Vonoprazan
Vonoprazan (trade name Takecab) is a first-in-class potassium-competitive acid blocker. It was approved in the Japanese market in February 2015.[1]
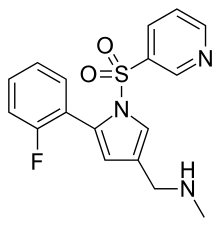 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Takecab |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Unknown |
| Protein binding | 80% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic, by cytochrome P450 (3A4, 2B6, 2C19, 2D6) |
| Elimination half-life | 7.7 h |
| Duration of action | > 24 h |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H16FN3O2S |
| Molar mass | 345.39 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Vonoprazan is used in form of the fumarate for the treatment of gastroduodenal ulcer (including some drug-induced peptic ulcers) and reflux esophagitis, and can be combined with antibiotics for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori.[2]
References
- Garnock-Jones KP (2015). "Vonoprazan: first global approval". Drugs. 75 (4): 439–43. doi:10.1007/s40265-015-0368-z. PMID 25744862.
- Echizen H (2016). "The First-in-Class Potassium-Competitive Acid Blocker, Vonoprazan Fumarate: Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Considerations". Clin Pharmacokinet. 55 (4): 409–18. doi:10.1007/s40262-015-0326-7. PMID 26369775.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.