Würzburg radar
The low-UHF band Würzburg radar was the primary ground-based gun laying radar for the Wehrmacht's Luftwaffe and Heer (German Army) during World War II. Initial development took place before the war and the apparatus entered service in 1940. Eventually, over 4,000 Würzburgs of various models were produced. It took its name from the city of Würzburg.
 Würzburg-Riese at Military History Museum, Gatow Airport, Berlin | |
| Country of origin | Germany |
|---|---|
| Introduced | 1940 |
| No. built | c. 4,000 |
| Type | Gun laying radar |
| Frequency | 560 MHz |
| PRF | 1875 per second |
| Pulsewidth | 2 μs |
| Range | up to 70 km (43 mi) |
| Diameter | 7.5 metres (25 ft) |
| Azimuth | 0–360° |
| Elevation | 0–90° |
| Precision | ±15 metres (49 ft) |
| Power | 8 kW |
There were two primary models of the system. The first Würzburg was a portable model that could be folded for transit and then brought into operation quickly after emplacement and leveling. The A models began entering service in May 1940 and saw several updated versions over the next year to improve accuracy, notably the addition of conical scanning in the D model of 1941. The larger Würzburg-Riese was based on the D model but used a much larger parabolic reflector to further improve resolution at the cost of no longer being mobile.
As one of German's primary radars, the British spent considerable effort countering it. This culminated in the February 1942 Operation Biting that captured a working example of a D model. Using the information from this unit, the Royal Air Force introduced a series of white noise radar jammers known as "Carpet" to interfere with their operation. Late in the war, the first jammers using the more advanced angle deception jamming technique were introduced.
Development
In January 1934, Telefunken met with German radar researchers, notably Dr. Rudolf Kühnhold of the Communications Research Institute of the Kriegsmarine and Dr. Hans Hollmann, an expert in microwaves, who informed them of their work on an early warning radar. Telefunken's director of research, Dr. Wilhelm Runge, was unimpressed and dismissed the idea as science fiction. The developers then went their own way and formed GEMA (Gesellschaft für Elektroakustische und Mechanische Apparate) eventually collaborating with Lorenz on the development of the Freya and Seetakt systems.
By the spring of 1935, GEMA's successes made it clear to Runge that the idea was workable after all, so he started a crash program at Telefunken to develop radar systems. With Lorenz already making progress on early warning devices, Runge had the Telefunken team concentrate on a short-range gun laying system instead. Management apparently felt it to be as uninteresting as Runge had a year earlier and assigned it a low priority for development. By the summer they had built a working experimental unit in the 50 cm band that was able to generate strong returns off a target Junkers Ju 52. By the next summer, the experimental set-up had been developed into a prototype known as the Darmstadt, which offered a range accuracy of 50 metres (55 yd) at 5 kilometres (3.1 mi), not nearly enough for gun laying. Attitudes changed in late 1938, when a full development contract was received from the Luftwaffe.
The resulting system, known as the FuMG 62, as well as the prototype system FuMG 39T Darmstadt were demonstrated to Hitler at Rechlin in July 1939. The Telefunken team developed an accurate system based on a klystron microwave tube operating in the range of 54–53 cm (553–566 MHz)—an extremely short wavelength for the time—with a pulse length of 2 microseconds, a peak power of 7–11 kW and a pulse repetition frequency (PRF) of 3,750 Hz. It had a maximum range of about 29 kilometers (18 mi) and was accurate to about 25 metres (27 yd) in range. Würzburg used a 3-metre (3.3 yd) paraboloid dish antenna, which could be "folded" along the horizontal midline for travel on a wheeled trailer. The system was first accepted into service in 1940 and 4,000 of this basic layout were delivered.
Operational models

Several versions of the basic Würzburg system were deployed over the course of the war. The first, Würzburg A, was operated manually and required the operators to pinpoint the target by maintaining a maximum signal on their oscilloscope display. Since the signal strength changed on its own for various reasons as well as being on or off target, this was inaccurate and generally required the use of a searchlight to spot the target once the radar had settled on an approximate position. Nevertheless, one of the first Würzburgs in service directly assisted in the shooting-down of an aircraft in May 1940 by orally relaying commands to a flak unit. An experimental Würzburg B added an infra-red detector for fine tuning, but in general these devices proved to be unusable and production was discontinued.

Würzburg C featured lobe switching to improve aiming accuracy. It sent the signal out of one of two slightly off-centre antennas in the middle of the reflector, with the signal being switched rapidly between the dipoles. After slightly delaying the signal from one of the dipoles, the returns were sent to an oscilloscope display. The result appeared as two closely separated blips which the operator attempted to keep at the same height on the display. This system offered much faster feedback on changes in target position. Changes in signal strength, due to changes in the reflection off the target, affected both lobes equally, eliminating common reading errors. An almost identical system was used in the United States's first gun-laying radar, the SCR-268.
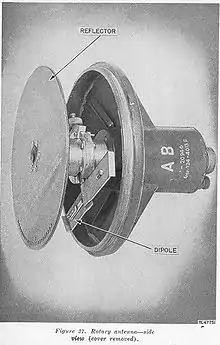
The Würzburg D was introduced in 1941 and added a conical scanning system using an offset receiver feed called a Quirl (German for whisk) that spun at 25 Hz. The resulting signal was slightly offset from the centreline of the dish, rotating around the axis and overlapping it in the centre. If the target aircraft was to one side of the antenna's axis, the strength of the signal would grow and fade as the beam swept across it, allowing the system to move the dish in the direction of the maximum signal and thereby track the target. The angular resolution could be made smaller than the beamwidth of the antenna, leading to much improved accuracy, on the order of 0.2 degrees in azimuth and 0.3 degrees in elevation. Earlier examples were generally upgraded to the D model in the field.
Even the D model was not accurate enough for direct laying of guns. In order to provide the system with much greater accuracy, the FuMG 65 Würzburg-Riese (known as the "Giant Würzburg") was developed. Based on the same circuitry as the D model, the new version featured a much larger 7.4 metres (24 ft) antenna and a more powerful transmitter with a range of up to 70 kilometers (43 mi). Azimuth and elevation accuracy was 0.1-0.2 degrees, which was more than enough for direct gun-laying. The system was too large to be carried on a truck trailer and was adapted for operation from a railway carriage as the Würzburg-Riese-E, of which 1,500 were produced during the war. The Würzburg-Riese Gigant was a very large version with a 160 kW transmitter, which never entered production.
Countermeasures
As one of the most common radars in German use, the British spent considerable effort countering the system during the war. In February 1942, a Würzburg system at Bruneval on the coast of France was captured by British Paratroopers in Operation Biting. Several key components were returned to the UK, which allowed the operational parameters of the system to be accurately determined. This led to the modification of existing transmitter systems to produce the "Carpet" system that broadcast noise on the frequencies used by particular Würzburg systems.[1] Several updated versions of Carpet were introduced; Carpet II was the primary UK version while Carpet III was its US-built counterpart.[2]
Operation Bellicose bombed the suspected Würzburg radar factory. The Operation Hydra bombing of Peenemünde did not affect the nearby Giant Würzburg at the Lubmin guidance and control station used for the V-2 rocket.[3]
Post-War Use in Astronomy
Dutch scientists brought several of the surplus German coastal Würzburg radars to the Radio Transmitting Station in Kootwijk, Netherlands in the early 1950s. There, they were used in experiments important in the development of early radio astronomy, specifically the discovery of the Hydrogen line and subsequent mapping of the spiral arms of the Milky Way Galaxy. [4]
German radar equipment including two Würzburg antennae (obtained from RAE Farnborough) was used by Martin Ryle and Derek Vonberg at the Cavendish Laboratory from 1945 to observe sunspots.[5]
Two FuSE 65 Würzburg radars were installed around 1956 at the Ondřejov Observatory in Czechoslovakia. The first radar served until 1994 to measure solar radiation flux, later was moved to the Military museum Lešany. The second radar was used to measure solar spectrum in range 100-1000 MHz. Since 1994, it has been used only for occasional experiments.[6][7]
See also
Notes
- Royal Air Force Historical Society (28). 2003. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - "Jamming Devices".
- Ordway, Frederick I., III.; Sharpe, Mitchell R. The Rocket Team. Apogee Books Space Series 36. p. 292.
- Hugo van Woerden and Richard G. Strom. Journal of Astronomical History and Heritage , 9(1), 3-20 (2006) http://www.lightcurvefilms.com/spiralgalaxy/nl/pubs/Radiosterrenkunde_NL_JAHH9_2006.pdf
- CAVMAG - News from the Cavendish Laboratory, August 2015, Page 20
- Article and photogallery about Würzburg radars at Ondřejov Observatory (in Czech language)
- Würzburg in military museum Lešany (in Czech language)
References
- Swords, Sean S. (1986). Technical History of the Beginnings of Radar. London: IEE/Peter Peregrinus. ISBN 0-86341-043-X.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Würzburg (radar). |
- ORIGINS OF GERMAN RADAR: SEETAKT, FREYA, WUERZBURG. There is an open source verification for this text on the home page Greg Goebel / In The Public Domain.
- Radar Development in Germany on the Radar World website
- The Radar War (PDF) by Gehard Hepcke, translated into English By Hannah Liebmann on the Radar World website
- MUSEUM "WAALSDORP" - Radio Communication with an antenna built during World War II
- A captured Würzburg radar unit is used to develop World War II countermeasures.