Sultan Agung of Mataram
Sultan Hanyakrakusuma is known as Sultan Agung (Javanese: ꦱꦸꦭ꧀ꦠꦤ꧀ꦲꦒꦸꦁꦲꦢꦶꦥꦿꦧꦸꦲꦚꦏꦿꦏꦸꦱꦸꦩ, romanized: Sultan Agung Hadi Prabu Hanyakrakusuma) was the third Sultan of Mataram in Central Java ruling from 1613 to 1645. A skilled soldier he conquered neighbouring states and expanded and consolidated his kingdom to its greatest territorial and military power.
| Hanyakrakusuma | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paduka Ingkang Sinuhun Kangjeng Sultan Agung Hadi Prabu Hanyakrakusuma Panembahan HanyakrakusumaPrabu Pandita HanyakrakusumaSusuhunan Hanyakrakusuma | |||||||||
 Potrait of Sultan Agung | |||||||||
| 4th Sultan of Mataram | |||||||||
| reign | 1613–1645 | ||||||||
| Preceded by | Duke Martapura | ||||||||
| Succeeded by | Amangkurat I | ||||||||
| Born | Raden Mas Jatmika 1593 Kutagede, Mataram | ||||||||
| Died | 1645 Karta, Mataram | ||||||||
| Burial | Astana Kasultan Agungan | ||||||||
| Queen consort | Ratu Kulon (first) Ratu Wetan (second) | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Dynasty | Mataram | ||||||||
| Father | Hanyakrawati | ||||||||
| Mother | Dyah Banawati | ||||||||
| Religion | Islam | ||||||||
| National Hero of Indonesia S.K. President No. 106 / TK / 1975 dated November 3, 1975. | |||||||||
Sultan Agung or Susuhunan Agung (literally, "Great Sultan" or "Majestic Sultan") is subject of a substantial amount of literature due to his legacy as a Javanese ruler, a fighter against the incursions of the Dutch East India Company, a conqueror, and his existence within a cultural framework where myth and magic are well intertwined with verifiable historical events and personages. The Dutch literature wrote his name by Agoeng de Grote (literally, "Agung the Great").
For his service as a fighter and cultural observer, Sultan Agung has been declared as National Hero of Indonesia based on Presidential Decree no. 106/TK/1975, issued on November 3, 1975.
Genealogy
His original name was Raden Mas Jatmika, also popularly known as Raden Mas Rangsang. He was the son of Panembahan Hanyakrawati and Ratu Mas Adi Dyah Banawati. His father was Mataram's second monarch, and his mother was the daughter of Prince Benawa, the last Sultan of Pajang.
Another version said that Sultan Agung was the son of Prince Purbaya (Panembahan Hanyakrawati's brother). It was said that Prince Purbaya exchanged the baby born by his wife with the one born by Dyah Banawati. This version is an opinion of minority whose truth has to be proven.
Like other Mataram's monarchs, Sultan Agung had 2 main queen consorts:
- Ratu Kulon, born as Ratu Mas Tinumpak, daughter of Panembahan Ratu, Sultan of Cirebon, who gave birth RM. Syahwawrat alias Prince Alit.
- Ratu Wetan, daughter of Duke of Batang (Ki Juru Martani's granddaughter), who gave birth RM. Sayidin (later Amangkurat I).
From his queen consorts, Sultan Agung has 9 children:
- Raden Mas Sahwawrat alias Pangeran Temenggong Pajang
- Raden Mas Kasim alias Pangeran Demang Tanpa Nangkil
- Pangeran Ronggo Kajiwan
- Gusti Ratu Ayu Winongan
- Pangeran Ngabehi Loring Pasar
- Pangeran Ngabehi Loring Pasar
- Raden Mas Sayidin (later became Sunan Prabu Amangkurat Agung / Amangkurat I (Sultan Agung's successor, reigning between 1645-1677)).
- GRAy. Wiromantri
- Prince Danupoyo alias Raden Mas Alit
Titles
In his early reign, RM. Rangsang's title was Panembahan Hanyakrakusuma or Prabu Pandita Hanyakrakusuma. After conquering Madura in 1624, he changed his titles as Susuhunan Agung Hanyakrakusuma, abbreviated as Sunan Agung Hanyakrakusuma.
In 1640s, he used title Sultan Agung Senapati ing Alaga Abdurrahman. In 1641, Sunan Agung got Arabic title, Sultan Abdullah Muhammad Maulana of Mataram, bestowed by Kaaba imams in Mecca.
For the sake of convenience, the name used in this article is the most common and popular name: Sultan Agung.
Early reign
RM. Rangsang ascended to throne when he was 20 years old, succeeding his half-brother, Duke Martapura, who became Sultan of Mataram for one day. RM. Rangsang was technically the fourth Sultan of Mataram, but he was commonly considered as the third sultan, because the coronation of his mentally retarded half-brother was just to fulfill his father's promise to his wife, Queen Tulungayu, Duke Martapura's mother.
In Sultan Agung's second year reign, Patih Mandaraka died of old age, and his position as patih (viceregent) was occupied by Tumenggung Singaranu.
The capital of Mataram in the era of his coronation was still located in Kotagede. In 1614, a new palace was built in Karta, approximately 5 km in the southwest of Kotagede, which began to occupy 4 years later.
Territorial conquests
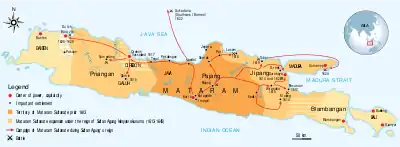
Sultan Agung became the ruler of Mataram in 1613 and the next year attacked Surabaya, as well as Malang which lies south of Surabaya, and the eastern end of the Java island, but failed to conquer them both. He was however able to extract a significant indemnity and used this in 1615, to conquer Wirasaba (present day Mojoagung, near Mojokerto), an operation which he personally lead. In 1616, Surabaya attempted to attack Mataram in retaliation, but lacking allies the Surabaya army was crushed by Sultan Agung's forces in Siwalan, Pajang (near Surakarta). The coastal city of Lasem, near Rembang, was conquered later in 1616, and Pasuruan, south-east of Surabaya, was taken in 1617. Tuban, one of the oldest and biggest cities on the coast of Java, was taken in 1619.
Surabaya had been Mataram's most formidable adversary thus far. Agung's grandfather, Senapati or Senopati, had not felt strong enough to attack this powerful city, and his father, Panembahan Seda Krapyak, attacked it to no avail. Sultan Agung weakened Surabaya by capturing Sukadana, Surabaya's ally in southwest Kalimantan, in 1622, and the island of Madura, another ally of Surabaya, in 1624 after a fierce battle. After five years of war Agung finally conquered Surabaya in a siege in 1625. With Surabaya brought into the empire, the Mataram kingdom encompassed all of central and eastern Java, and Madura, except for the west and east end of the island and its mountainous south (except for Mataram, of course). In the west Banten and the Dutch settlement in Batavia remained outside Agung's control.
The economy of Mataram was centered on agriculture, thus Sultan Agung who was openly contemptuous of trade, saw no need to maintain significant naval forces. This was later to prove costly when in 1629 he attacked and attempted to drive the Dutch out of their base at the coastal city of Jakarta. Though he possessed larger and superior land based forces, the Dutch had decisive advantages in naval power and were able to withstand the Siege of Batavia.
After the failure of the siege, Agung turned against the Balinese, then controlling Balambangan in East Java, in a “holy war” against infidels. His campaign was successful in Java, but he was unable to extend his power to the island of Bali itself. Bali thus retained its identity as a Hindu state in the midst of the predominantly Muslim states of the archipelago.
Apart from his conquests the Sultan also sought to rationalize and improve the internal government of his kingdom. He reformed the tax-code and brought the courts and judicial system more in line with Qurʾānic precepts. He commissioned the building of the Karta Palace in 1614, the Royal Graveyard of Imogiri, as well as other social and civic structures within the kingdom.
Rebellions
By 1625, Mataram was the undisputed ruler of most of Java.[1]:31 However, its military strength did not deter Mataram's vassals from rebellion, due to his inability to conquer Batavia. Pajang rebelled in 1617, and Pati rebelled in 1627. Following the capture of Surabaya in 1625, expansion halted as the empire was beset by rebellions. In 1630, Mataram crushed a rebellion in Tembayat (southeast of Klaten). However, in 1631-36, Mataram had to suppress the rebellion of Sumedang and Ukur in West Java. Agung's attempt to capture Batavia in 1628-29, and drive the Dutch from Java ended in failure.[2][3]
Rebellions still continued, now Mataram had to see Giri Kedaton rebellion, who was unwilling to submit to Mataram. As Mataram's troops still respected Giri Kedaton's soldiers which was considered as the descendant of Sunan Giri, a member of Walisanga, Sultan Agung assigned Pangeran Pekik, a descendant of Sunan Ampel (Sunan Giri's father-in-law), to suppress the rebellion. Pangeran Pekik himself had been married to Queen Pandansari, Sultan Agung's sister, in 1633. Giri Kedaton rebellion could be suppressed by them 3 years later.
Death

In 1632 Sultan Agung began building Imogiri, his burial place, about 15 kilometers south of Yogyakarta. Imogiri remains the resting place of most of the royalty of Yogyakarta and Surakarta to this day which in Agung's complex buried Sultan Agung, Queen Batang, and their sons. Agung died in the spring of 1645, leaving behind an empire that covered most of Java and stretched to its neighboring islands.
In accordance to his will, Sultan Agung was succeeded by his son, RM. Sayidin, styled Amangkurat I.
Historical reputation
The development of the sacred dance bedhaya, and important developments in gamelan and wayang are attributed to the court of Sultan Agung. However, there is almost no historical evidence for the claims of high artistic achievement, and there is little information at all about the arts in the court. Some written evidence comes from a handful of mentions in Dutch accounts, which can be difficult to interpret.[4] However within the complex field of folklore that attributes Sultan Agung with various powers and activities, the field of achievements is much greater. Sultan Agung is also attributed with the founding of the unique Javanese calendar – this established a uniquely indigenous calendar which is still in use. Besides of it, Sultan Agung had written a mystical manuscript, entitled Sastra Gending.
In the environment of Mataram Palace, Sultan Agung established a standard language called bagongan obliged to use by Mataram noblemen and officials to eradicate imbalance between them. The language was created to form unity between royal court officials.
The Sundanese language had been changed since Mataram's rule in West Java, marked by the creation of refined language only previously known in Central Java.
Sultan Agung's major legacy lies however in the administrative reforms he undertook in the conquered territories. The ever-increasing large territorial extent of these territories led him to create an innovative and rational administrative structure.[5] He created "provinces" by appointing people as adipati (equivalent to Duke) at the head of territories called kadipaten (Duchy), particularly those territories in the western part of Java, where Mataram was facing Banten and Batavia, two places who resisted his wars of conquest. A kabupaten like Karawang, for instance, was created when Sultan Agung appointed prince Kertabumi as its first adipati in 1636. When the V.O.C. (the Dutch East India Company) took control of Mataram territories, it kept the kadipaten structure. Under the colonial administration of the Netherlands Indies, adipati, now called bupati, were called regenten and kadipaten, now kabupaten, regentschappen. The title of a bupati consisted generally in a formal name, for instance "Sastradiningrat" in the case of Karawang, preceded by "Raden Aria Adipati", hence "Raden Aria Adipati Sastradiningrat" (shortened into R. A. A. Sastradiningrat). The word adipati survived in the colonial system.
The Dutch had grouped kabupaten into regions under a resident, called residenties. The Indonesian government kept the kabupaten but disbanded the residenties in the 1950s, resulting in kabupaten being administrative subdivisions directly under a province. The laws on regional autonomy promulgated in 1999 give a high degree of autonomy to the kabupaten, not to the provinces. Sultan Agung's legacy is also recognised by modern Indonesia.
Sultan Agung is revered in contemporary Java both for his unification of Java, modernizing reforms, as well as his wars with the Dutch. In the Sukarno era he was nominated and confirmed as a National Hero of Indonesia (Pahlawan Nasional Indonesia). His existence within a cultural framework where myth and magic are intertwined and the scarcity of verifiable records of his early life have elevated him to heroic and near-mythical status. In the syncretic religious culture of Java, with its mixture of Hinduism, Buddhism and Islam; pilgrimage to his graveyard complex is considered auspicious, and many make considerable effort to go to Imogiri at appropriate times and days in the Javanese and Islamic calendars.
References
- Drakeley S. The History of Indonesia. Greenwood, 2005. ISBN 9780313331145
- Montanus, A. "Oud en nieuw Oost-Indien", hal. 358
- Afbeelding - AMH (Berkas AMH)
- Sumarsam. Gamelan: Cultural Interaction and Musical Development in Central Java. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1995. Page 20.
- Bertrand, Romain, Etat colonial, noblesse et nationalisme à Java, Paris, 2005
Further reading
- Pranata, Sultan Agung Hanyokrokusumo, Jakarta: Yudha Gama (In Indonesian)
| Preceded by Duke Martapura |
Sultan of Mataram 1613–1645 |
Succeeded by Amangkurat I |