Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites
Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites is a UNESCO World Heritage site (WHS) located in Wiltshire, England. The WHS covers two large areas of land separated by nearly 30 miles (48 km), rather than a specific monument or building. The sites were inscribed as co-listings in 1986. Some of the large and well known monuments within the WHS are listed below, but the area also has an exceptionally high density of small-scale archaeological sites, particularly from the prehistoric period. More than 700 individual archaeological features have been identified. There are 160 separate Scheduled Monuments, covering 415 items or features.[1]
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
|---|---|
 Avebury Stonehenge | |
| Location | Wiltshire, England, United Kingdom |
| Includes | |
| Criteria | Cultural: (i), (ii), (iii) |
| Reference | 373bis |
| Inscription | 1986 (10th session) |
| Extensions | 2008 |
| Area | 4,985.4 ha (19.249 sq mi) |
| Coordinates | 51°10′44″N 1°49′31″W |
 Location of Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites in the United Kingdom | |
Stonehenge and Associated Monuments

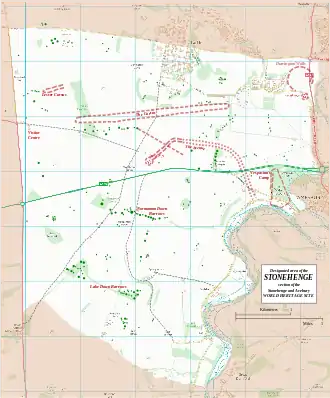
The Stonehenge area of the WHS is located in south Wiltshire. It covers an area of 26 square km and is centred on the prehistoric monument of Stonehenge. Ownership is shared between English Heritage, the National Trust, the Ministry of Defence, the RSPB, Wiltshire Council, and private individuals and farmers.[2]
Monuments in the Stonehenge WHS
- Stonehenge
- Stonehenge Avenue
- Stonehenge Cursus
- The Lesser Cursus
- Cursus Barrows
- Durrington Walls
- Woodhenge
- Cuckoo Stone
- Coneybury Henge (a henge that has been ploughed flat)
- King Barrow Ridge[3]
- Winterbourne Stoke Barrows
- Normanton Down Barrows, including Bush Barrow
- Vespasian's Camp
- Robin Hood's Ball (an associated monument located just north of the WHS boundary)
- West Amesbury Henge, also known as Bluestonehenge
- Stonehenge Landscape
Avebury and Associated Monuments

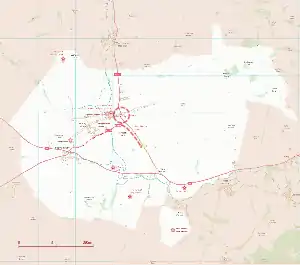
The Avebury area of the WHS is in northern Wiltshire. It covers an area of 22.5 km² and is centred on the prehistoric Avebury Henge.
Monuments in the Avebury WHS
Museum and archive collections
The main museums are the Alexander Keiler Museum at Avebury, Salisbury Museum, and Wiltshire Museum in Devizes.
Other museums with material from Stonehenge and Avebury include the British Museum, National Museum of Wales, Cambridge University Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology and the Ashmolean Museum. Other archives include the Historic England Archive in Swindon, the Wiltshire and Swindon History Centre in Chippenham, and the Bodleian Library at Oxford.
See also
References
- Stonehenge Management Plan, 2009, English Heritage, p.22
- Hicks, Dan. "Why are England's heritage bodies supporting the Stonehenge Bypass?". Apollo Magazine. Retrieved 11 July 2017.
- King Barrow Ridge Research report Archived 2015-12-22 at the Wayback Machine, English Heritage, 2011
