William Mactavish all warned the federal government that such surveys would precipitate unrest. Headed by Colonel John Stoughton Dennis, the survey party arrived at Fort Garry on August 20, 1869. The Métis were anxious about it, as they did not possess clear title to their lands but held a tenuous right of occupancy. In addition, the lots had been laid out according to the French seigneurial colonial system, with long, narrow lots fronting the river, rather than the square lots preferred by the English.[6] The Métis considered the survey to be a forerunner of increased Canadian migration to the territory, which they perceived as a threat to their way of life — more specifically, they feared to lose their farms.[7] The larger fear was for losing their language and Catholic religion, and facing marginalization and discrimination in their homeland.
Riel emerges as a leader

The Canadian government appointed the notoriously anti-French McDougall as the Lieutenant Governor of the North-West Territories-designate on September 28, 1869, in anticipation of a formal transfer to take effect on December 1. This increased tensions among the Métis. In July 1869, the Metis suspicions had increased when McDougall ordered a survey of the settlement. Emerging as a leader, Louis Riel, who had been formally educated in European-style schools, denounced the survey in a speech delivered in late August from the steps of Saint Boniface Cathedral. His lifestyle was very different from those of buffalo-hunting Metis. When Riel returned to the west, it was apparent that MacDonald fearing the United States was negotiating with HBC for the transfer Rupert's land without consulting the Red River population and the Council of Assiniboia. On October 11, 1869, Riel and other Métis disrupted the survey's work. On October 16 this group organized the "Métis National Committee" to represent Métis interests. Riel was elected secretary, John Bruce as president, and two representatives were elected from each parish.[8][9]
There were originally two resistance groups in Red River. One was led by Riel, while the other was led by a Metis named William Dease. Dease expressed the Metis values in his oppositions. For a long time, they were locked in a power struggle. The struggle was on a symbolic level, in while the two sides offered different perspectives on Metis unity. It wasn't until Riel had defeated Dease for the leadership of the resistance and consolidated his support system within the French Metis community that he felt strong enough to initiate the breach of October 1869.[10]
Because the Hudson's Bay Company's Council of Assiniboia still had authority over the area, its representatives summoned Riel on October 25 to explain the actions of the committee.[10] On October 30, McDougall had reached the border despite the written order from Riel. Riel declared that any attempt by McDougall to enter the Red River Colony would be blocked unless the Canadians first negotiated terms with the Métis and with the general population of the settlement.
On November 2 under the command of Ambroise-Dydime Lépine, the Métis turned back McDougall's party near the United States border and forced them to retreat to Pembina, Dakota Territory.[11] The number of Riel's followers had grown rapidly. That same day Riel led about 400, who were recruited from the fur-brigades who had recently returned to the settlement for the season, in seizing Fort Garry without bloodshed.[12] This would come to be known as one of Riel's most brilliant moves, as control of the fort symbolized control of all access to the settlement and the northwest.
Residents of the Red River Colony disagreed over how to negotiate with Canada; in particular, the French- and English-speaking inhabitants did not have a consensus on how to proceed. In a conciliatory gesture, Riel on November 6 asked the Anglophones to select delegates from each of their parishes to attend a convention with the Métis representatives. After few accomplishments at the first meeting, James Ross expressed displeasure at Riel's treatment of McDougall. Riel angrily denied this. It was then that he also stated that he had no intentions of invoking American interventions, and instead throughout the entire resistance he insisted that he and the Metis were loyal subjects of the queen.[13]
On November 16, the Council of Assiniboia made a final attempt to assert its authority when Governor Mactavish issued a proclamation ordering the Métis to lay down their arms. Instead, on November 23 Riel proposed the formation of a provisional government to replace the council of Assiniboia to enter into direct negotiations with Canada. The Anglophone delegates requested an adjournment to discuss matters. They did not succeed in rallying the English-speaking parishes behind this move. Nor did they originally approve of the “List of Rights”, which was presented to the convention on December 1, after McDougall's proclamation. Despite his Métis sympathies, Governor Mactavish did not do enough to end the conflict, and was imprisoned by Riel shortly after.[14]
On December 1, McDougall proclaimed that the Hudson's Bay Company was no longer in control of Rupert's Land and that he was the new lieutenant-governor. This proclamation was to later prove problematic, as it effectively ended the authority of the council while failing to establish Canadian authority. Unbeknownst to McDougall, the transfer had been postponed once news of the unrest reached Ottawa.
Near the middle of December 1869, Riel presented the convention with a list of 14 rights as a condition of union. These included representation in Parliament, a bilingual legislature and chief justice, and recognition of certain land claims. While the convention did not adopt the list at the time, once the list of rights was generally known, the majority of Anglophones accepted most of the demands as reasonable.
While much of the settlement was moving toward the Métis point of view, a passionately pro-Canadian minority was becoming more resistant. It was loosely organized as the Canadian Party and led by Dr. John Christian Schultz and Charles Mair. Colonel Dennis and Major Charles Boulton also supported it. McDougall appointed Dennis to raise a militia to arrest the Métis who were occupying Upper Fort Garry. The Anglophone settlers largely ignored this call to arms, and Dennis withdrew to Lower Fort Garry. Schultz, however, was emboldened to fortify his house and store and attracted approximately 50 recruits.[15]
Riel took the threat seriously and ordered Schultz's home surrounded. The resisters surrendered on December 7 and were imprisoned in Fort Garry.[16] Given the unrest and absence of a clear authority, the Métis National Committee declared a provisional government on December 8. Having received notification of the delay in the union until the British government of the HBC could guarantee a peaceful transfer, McDougall and Dennis departed for Ontario on December 18. Major Boulton fled to Portage la Prairie.
Provisional government

In Ottawa, Governor General Lord Lisgar had, at the behest of Prime Minister John A. Macdonald, proclaimed an amnesty on December 6 for all in the Red River area who would lay down their arms. He dispatched the Abbé Jean-Baptiste Thibault and Charles-René d'Irumberry de Salaberry on a mission of reconciliation, but failed to give them the authority to negotiate on behalf of the Government. Macdonald appointed HBC representative Donald Alexander Smith as special commissioner with greater authority to negotiate.[12][17]
On December 27, John Bruce resigned as president of the provisional government, and Riel was elected president. On the same day, Donald Smith arrived in the settlement, followed shortly by de Salaberry, joining Thibault, who had arrived on Christmas Day. They met with Riel on January 5, 1870, but reached no conclusions. The next day, Riel and Smith had another meeting. At this time Smith concluded that negotiation with the committee would be fruitless. He maneuvered to bypass them and present the Canadian position at a public meeting.[18]
Meetings were held on January 19 and January 20. With Riel acting as translator, Smith assured the large audiences of the Canadian government's goodwill, intention to grant representation, and willingness to extend concessions with respect to land claims. With the settlement now solidly behind him, Riel proposed the formation of a new convention of forty representatives, split evenly between French- and English-speaking settlers, to consider Smith's instructions. This was accepted. A committee of six outlined a more comprehensive list of rights, which the convention accepted on February 3. Following meetings on February 7 wherein the new list of rights were presented to Thibault, de Salaberry, and Smith, Smith proposed that a delegation be sent to Ottawa to engage in direct negotiations with Canada, a suggestion eagerly accepted by Riel.[18] At this time Riel also proposed that the provisional government should be reformed so as to be more inclusive of both language groups. A constitution enshrining these goals was accepted by the convention on February 10. An elected assembly was established, consisting of 12 representatives from anglophone parishes and 12 representatives from francophone parishes.
Canadian resistance and the execution of Scott
Despite the progress on the political front and the inclusion of Anglophones within the provisional government, the Canadian contingent was not yet silenced. On January 9 many prisoners escaped from the prison at Fort Garry, including Charles Mair, Thomas Scott and ten others. John Schultz escaped on January 23. By February 15, Riel freed the remaining prisoners on parole to refrain from engaging in political agitation. Schultz, Mair, and Scott intended to continue to work to depose the Métis from power.[1]

Mair and Scott proceeded to the Canadian settlements surrounding Portage la Prairie, where they met Boulton, while Schultz sought recruits in the Canadian parishes downstream. On February 12, Boulton led a party from Portage la Prairie to rendezvous at Kildonan with Schultz's men. They intended to overthrow the provisional government. Boulton had misgivings, and turned the party back. Riel's forces detected the men, and on February 17, Boulton, Scott and 46 other men were captured near Fort Garry. On hearing this news, Schultz and Mair fled to Ontario.
Riel demanded that an example be made of Boulton. He was tried and sentenced to death for his interference with the provisional government. Intercessions on his behalf by Donald Smith and others resulted in his pardon, but only after Riel obtained assurances from Smith that he would persuade the English parishes to elect provisional representatives. However, the prisoner Thomas Scott, an Orangeman, interpreted Boulton's pardon as weakness on the part of the Métis, whom he regarded with open contempt. After he repeatedly quarreled with his guards, they insisted that he be tried for insubordination. At his trial, which was overseen by Ambroise-Dydime Lépine, he was found guilty of insulting the president, defying the authority of the provisional government, and fighting with his guards. He was sentenced to death despite the fact that these were not considered capital crimes at the time. Smith and Boulton asked Riel to commute the sentence, but Smith reported that Riel responded to his pleas by saying
- "I have done three good things since I have commenced; I have spared Boulton's life at your instance, I pardoned Gaddy, and now I shall shoot Scott."[19]
Scott was executed by a firing squad on March 4, 1870. Historians have debated Riel's motivations for allowing the execution, as they consider it his one great political blunder. His own justification was that he felt it necessary to demonstrate to the Canadians that the Métis must be taken seriously.[1]
Creation of Manitoba
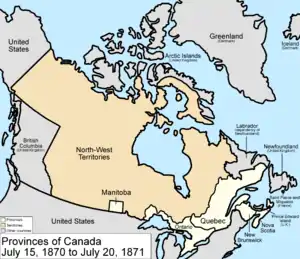
Upon receiving news of the unrest, Bishop Taché was recalled from Rome. He arrived back in the colony on March 8, whereupon he conveyed to Riel his mistaken impression that the December amnesty would apply to both Riel and Lépine. On March 15 he read to the elected assembly a telegram from Joseph Howe indicating that the government found the demands in the list of rights to be " in the main satisfactory". Following the preparation of a final list of rights, which included new demands such as a general amnesty for all members of the provisional government and provisions for separate francophone schools, delegates Abbé Joseph-Noël Ritchot, Judge John Black and Alfred Henry Scott departed for Ottawa on March 23 and 24.[8]
Shortly after this, Mair and Schultz arrived in Toronto, Ontario. Assisted by George Taylor Denison III, they immediately set about inflaming anti-Métis and anti-Catholic sentiment in the editorial pages of the Ontario press over the execution of Scott. But, Macdonald had decided before the provisional government was established that Canada must negotiate with the Métis. Although the delegates were arrested following their arrival in Ottawa on April 11 on charges of abetting murder, they were quickly released. They soon entered into direct talks with Macdonald and Cartier, wherein Ritchot emerged as an effective negotiator; an agreement enshrining many of the demands in the list of rights was soon reached. This formed the basis for the Manitoba Act of May 12, 1870, which admitted Manitoba into the Canadian confederation on July 15.[20][21]
The government had to deal with several issues before peace could be made, fortunately for the government, they would reach an agreement. With the creation of Manitoba, the government would gain control over a new area and not have to worry about the Metis being upset as they would also be gaining control over the land.
On May 12, 1870, the Metis had been given two hundred thousand hectares of land which would make up the province of Manitoba. This would allow for the Metis to hunt freely in their land and have some form of government with legitimate powers to run the province and protect the Metis rights. Even though the government had created the province of Manitoba for the Metis, it also allowed the government to have control over the province without being responsible for any events that may occur within the province. Manitoba would be the first province created from the Northwest Territories.
Significantly, however, Ritchot could not secure a clarification of the Governor General's amnesty — anger over Scott's execution was growing rapidly in Ontario, and any such guarantee was not politically expedient. The delegates returned to Manitoba with only a promise of a forthcoming amnesty.[7]
The Wolseley expedition

A military expedition had in any case been decided on as a means of exercising Canadian authority in the Red River settlement and dissuading the Minnesota expansionists: in May it embarked, under Colonel Garnet Wolseley, and made its way up the Great Lakes. Ontarians especially believed the Wolseley Expedition was intended to suppress the rebellion, although the government described it as an "errand of peace". Knowing he would be arrested and charged with criminal acts, and believing that members of the Canadian militia in the expedition meant to lynch him, Riel and his followers fled hurriedly when the troops arrived unexpectedly at Fort Garry on August 24 in pouring rain.[22] The arrival of the expedition at Fort Garry marked the effective end of the Red River Rebellion.[8]
Legacy
The Red River resistance was described as a rebellion only after sentiment grew in Ontario against the execution of Thomas Scott. Historian A. G. Morice suggests that the phrase "Red River Rebellion" owes its persistence to alliteration, a quality that made it attractive for publication in newspaper headlines (Critical History of The Red River Insurrection [1935]).
In 1875, Riel was formally exiled from Canada for five years. Under pressure from Quebec, the government of Sir John A. Macdonald took no more vigorous action. Riel was elected to the Canadian parliament three times while in exile, but never took his seat. He returned to Canada in 1885 to lead the ill-fated North-West Rebellion. He was subsequently tried and convicted for high treason and executed by hanging.[8]
In popular culture
Canadian folk singer-writer James Keelaghan wrote a song "Red River Rising" about the Red River Rebellion.[23]
References
- Scott, Thomas. "Dictionary of Canadian Biography". Retrieved 2013-12-21.
- A Collection of Treaties Between Great Britain and Other Powers (1790). See Article X, p.379.
- Joseph James Hargrave (1871), Red River (Red River. ed.), Montreal: Printed for the author by J. Lovell, p. 182, OCLC 5035707
- "American Expansionism". Library and Archives Canada. 2015-03-26. Retrieved 2015-05-10.
- McDougall, William. "Dictionary of Canadian Biography". Retrieved 2013-12-21.
- Dennis, John Stoughton. "Dictionary of Canadian Biography". Retrieved 2013-12-21.
- Richot, Noël-Joseph. "Dictionary of Canadian Biography". Retrieved 2015-05-20.
- "Louis Riel". Library and Archives Canada. 2015-03-26. Retrieved 2015-05-10.
- "Prologue to the Red River Resistance: Preliminal Politics and the Triumph of Riel" (PDF). The Canadian Historical Association. 1994. Retrieved 2017-12-06.
- "Canadian Confederation (John Black)". Library and Archives Canada. 2015-03-26. Retrieved 2015-05-10.
- Lépine, Ambroise-Dydime. "Dictionary of Canadian Biography". Retrieved 2014-12-26.
- "Manitoba (1870)". Library and Archives Canada. 2015-03-26. Retrieved 2015-05-10.
- Riel, Louis. "Dictionary of Canadian Biography". Retrieved 2017-12-07.
- "Biography – MACTAVISH, WILLIAM – Volume IX (1861-1870) – Dictionary of Canadian Biography". Retrieved 2018-01-23.
- Schultz, Sir John Christian. "Dictionary of Canadian Biography". Retrieved 2013-12-21.
- Mactavish, William. "Dictionary of Canadian Biography". Retrieved 2017-12-07.
- Martin, Joseph E. (2017). "Titans". Canada's History. 97 (5): 47–53. ISSN 1920-9894.
- Smith, Donald Alexander. "Dictionary of Canadian Biography". Retrieved 2015-05-20.
- Charles Arkoll Boulton (1985). I Fought Riel: A Military Memoir. James Lorimer & Company. p. 51. ISBN 978-0-88862-935-7.
- "Manitoba Act". Library and Archives Canada. 2015-03-26. Retrieved 2015-05-10.
- "Manitoba Act (Page 2)". Library and Archives Canada. 2015-03-26. Retrieved 2015-05-10.
- Wallace, Nesbitt Willougby. The Rebellion in the Red River Settlement (Peel's Prairie Provinces website), p. 29
- Marsh, James H., ed. (2000). "Red River Rising". The Canadian Encyclopedia. McClelland and Stewart. p. 1237. ISBN 0-7710 2099 6. Retrieved 14 October 2017.
Further reading
- Boulton, Charles A. (1886) Reminiscences of the North-West Rebellions. Toronto. Online text
- W. L. Morton. (1956) Alexander Begg's Red River Journal and Other Papers Relative to the Red River Resistance of 1869-1870. Toronto: Champlain Society Publications.
- Stanley, George F.G. (1963). Louis Riel. Ryerson Press, Toronto. ISBN 0-07-092961-0.
- Stanley, George F.G. (1989) Toil & Trouble: Military Expeditions to Red River. ISBN 1-55002-059-5
- Siggins, Maggie (1994). Riel: a life of revolution. HarperCollins, Toronto. ISBN 0-00-215792-6.