Yukhari Govhar Agha Mosque
Yukhari Govhar Agha Mosque (Azerbaijani: Yuxarı Gövhər Ağa məscidi) is a mosque located in Shusha, Azerbaijan. The mosque also bears the name Boyuk Juma (Great Mosque) of Govhar Agha (Azerbaijani: Gövhər Ağanın Cümə məscidi).[1]
| Yukhari Govhar Agha Mosque | |
|---|---|
 The mosque before the Armenian capture | |
| Religion | |
| Affiliation | Islam |
| Branch/tradition | Shia Islam |
| Location | |
| Location | Shusha, Azerbaijan |
| Geographic coordinates | 39.7600°N 46.7526°E |
| Architecture | |
| Architect(s) | Karbalayi Safikhan Karabakhi |
| Type | Mosque |
| Style | Islamic architecture |
| Founder | Ibrahim Khalil Khan |
| Date established | 1768–1885 |
| Minaret(s) | 2 |
History

The Yukhari Govhar Agha means "The Upper Govhar Agha Mosque" in Azerbaijani language, referring to location of the mosque in the upper section of Shusha town and to distinguish it from the Ashaghi Govhar Agha Mosque, the same-name mosque located in lower section of the town. Both mosques are considered symbols of Shusha and masterpiece of Eastern architecture.[2][3] The Yukhari Govhar Agha Mosque is located on Shusha's main square, Yusif Vazir Chamanzaminli street and makes up a big part of architectural complex including madrasa, shops and houses built by the same architect.[1][4] According to historian and author of "Karabakh-name", Mirza Jamal Karabakhi, construction of the mosque was started with orders of Ibrahim Khalil Khan in 1768 (1182 according to Islamic calendar) but was stopped for a long time. The construction was then restarted and completed in 1883–1885 by architect Karbalayi Safikhan Karabakhi ordered by Govhar Agha, daughter of Ibrahim Khalil Khan.
The exterior and interior

The prayer hall of Yukhari Govhar Agha Mosque is a three-nave in a square shape (190–185 meters) split by 6 stone columns. The three-beam veranda in the northern section of the mosque gives it a rectangular form (26.5 × 21.5 meters). The mosque has two minarets. The balconies used to host women's premises of the prayer hall. The interior of the prayer hall gets light from dual windows. The two minarets by the facade make up the veranda. The building of the mosque was constructed out of stone while the two minarets are made of bricks. The minarets have cylindric forms with horizontal belts with each section laid in distinguishing brick patterns. The same construction pattern can be viewed in most of the mosques throughout Karabakh built by Kerbalayi Safikhan Karabakhi.[1]
Current situation

In Soviet times the mosque was closed and used as a museum, but reopened as a functioning mosque in 1988. After the capture of Shusha by Karabakhi-Armenian forces in 1992, the mosque stopped functioning.[5] Following a minor restoration of the mosque in 2008–2009, fixing the roof,[6] officials from Nagorno-Karabakh Ministry of Economy ordered a restoration project, hiring Iranian experts to carry out the restoration works.[7] Azerbaijani officials expressed their unhappiness with the restoration project, with the Deputy Chairman of the State Committee for Work with Religious Organizations Gunduz Ismayilov claiming that "Armenia’s intention to restore the historical Azerbaijani mosque in Shusha is an attempt to cover up the vandalism it did to Azerbaijani cultural-religious monuments in the occupied territories".[8]
After several years of restoration work, the Yukhari Govhar Agha Mosque, neighboring madrasa, and park were formally opened for tourism with a ceremony on October 14, 2019.[9] The project was undertaken by the Initiative for Development of Armenia (IDeA) Foundation with the support of private donations, the largest of whom being Kazakh businessman Kairat Boranbayev.[10]
The complex was to be used as an Armenian-Iranian Cultural Center. Notably, there was no mention of the former Azeri presence and the complex was presented as an Iranian mosque.[11] There are now plans to convert the building back into a functioning mosque.
The first Friday prayer was held in the mosque, after 28 years, on 13 November 2020 by Azerbaijan soldiers.[12]
Gallery
 The mosque before the capture of Shusha by Armenian forces
The mosque before the capture of Shusha by Armenian forces The mosque before the capture of Shusha by Armenians
The mosque before the capture of Shusha by Armenians Mosque on the stamp of Azerbaijan
Mosque on the stamp of Azerbaijan.jpg.webp) View from south-west
View from south-west One of the newly restored minarets
One of the newly restored minarets View from the south-west in 2019 after restoration
View from the south-west in 2019 after restoration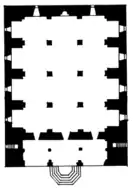 The architectural plan of the mosque
The architectural plan of the mosque
References
- "Shusha State Historical & Architectural Reserve". Retrieved 20 July 2010.
- "PACE – Urgency to prevent the destruction of cultural monuments in the Armenian-occupied town of Shusha of Azerbaijan". Retrieved 20 July 2010.
- "Чудеса Азербайджана". Retrieved 26 July 2010.
- "Наши культурные ценности – Шушинский район". Retrieved 26 July 2010.
- "Human Rights group". Retrieved 23 July 2010.
- Excavation works start in the Iranian Upper Mosque of Shushi
- Azerbaijan reacts to Iranian company restoring mosque in Shusha
- "Gohar Agha Upper Mosque restored, inaugurated as Armenian-Iranian Cultural Center in Artsakh". armenpress.am. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- Жуков, Иван (31 January 2018). "Кайрат Боранбаев жертвует средства на восстановление мечети в Нагорном Карабахе". www.forbes.kz. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- "Karabakh's contentious mosque restoration | Eurasianet". eurasianet.org. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- "İyirmi səkkiz ildən sonra Şuşada cümə namazı qılındı". azerbaijan-news.az. 13 November 2020.
External Link
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Yukhari Govhar Agha Mosque. |
