1953 West German federal election
Federal elections were held in West Germany on 6 September 1953 to elect the second Bundestag. The Christian Democratic Union emerged as the largest party.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
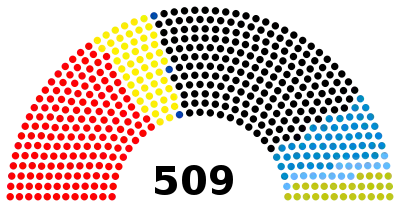
All 509 seats in the Bundestag 255 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Registered | 33,120,940 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 28,479,550 (86.0%)[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
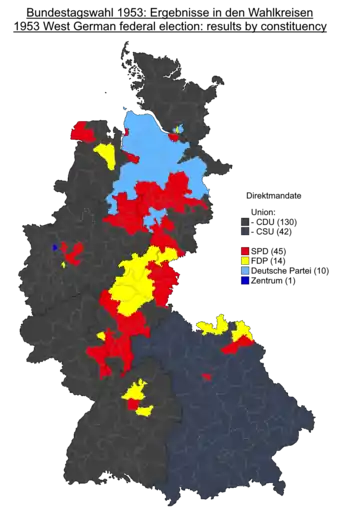 Results by constituency for the first votes. Grey denotes seats won by the CDU/CSU; red denotes seats won by the SPD; yellow denotes seats won by the FDP; light blue denotes seats won by the German Party; dark blue denotes the seat won by the Centre Party. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Campaign
Federal Chancellor Adenauer (who was also the Christian Democratic leader) campaigned on his policies of economic reconstruction and growth, moderate conservatism or Christian democracy, and close relations with the United States. The new Social Democratic leader – Kurt Schumacher had died in 1952 – was Erich Ollenhauer, who was more moderate in his policies than Schumacher had been. He did not oppose, in principle, the United States' military presence in Western Europe. In fact, he later – in 1957 – supported a military alliance of most European countries, including Germany.[3][4] Adenauer managed to convince clearly more West German voters of his leadership abilities and economic and political success to easily win a second term, although he had to form a coalition government with the Free Democrats and the conservative German Party to gain a majority in the Bundestag.
Results
 | ||||||||||||||||
| Parties | Constituency | Party list | Total seats | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | +/− | Seats | +/− | Votes | % | +/− | Seats | +/− | Seats† | +/− | % | ||||
| Christian Democratic Union (CDU) | 9,577,659 | 34.8 | +9.6 | 130 | +39 | 10,016,594 | 36.4 | +11.2 | 61 | +37 | 197 | +77 | 38.7 | |||
| Social Democratic Party (SPD) | 8,131,257 | 29.5 | +0.3 | 45 | −51 | 7,944,943 | 28.8 | −0.4 | 106 | +71 | 162 | +22 | 31.8 | |||
| Free Democratic Party (FDP) | 2,967,566 | 10.8 | −1.1 | 14 | +2 | 2,629,163 | 9.5 | −2.4 | 34 | −6 | 53 | −4 | 10.4 | |||
| Christian Social Union (CSU) | 2,450,286 | 8.9 | +3.1 | 42 | +18 | 2,427,387 | 8.8 | +3.0 | 10 | +10 | 52 | +28 | 10.2 | |||
| All-German Bloc/League of Expellees and Deprived of Rights (GB/BHE) | 1,613,215 | 5.9 | +5.9 | 0 | ±0 | 1,616,953 | 5.9 | +5.9 | 27 | +27 | 27 | +27 | 5.3 | |||
| German Party (DP) | 1,073,031 | 3.9 | –0.1 | 10 | +5 | 896,128 | 3.3 | −0.7 | 5 | −7 | 15 | -2 | 2.9 | |||
| Centre Party (Zentrum) | 55,835 | 0.2 | -2.9 | 1 | +1 | 217,078 | 0.8 | -2.3 | 2 | −8 | 3 | −7 | 0.6 | |||
| Communist Party (KPD) | 611,317 | 2.2 | −3.5 | 0 | ±0 | 607,860 | 2.2 | −3.5 | 0 | −15 | 0 | −15 | 0 | |||
| Bavaria Party (BP) | 399,070 | 1.5 | −2.7 | 0 | −11 | 465,641 | 1.7 | −2.5 | 0 | −6 | 0 | −17 | 0 | |||
| All-German People's Party (GVP) | 286,465 | 1.0 | +1.0 | 0 | ±0 | 318,475 | 1.2 | +1.2 | 0 | ±0 | 0 | ±0 | 0 | |||
| German Reich Party (DRP)‡ | 204,725 | 0.7 | −1.1 | 0 | ±0 | 295,739 | 1.1 | −0.7 | 0 | −5 | 0 | −5 | 0 | |||
| Dachverband der Nationalen Sammlung (DNS) | 78,356 | 0.3 | +0.3 | 0 | ±0 | 70,726 | 0.3 | +0.3 | 0 | ±0 | 0 | ±0 | 0 | |||
| South Schleswig Voter Federation (SSW) | 44,339 | 0.2 | −0.1 | 0 | ±0 | 44,585 | 0.2 | −0.1 | 0 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 0 | |||
| Schleswig-Holsteinische Bauern- und Landarbeiterdemokratie (SHBLD) | 6,269 | 0.0 | +0.0 | 0 | ±0 | – | – | – | – | – | 0 | ±0 | 0 | |||
| Patriotic Union | 2,531 | 0.0 | +0.0 | 0 | ±0 | – | – | – | – | – | 0 | ±0 | 0 | |||
| Party of the Good Germans | 654 | 0.0 | +0.0 | 0 | ±0 | – | – | – | – | – | 0 | ±0 | 0 | |||
| Electoral groups and independents | 17,185 | 0.1 | −4.7 | 0 | −3 | – | – | – | – | – | 0 | −3 | 0 | |||
| Invalid/blank votes | 959,790 | — | — | — | — | 928,278 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||
| Totals | 28,479,550 | 100 | ±0.0 | 242 | ±0 | 28,479,550 | 100 | ±0.0 | 245 | +85 | 509 | +88 | ±0 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 33,120,940 | 86.0 | — | — | — | 33,120,940 | 86.0 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||
| Source: Federal Returning Officer | ||||||||||||||||
- ^† — includes the non-voting delegates for West Berlin (11 SPD, 6 CDU, 5 FDP).
- ^‡ — previously the German Right Party.
| 249 | 53 | 27 | 15 | 162 | |
| CDU/CSU | FDP | GB/BHE | DP | SPD |
Aftermath
Konrad Adenauer remained Chancellor, governing in a broad coalition (two-thirds majority) with most of the minor parties except for the SPD and Centre Party.
References
- "Wahl zum 2. Deutschen Bundestag am 6. September 1953" (in German). Bundeswahlleiter. Archived from the original on 29 March 2009. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- "Voter turnout by election year". Website of the Federal Returning Officer's Office. The Federal Returning Officer. Archived from the original on 8 September 2013. Retrieved 7 November 2014.
- Erling Bjöl, Grimberg's History of the Nations, volume 23: The Rich West, "A Giant Dwarf: West Germany," Helsinki: WSOY, 1985
- Dennis L. Bark and David R. Gress, A History of West Germany: Volume 1: 1945–1963: From Shadow to Substance, London, UK: Basil Blackwell, 1989
.jpg.webp)

