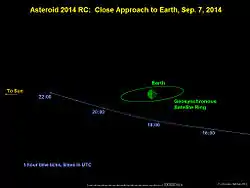
2014 RC
2014 RC is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object of the Apollo group. On 7 September 2014, it passed within 0.000267 AU (39,900 km; 24,800 mi) (0.1 LD) of Earth. The asteroid is approximately the diameter of the Chelyabinsk meteor,[4] and passed almost as close to Earth as 367943 Duende (2012 DA14) did in 2013.
 2014 RC imaged by the Goldstone Radar on 7 September 2014 | |
| Discovery[1][2] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | |
| Discovery date | 1–2 September 2014 |
| Designations | |
| Orbital characteristics[3] | |
| Epoch 13 January 2016 (JD 2457400.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 2 | |
| Observation arc | 18 days w/Radar |
| Aphelion | 1.803891 AU (269.8583 Gm) |
| Perihelion | 0.8206096 AU (122.76145 Gm) |
| 1.312251 AU (196.3100 Gm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.3746548 |
| 1.50 yr (549.06 d)[3] | |
| 287.9332° | |
| 0° 39m 20.377s / day | |
| Inclination | 4.573941° |
| 345.005065° | |
| 71.17158° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.000643292 AU (96,235.1 km) |
| Jupiter MOID | 3.5698 AU (534.03 Gm) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | |
Mean density | >2.5 (assumed based on rotation/spectra) |
| Sq-class[4] | |
| |
| 26.8[3] | |
With an absolute magnitude of 26.8,[3] the asteroid is about 11–25 meters (36–82 ft) in diameter depending on the albedo.[5] Observations by the NASA Infrared Telescope Facility conclude the asteroid is a fairly bright Sq-class asteroid which have an average albedo of around 0.24, and would give the asteroid a spherical equivalent diameter of 12 meters (39 ft).[4] Measurements by multiple telescopes indicate that the asteroid rotates in 15.8 seconds making it one of the fastest rotating asteroids so far discovered.[4] Using the 15.8 second rotation period, more accurate radar observations by Goldstone shows the asteroid has a largest axis of at least 22 meters (72 ft).[4] Due to the asteroid's fast rotation, it is a monolith and not a rubble pile.
On 8 September 2115 the asteroid will pass about 0.0053 AU (790,000 km; 490,000 mi) from the moon.[3] On 5 September 1973, the asteroid passed between 0.01052 AU (1,574,000 km; 978,000 mi) and 0.01207 AU (1,806,000 km; 1,122,000 mi) from Earth.[3] 2014 RC was removed from the JPL Sentry Risk Table on 5 September 2014 and there are no known possible impact dates in the next 100 years.[6]
2014 approach
It made a close approach to Earth of 0.000267 AU (39,900 km; 24,800 mi) (0.1 lunar distances) around 18:02 UTC on 7 September 2014.[3][7][8] The asteroid briefly brightened to about apparent magnitude 11.5,[9] but it was still not visible to the naked eye or common binoculars. At the peak brightness the asteroid had a declination of –47,[9] and was most easily visible over New Zealand. During 2014, asteroids 2014 AA and 2014 LY21 have come closer to Earth.
The Managua explosion on 6 September 2014 may or may not have been created by a bolide that was missed by millions of people, but either way it was not caused by the close approach of 2014 RC.[4]
Orbital shift
During the 2014 Earth close approach the orbital period of 2014 RC was reduced from 600 days to 549 days.[10] The orbital eccentricity decreased while the orbital inclination increased.
| Parameter | Epoch | Aphelion (Q) |
Perihelion (q) |
Semi-major axis (a) |
Eccentricity (e) |
Period (p) |
Inclination (i) |
Longitude ascending node (Ω) |
Mean anomaly (M) |
Argument of perihelion (ω) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units | AU | (days) | (°) | |||||||
| Pre-flyby | 2014-09-01 | 1.9488 | 0.8344 | 1.3916 | 0.4004 | 599.62 | 1.4395° | 345.48° | 326.12° | 65.879° |
| flyby | 2014-09-07 18:02 UTC | 2.0284 | 0.8150 | 1.4217 | 0.4267 | 619.17 | 1.4217° | 345.09° | 330.91° | 68.602° |
| Post-flyby | 2014-10-01 | 1.8042 | 0.8207 | 1.3124 | 0.3747 | 549.18 | 4.5744° | 345.01° | 340.41° | 71.187° |
Close-approach table
| Object | Date (UTC) | Date error (hours) |
Nominal distance (AU) |
Nominal distance (LD) |
Minimum distance (AU) |
Minimum distance (LD) |
Apparent magnitude (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Earth | 1945-09-06 05:53 | 47.16 | 0.00442 | 1.72 | 0.00101 | 0.39 | 17.3 |
| Moon | 1945-09-06 14:33 | 52.48 | 0.00508 | 1.98 | 0.00103 | 0.40 | – |
| Mars | 1957-10-09 13:55 | 5.40 | 0.06371 | 24.78 | 0.05267 | 20.49 | – |
| Earth | 1973-09-05 21:42 | 0.62 | 0.01169 | 4.55 | 0.01089 | 4.24 | 19.3 |
| Earth | 1987-01-17 01:02 | 0.30 | 0.03724 | 14.49 | 0.03686 | 14.34 | 22.4 |
| Earth | 1991-09-27 05:38 | 1.03 | 0.09911 | 38.55 | 0.09878 | 38.43 | 27.0 |
| Mars | 1999-09-22 14:00 | <0.01 | 0.03739 | 14.54 | 0.03712 | 14.44 | – |
| Earth | 2009-12-30 13:10 | 0.28 | 0.08634 | 33.59 | 0.08622 | 33.54 | 26.0 |
| Moon | 2014-09-07 08:47 | <0.01 | 0.000845 | 0.329 | 0.000845 | 0.329 | – |
| Earth | 2014-09-07 18:02 | <0.01 | 0.000267 | 0.104 | 0.000267 | 0.104 | 15.9 |
| Earth | 2017-09-11 13:50 | 0.15 | 0.03864 | 15.03 | 0.03850 | 14.98 | 23.3 |
| Earth | 2020-09-22 21:24 | 0.35 | 0.09908 | 38.54 | 0.09893 | 38.48 | 26.1 |
| Earth | 2039-01-21 23:38 | 0.13 | 0.06224 | 24.21 | 0.06215 | 24.18 | 24.0 |
| Earth | 2042-01-27 18:19 | 0.10 | 0.06322 | 24.59 | 0.06313 | 24.56 | 23.6 |
| Earth | 2109-09-01 16:27 | 0.07 | 0.09959 | 38.74 | 0.09945 | 38.69 | 24.7 |
| Earth | 2112-09-06 21:13 | 0.08 | 0.02253 | 8.76 | 0.02241 | 8.72 | 21.1 |
| Moon | 2115-09-08 19:11 | 0.15 | 0.00558 | 2.17 | 0.005350 | 2.08 | – |
| Earth | 2115-09-08 22:50 | 0.17 | 0.00785 | 3.05 | 0.00763 | 2.97 | 18.5 |
| Mars | 2140-10-13 22:42 | 2.85 | 0.07152 | 27.82 | 0.05471 | 21.28 | – |
| Earth | 2159-02-02 22:17 | 16.90 | 0.08084 | 31.45 | 0.05563 | 21.64 | 24.2 |
| Earth | 2162-01-19 14:04 | 38.85 | 0.09376 | 36.47 | 0.07273 | 28.29 | 25.2 |
| Earth | 2170-09-19 02:08 | 9.12 | 0.07413 | 28.84 | 0.06707 | 26.09 | 25.1 |
| Earth | 2173-09-04 16:52 | 1.38 | 0.06123 | 23.82 | 0.05950 | 23.15 | 23.5 |
References
- "MPEC 2014-R23 : 2014 RC". IAU Minor Planet Center. 3 September 2014. Retrieved 5 September 2014. (K14R00C)
- "MPEC 2014-R26 : 2014 RC". IAU Minor Planet Center. 3 September 2014. Retrieved 5 September 2014.
- "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: (2014 RC)" (last observation: 7 September 2014; arc: 18 days). Retrieved 4 April 2016.
- "Reports of Meteorite Strike in Nicaragua and Update on Asteroid 2014 RC". NASA/JPL Near-Earth Object Program Office. Archived from the original on 11 October 2014. Retrieved 9 September 2014.
- "JPL – Absolute Magnitude". NASA. Retrieved 4 September 2014.
- "Date/Time Removed". NASA/JPL Near-Earth Object Program Office. Retrieved 5 September 2014.
- "NASA reports asteroid to pass close, but safely past Earth". clarksvilleonline.com. Clarksville Online. 4 September 2014. Retrieved 4 September 2014.
- Agle, DC; Brown, Dwayne (3 September 2014). "Small Asteroid to Safely Pass Close to Earth Sunday". NASA. Retrieved 7 September 2014.
- "2014RC Ephemerides for 7 September 2014". NEODyS (Near Earth Objects – Dynamic Site). Retrieved 5 September 2014.
- Horizons output. "Horizon Online Ephemeris System". Retrieved 7 September 2014. ("Ephemeris Type: Elements" PR value)
External links
- ASTEROID 2014 RC Tracking
- Close Approach of Asteroid 2014 RC (Remanzacco Observatory)
- Small Asteroid Will Pass Earth Closely but Safely on Sunday (Phil Plait)
- 2014 RC at NeoDyS-2, Near Earth Objects—Dynamic Site
- Ephemeris · Obs prediction · Orbital info · MOID · Proper elements · Obs info · Close · Physical info · NEOCC
- 2014 RC at ESA–space situational awareness
- 2014 RC at the JPL Small-Body Database