Shortstown
Shortstown is a village and civil parish on the outskirts of Bedford, on a ridge above the River Great Ouse, originally called Tinkers Hill.[2]
| Shortstown | |
|---|---|
 The Shorts Building | |
 Shortstown Location within Bedfordshire | |
| Area | 0.905 km2 (0.349 sq mi) |
| Population | 2,392 (2016 Census)[1] |
| • Density | 2,643/km2 (6,850/sq mi) |
| OS grid reference | TL072594 |
| Civil parish |
|
| Unitary authority | |
| Ceremonial county | |
| Region | |
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | BEDFORD |
| Postcode district | MK42 |
| Dialling code | 01234 |
| Police | Bedfordshire |
| Fire | Bedfordshire and Luton |
| Ambulance | East of England |
| UK Parliament | |
| Website | eastcottsparishcouncil |
This ridge also overlooks the two other parts of Eastcotts – Harrowden to the north and Cotton End to the south. The name is taken from Short Brothers. The Admiralty established an airship works for the company in 1916. The company pulled out of airship work just three years later, but the name Shortstown stuck.
Transport
Road access to the village is provided by the A600 road.[3] The Stagecoach bus also runs frequent routes in the village, with Route 9 running to and from the town centre at frequent intervals.[4] Routes 9A and 9B also provide connections to Bedford as well as the nearby locations of Cotton End and Shefford, continuing on to Hitchin.
Village history
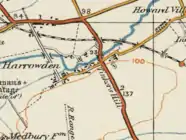
Shortstown was built on Tinker's Hill, Harrowden. Before it was built, a windmill stood on the site from 13th to 16th century. From 17th to 18th century, the area was known as Windmill Hill.[6] Shortstown started with the establishment of the Airship Works in 1917 when housing for the workforce was built next to the airfield. In 1918 and 1927, sheds (later Grade II* listed buildings) were built for the R100 and R101 airships which then represented the latest passenger flight technology. The village was originally built by the Short Brothers for its workers,[7] but evolved into a settlement for people working at the RAF Cardington base.
Shortstown was only created from 1916 onwards. The land originally lay in the township of Eastcotts which was itself a part of the ancient parish of Cardington. Eastcotts became a separate civil parish in 1866.

Early in 1916 the Admiralty was seeking a site for an airship works for Messrs. Short Brothers and after a two-month search the Naval Director of Air Services reported in March 1916 that a site had been selected at Cardington. It was picked as it was well served by roads and railways, was within easy reach of London by steam train and was a broad, flat valley running east-west without any obstructions. It was beyond the range of then known German bombers in Belgium, while "penetration by submarine landed agents was not considered likely due to the distance from the coast which it would be necessary to travel". There was also suitable surplus labour available in Bedford, and "the river affords a means of disposing of the effluent from sewage disposal works if such are established".
The whole site was bought by the Admiralty from the Whitbread Estate for £110,000 and in October 1916 Short Brothers made proposals for housing the employees required at the airship works. They estimated that for 1917 they would require 800 workers, 500 men and 300 women – of which 200 (mainly women) they hoped to obtain in Bedford. The rest would be housed in an entirely new "Garden City[9]" type settlement alongside the works.
The Building of Shortstown
By June 1919 the first phase of 151 houses had been built. This consisted of 12 six-roomed houses, 39 five-roomed houses, 64 four-roomed houses and 36 flats of three rooms each. The general layout and the design of the houses and airship works were by the architects Robert Burns Dick and James Cackett, of Cackett & Burns Dick of Newcastle-upon-Tyne. Work was carried out by them under the control of the Director of Works, Admiralty, and no local contractors were used.

The houses in this initial development are in a simplified neo-Georgian style, mainly red brick with dark red tile roofs, and are more reminiscent of Hampstead Garden Suburb in London than the original Garden City at Letchworth. Although the road layout is fairly formal and most of the houses are terraced, regimentation is avoided by arranging groups of houses around curves in a butterfly pattern or by setting some houses back and some forward in a particular terrace.
Further houses were envisaged to the south and west, but in the event, these were not built until many years later and had little regard to the original style and layout. Similarly, the original plan made provision for shops, churches, a cinema and a hall in the centre, but all that was built was a social club.[10]
The Royal Airship Works
As a result of the building of Shortstown, the population of Eastcotts rose from 848 in 1911 to 2,065 by 1921.[11] However, in the meantime, Short Brothers, who were experiencing various difficulties, withdrew from airship manufacture and the Cardington Venture with effect from 1 April 1919 and moved to Rochester in Kent. The Cardington Works was, therefore, taken over directly by the government and renamed the Royal Airship Works,[12] but the associated settlement has retained its original name of Shortstown.

During the 1920s the giant airship R101 was built at Cardington, while its sister ship, the R100 was brought to Cardington in December 1929. The R101 set off for its maiden flight to India on the evening of 4 October 1930 but in the early hours of the next morning, it crashed into a hillside at Beauvais in France, killing all but six of its fifty-four crew and passengers.[13] The shock of this tragedy brought an abrupt end to this phase of British airship manufacture and the R100 was broken up.
Shorts Building
The shorts building was built in 1917. It has taken on many guises ranging from an Administration Block in the early airship days to Station HQ in WW2 and in more recent years as a training centre for the Civil Service. However, despite its many uses, it is still referred to today as The Shorts Building and now over 90 years later has been restored to its former glory as part of the new Bellway development.[14]
The building was refurbished in 2011 and a new site called New Cardington was also built. It is now used for 20 residential apartments and has a Public Common Hall, that shows a permanent display of 17 enhanced historic R101 photographs taken from The Airship Heritage Trust collection. There are also additional community rooms and Eastcotts Children's Centre is based here too.[14]

RAF Cardington
The Royal Airship Works was put on a care and maintenance basis until 1938 when it was renamed the Balloon Development Establishment. However, the social club at Shortstown was still known as the Royal Airship Works and Shortstown Club in the 1980s.
In the meantime, in 1936, an RAF station had opened at Cardington, being particularly concerned with producing gas for barrage balloons and training barrage balloon crews as well as more general training of recruits and NCOs. Throughout the 1940s Cardington remained a busy RAF station and from 1953 it became the RAF's main recruitment centre.
After the Second World War, further houses were built at Shortstown as married quarters for RAF personnel. The three avenues off the southern extension of Greycote are named after three prominent victims of the R101 disaster: Brigadier-General Lord Thomson of Cardington, Secretary of state for Air; Air Vice Marshal Sir W. Sefton Brancker, director of Civil aviation at the Air Ministry and Major George Herbert Scott, Assistant director of Airship Development (Flying and Training) at the Royal Airship Works.
The roads of the western half of the site are all named after Second World War bomber aircraft.

With the ending of National service and cuts in the armed forces the RAF's presence at Cardington began to dwindle and largely disappeared in the 1970s. As a result, the population of Eastcotts declined from 3,675 in 1951 to 1,710 in 1981.
Shortstown today
Since 2012 there has been significant housing development on land to the east of the A600, this part of the village is marketed as New Cardington and Eastcotts Green to appeal as more upmarket than Shortstown. Over half of homes on New Cardington development are for Housing Associations. Since New Cardington homes went on the market, house prices in old Shortstown have risen by more than 20%. Also built new school and shops in the centre of shortstown Although Bellway homes marketed the development as New Cardington, in fact it remains an extension of Shortstown.
In May 2017, Shortstown had its Centenary, which took place in June, called Shortstown Fun Day. There was also a firework display that took place in September and a Centenary Reunion that took place in November.[15]
In April 2019 Shortstown became its own civil parish, having previously been part of the parish of Eastcotts.[16][17]
Education

Despite houses having been built from 1917 onwards, Shortstown had no school until the mid 1950s. Some children from Shortstown seem to have attended that school as well as going to Cotton End School.[19]

The first headmaster of this school was Mr Evans. A road in the village was supposedly named after him.[18]
A new school named Shortstown Primary School was built in New Cardington: starting construction in late 2012 and completed in September 2013. This school replaced the old, and now demolished school named Shortstown Lower School, where new houses now stand.[20]
Notable people
- Eustace Short (1875–1932) – Aerospace engineer[21]
- Horace Short (1872–1917) – Aerospace engineer[21]
- Oswald Short (1883–1969) – Aerospace engineer[21]
- Alfred Pugsley (1903–1903) – Structural engineer[22]
- John Fleetwood Baker (1901–1985) – Scientist and Structural engineer[22]
- Neville Shute (1899–1960) – Novelist and Aeronautical engineer[22]
- Walter William Bygraves (1922–2012) – Comedian, Singer and actor[22]
- Thomas Dobney (1926)[22]
- Bill Wyman (1936–present) – Musician, Songwriter and photographer[22]
- Donald Campbell (1921–1967) – Record Breaker[22]
- Alan Ayckbourn (1939–present) – Playwright and director[22]
Geology
The solid or underlying geology is a mudstone called Oxford Clay Formation. This was laid down between 154 and 164 million years ago in the warm, shallow seas of the Jurassic period.[23] The northern part of the area has a superficial geology consisting of river terrace deposits of sand, gravel, clay and silt. A similar mixture, called head, lies in the southern part of the community.[24] There is a woodland created by the Forest of Marston Vale called Shocott Spring, which is between Shortstown and Cotton End.[25]
References
- "Shortstown (Bedford, East of England, United Kingdom) – Population Statistics, Charts, Map, Location, Weather and Web Information". citypopulation.de. Retrieved 13 June 2018.
- "The Community of Shortstown in General". Government of the United Kingdom. Retrieved 12 May 2018.
- "Roads". Bedfordshire Streetlighting. Retrieved 30 July 2018.
- "Stagecoach Bus Route 9".
- "Sheet 84. Bedford. – David Rumsey Historical Map Collection". davidrumsey.com. Retrieved 18 May 2018.
- "The Development of Shortstown". Government of the United Kingdom. Retrieved 12 May 2018.
- "Shortstown 1917–1924 – Shortstown heritage". shortstownheritage.co.uk. Retrieved 11 May 2018.
- "Sheet 147. Bedford and Luton. – David Rumsey Historical Map Collection". davidrumsey.com. Retrieved 18 May 2018.
- "Gasbag Magazine – Shortstown heritage". shortstownheritage.co.uk. Retrieved 11 May 2018.
- "Land at Shortstown pdf" (PDF).
- "The Development of Shortstown". Government of the United Kingdom. Retrieved 13 May 2018.
- "The Royal Airship Works Shortstown". Government of the United Kingdom. Retrieved 12 May 2018.
- "Construction and Destruction of the R101". Government of the United Kingdom. Retrieved 12 May 2018.
- "Recent updates – Shortstown heritage". shortstownheritage.co.uk. Retrieved 12 May 2018.
- "Shortstown Centenary Fun Day". WhereCanWeGo. Retrieved 30 July 2018.
- "The Borough of Bedford (Reorganisation of Community Governance) Order 2019" (PDF). Local Government Boundary Commission for England. Retrieved 8 July 2020.
- http://www.councillorsupport.bedford.gov.uk/mgAi.aspx?ID=23883
- "Recent updates – Shortstown heritage". shortstownheritage.co.uk. Retrieved 11 May 2018.
- "Shortstown School". Government of the United Kingdom. Retrieved 12 May 2018.
- "A Brand New Primary School for Shortstown – Children Mark the Start of Building Work". Mayordave.org. Retrieved 6 July 2018.
- "The Short Brothers – Shortstown heritage". shortstownheritage.co.uk. Retrieved 14 May 2018.
- "Interesting People – Shortstown heritage". shortstownheritage.co.uk. Retrieved 6 July 2018.
- "Geology with Oxford Clay Formation". Bgs.ac.uk. Retrieved 6 July 2018.
- "The Community of Shortstown in General". Government of the United Kingdom. Retrieved 6 July 2018.
- "Shocott Spring". The Forest of Marston Vale Trust. Retrieved 30 July 2018.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Shortstown. |
