Shaoguan
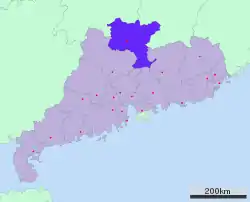
Shaoguan[1] (Chinese: 韶关; Hakka: Seukoan) is a prefecture-level city in northern Guangdong Province, China, bordering Hunan to the northwest and Jiangxi to the northeast. It is home to the mummified remains of the sixth Zen Buddhist patriarch Huineng. Its built-up or metro area made up of Zhenjiang and Wujiang urban districts was home to 688,229 inhabitants at the 2010 census.[2]
Shaoguan
韶关市 Shiukwan | |
|---|---|
 Aerial view of Shaoguan in February 2016 | |
| |
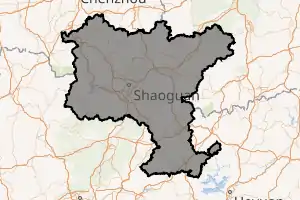
 Location of Shaoguan City jurisdiction in Guangdong | |
 Shaoguan Location in China | |
| Coordinates (Shaoguan municipal government): 24°48′40″N 113°35′49″E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Guangdong |
| County-level divisions | 10 |
| Municipal seat | Zhenjiang District |
| Government | |
| • CPC Secretary | Jiang Ling (江凌) |
| • Mayor | Luo Weifeng (骆蔚峰) |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 18,645 km2 (7,199 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 2,870.7 km2 (1,108.4 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,249.9 km2 (482.6 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 59 m (194 ft) |
| Population (2010 census) | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 2,826,246 |
| • Density | 150/km2 (390/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 991,600 |
| • Urban density | 350/km2 (890/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 688,229 |
| • Metro density | 550/km2 (1,400/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Area code(s) | (0)751 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-GD-02 |
| Licence plate prefixes | 粤F |
| Local dialect | Hakka (regional) Cantonese (native; provincial level) |
| Major Nationalities | Han |
| Shaoguan | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 "Shaoguan" in Traditional (top) and Simplified (bottom) Chinese characters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 韶关 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 韶關 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Postal | Shiukwan Shiuchow (former) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | Beautiful pass | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
History
Shaozhou was a prefecture under the Tang and Song.
In 1589, Matteo Ricci relocated his mission house – the first ever Jesuit mission in mainland China – to Shaoguan after a fallout with the authorities in Zhaoqing. He remained in Shaoguan for a few years, eventually benefiting from Shaoguan's location on the important north-south travel route to establish connections with traveling dignitaries that allowed him to move north, to Nanchang, Nanjing, and Beijing.[3]
During World War II the city, then called Kukong, was the temporary capital of Guangdong Province.
In June 2009, Uyghurs and Han workers clashed at a toy factory in Shaoguan, which was followed by the Ürümqi riots in July.
Geography
.jpg.webp)
Shaoguan is the northernmost prefecture-level city of Guangdong, bordering Chenzhou (Hunan) to the northwest and north, Ganzhou (Jiangxi) to the northeast, Heyuan to the east, Guangzhou and Huizhou to the south, and Qingyuan to the west. It spans latitude 23° 05'−25° 31' N and longitude 112° 50'−114° 45' E. It is situated at the southern end of the Nan Mountains (Nan Ling), which primarily run east-west here, and is marked by numerous erosion-created valleys; within its borders lies the 1,902 m (6,240 ft) Mount Shikeng (石坑崆), the highest point in the province. The city is located on the Jingguang Railway (Beijing−Guangzhou) about 221 kilometres (137 mi) north of the provincial capital of Guangzhou. Shaoguan is also readily accessible by road as it is adjacent to the G4 Beijing–Hong Kong–Macau Expressway as well as numerous other National Highways.
At Shaoguan, the Wu River from the northwest and the Zhen River from the northeast join up to create the North River (Bei Jiang) which flows south to Guangzhou. The downtown part of Shaoguan is located on a peninsula between the Wu and Zhen Rivers. The rivers are maintained at a constant level by a dam about 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) downstream from the city. The city has about 20 kilometres (12 mi) of tree-lined riverside esplanades along the banks of the rivers. There are seven bridges crossing the three rivers.
Climate
Shaoguan has a monsoon-influenced humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cfa), with short, mild, damp winters, rainy springs, long, hot, and humid summers, and relatively sunny autumns. Due to the city's location far inland, winters are significantly cooler than in the rest of the province, with freezing rain possible in the nearby mountain passes in some years. Winter begins dry and relatively sunny but becomes progressively cloudier and damper. Spring is the cloudiest and wettest season, with the sun shining less than 30% of the time. The annual rainfall is around 1,600 mm (63 in), much of it delivered from April thru June. The monthly 24-hour average temperature ranges from 10.3 °C (50.5 °F) in January to 29.0 °C (84.2 °F) in July; the annual mean is 20.5 °C (68.9 °F). With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 16% in March to 54% in July, the city receives 1,617 hours of bright sunshine annually.
| Climate data for Shaoguan (1981−2010 normals) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 26.7 (80.1) |
30.5 (86.9) |
32.6 (90.7) |
33.7 (92.7) |
35.9 (96.6) |
38.5 (101.3) |
40.4 (104.7) |
40.3 (104.5) |
38.3 (100.9) |
36.6 (97.9) |
34.0 (93.2) |
28.5 (83.3) |
40.4 (104.7) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 15.1 (59.2) |
16.4 (61.5) |
19.2 (66.6) |
24.6 (76.3) |
28.9 (84.0) |
31.6 (88.9) |
34.0 (93.2) |
33.9 (93.0) |
31.5 (88.7) |
28.0 (82.4) |
22.7 (72.9) |
17.8 (64.0) |
25.3 (77.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 10.3 (50.5) |
12.3 (54.1) |
15.3 (59.5) |
20.7 (69.3) |
24.6 (76.3) |
27.3 (81.1) |
29.0 (84.2) |
28.7 (83.7) |
26.4 (79.5) |
22.5 (72.5) |
17.0 (62.6) |
11.9 (53.4) |
20.5 (68.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 7.2 (45.0) |
9.4 (48.9) |
12.5 (54.5) |
17.8 (64.0) |
21.5 (70.7) |
24.4 (75.9) |
25.6 (78.1) |
25.2 (77.4) |
22.9 (73.2) |
18.5 (65.3) |
13.0 (55.4) |
7.9 (46.2) |
17.2 (62.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −2.5 (27.5) |
0.1 (32.2) |
0.9 (33.6) |
6.2 (43.2) |
12.7 (54.9) |
16.6 (61.9) |
21.3 (70.3) |
20.8 (69.4) |
15.1 (59.2) |
6.3 (43.3) |
2.5 (36.5) |
−4.3 (24.3) |
−4.3 (24.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 69.3 (2.73) |
106.0 (4.17) |
177.9 (7.00) |
221.1 (8.70) |
248.9 (9.80) |
249.6 (9.83) |
159.4 (6.28) |
129.1 (5.08) |
100.8 (3.97) |
43.8 (1.72) |
51.9 (2.04) |
41.7 (1.64) |
1,599.5 (62.96) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 11.4 | 14.8 | 19.1 | 18.8 | 19.3 | 17.1 | 13.6 | 14.7 | 10.1 | 7.8 | 6.9 | 6.8 | 160.4 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 75 | 79 | 82 | 82 | 80 | 80 | 75 | 77 | 76 | 71 | 72 | 72 | 77 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 89.7 | 67.5 | 57.6 | 75.5 | 113.9 | 150.5 | 226.6 | 206.7 | 177.6 | 164.0 | 147.0 | 140.8 | 1,617.4 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 27 | 21 | 16 | 20 | 28 | 37 | 54 | 51 | 48 | 46 | 45 | 43 | 36 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration (precipitation days and sunshine 1971–2000)[4][5] | |||||||||||||
Administrative divisions
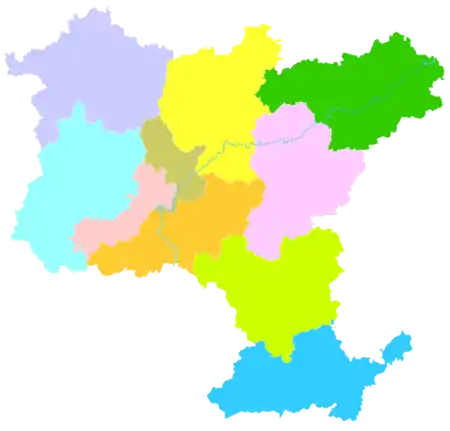
Shaoguan has direct jurisdiction over 3 districts, 2 county-level cities and 5 counties:
| Map | Name | Simplified Chinese | Hanyu Pinyin | Population (2010 census) |
Area (km2) |
Density (/km2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhenjiang District | 浈江区 | Zhēnjiāng Qū | 393,521 | 572.11 | 688 | ||||||
| Wujiang District | 武江区 | Wǔjiāng Qū | 294,708 | 677.78 | 435 | ||||||
| Qujiang District | 曲江区 | Qǔjiāng Qū | 303,371 | 1,620.77 | 187 | ||||||
| Shixing County | 始兴县 | Shǐxīng Xiàn | 205,452 | 2,131.91 | 96 | ||||||
| Renhua County | 仁化县 | Rénhuà Xiàn | 200,354 | 2,223.22 | 99 | ||||||
| Wengyuan County | 翁源县 | Wēngyuán Xiàn | 331,120 | 2,174.87 | 152 | ||||||
| Xinfeng County | 新丰县 | Xīnfēng Xiàn | 206,091 | 1,967.39 | 105 | ||||||
| Ruyuan Yao Autonomous County | 乳源瑶族自治县 | Rǔyuán Yáozú Zìzhìxiàn | 177,471 | 2,299.01 | 77 | ||||||
| Lechang City | 乐昌市 | Lèchāng Shì | 397,779 | 2,419,28 | 164 | ||||||
| Nanxiong City | 南雄市 | Nánxióng Shì | 316,179 | 2,326,18 | 136 | ||||||
Tourism
The Fengcai Tower (Chinese: 风采楼; pinyin: fēngcǎi lóu) in the centre of Shaoguan was built in the Ming Dynasty. To the south of the tower, at the other end of a pedestrian shopping street, the Dajian Monastery was founded in 660.
Near Shaoguan is the town of Maba, home of relics and museum of the Maba Man, Chinese Neanderthals. Near Maba is Nanhua Temple, which was founded by Huineng, the Sixth Patriarch of Zen Buddhism. Shaoguan Iron and Steel is also located near Maba.
Danxia Mountain is located in Renhua County, Shaoguan.
Northwest of Shaoguan, at the town of Pingshi, a stretch of river known as the Nine Torrents and Eighteen Shoals is a popular place for white-water rafting.
Education
Shaoguan University (a xueyuan) is in the city.
Language
The main languages spoken are Hakka and Shaozhou Tuhua, related to Ping Chinese. Shaozhounese is spoken in Shaozhou city and Hakka (mainly Yetpet and Seunan dialects) are spoken in neighboring counties.
Gallery
 Zhongshan Park
Zhongshan Park Central Shaoguan
Central Shaoguan Guangdong Grand Canyon in Shaoguan
Guangdong Grand Canyon in Shaoguan
See also
References
- Alternative transliterations include Shiuchow (postal), Shiukwan (postal), Shaokwan, Shao-chow, Xaocheu (Willem Blaeu's maps) and Chau Chew (Johan Nieuhof's illustration)
- http://www.citypopulation.de/php/china-guangdong-admin.php
- De Christiana expeditione apud Sinas
- 中国气象数据网 - WeatherBk Data (in Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 2020-04-15.
- 中国地面国际交换站气候标准值月值数据集(1971-2000年). China Meteorological Administration. Archived from the original on 2013-09-21. Retrieved 2010-05-25.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Shaoguan. |
- http://www.shaoguan.gov.cn/ (in Chinese)
- https://web.archive.org/web/20040924085950/http://shaoguan.com.cn/ (in Chinese)
- Shaoguan, China