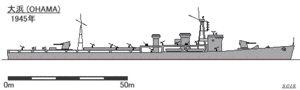
Ōhama-class target ship
The Ōhama-class target ship (大濱型標的艦, Ōhama-gata hyōtekikan) was a bombing target ship class of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during World War II. 5 vessels were planned under the Kai-Maru 5 Programme (Ship #5411–5415), however, only the lead ship Ōhama was completed.
 | |
| Class overview | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Ōhama-class target ship |
| Builders: | Mitsubishi Heavy Industries |
| Operators: |
|
| Preceded by: | Hakachi |
| Cost: | 10,064,000 JPY[1] |
| Built: | 1943–1945 |
| In commission: | 1945 |
| Planned: | 5 |
| Completed: | 1 |
| Cancelled: | 4 |
| Lost: | 2 |
| General characteristics [2] | |
| Type: | Target ship |
| Displacement: | 2,580 long tons (2,621 t) standard |
| Length: |
|
| Beam: | 11.55 m (37 ft 11 in) |
| Draught: | 4.10 m (13 ft 5 in) |
| Propulsion: |
|
| Speed: | 33 knots (38 mph; 61 km/h) |
| Range: | 4,000 nmi (7,400 km) at 18 kn (21 mph; 33 km/h) |
| Endurance: | Fuel: 500 tons oil |
| Complement: | 173 |
| Sensors and processing systems: |
|
| Armament: |
|
| Armour: |
|
Design and Construction
Project number J36. In 1941, the IJN had decided to build the bombing target ship Hakachi, with a speed under 20 knots. However, what the IJN required was target ship which could emulate the higher speed of the Essex-class aircraft carriers and Iowa-class battleships. The class specification given was therefore 33 knots, use of a destroyer hull, equipped with the Akizuki-class machinery, enabled this to be achieved and able to withstand a 10 kilogram bomb dropped from 4,000 m (13,000 ft) meters. Her armament consisted initially of only four anti-aircraft machine guns,.[3] However, the significant loss of destroyers between 1942 and 1944 together with delays in mass production of the escort shipsKaibokan caused Ōhama to be converted. Thus rearmed for this escort role with many anti-aircraft arms and anti-submarine weapons, the lead ship Ōhama was completed on the 10th of January 1945.
Service
Ōhama was assigned to the Combined Fleet on 10 January 1945. However, she did not take up any target ship duties, due to the significant losses resulting from the Battle of the Philippine Sea and Battle of Leyte Gulf. Rather she was deployed to convoy escort duties in the Yokosuka area. In August 1945, she was dispatched to Onagawa Local Defense Squadron and on 9 August 1945 sunk by carrier aircraft. The second ship laid down, Ōsashi was discontinued in 1945. Whilst three other class vessels were cancelled in 1944.
Ships in class
| Ship # | Ship | Builder | Laid down | Launched | Completed | Fate |
| 5411 | Ōhama (大濱) | Mitsubishi, Yokohama shipyard | 2 October 1943 | 29 March 1944 | 10 January 1945 | Sunk by air raid at Onagawa on 9 August 1945; struck off 15 September 1945; salvaged and scrapped postwar. |
| 5412 | Ōsashi (大指) | Mitsubishi, Yokohama shipyard | 7 January 1944 | 16 February 1945 | 95% complete; construction stopped on 23 June 1945. Collided with army oiler Yamashio Maru and sank in shallow water on 6 March 1946;[4][5] later salvaged and scrapped. | |
| 5413 5414 5415 |
Yagoshi (矢越) Anori (安乗) Ōbatake (大畠) |
Cancelled on 5 May 1944.[6] | ||||
Footnotes
- Senshi Sōsho Vol.88 (1975), p.37
- Ships of the world No.522 (1997), p.43
- SNAJ (1977), p.794–795, p.815
- The Maru Special No.38 (1980), p.64
- Shizuo Fukui (1994), third separate volume, p.31
- Senshi Sōsho Vol.88 (1975), p.95
Bibliography
- Ships of the World No.522, Auxiliary Vessels of the Imperial Japanese Navy, "Kaijinsha"., (Japan), March 1997
- The Maru Special, Japanese Naval Vessels No.34 Japanese auxiliary vessels, Ushio Shobō (Japan), December 1979
- The Maru Special, Japanese Naval Vessels No.38 Japanese aircraft carriers II, Ushio Shobō (Japan), March 1980
- Senshi Sōsho Vol.88, Naval armaments and war preparation (2), "And after the outbreak of war", Asagumo Simbun (Japan), October 1975
- "The Society of Naval Architects of Japan". (SNAJ), Histories of shipbuilding in Shōwa period (1), "Hara Shobō". (Japan), September 1977
- Shizuo Fukui, FUKUI SHIZUO COLLECTION "Japanese Naval Vessels 1869–1945", KK Bestsellers (Japan), December 1994