Amiiformes
The Amiiformes /ˈæmi.ɪfɔːrmiːz/ order of fish has only one extant species, the bowfin (Amia calva). These Amiiformes are found in the freshwater systems throughout North America and parts of southern Canada. They live in freshwater streams, rivers, and swamps. These bowfin fish are not on the endangered list. They have the ability to go to the surface to breathe if the water level is too low. The extinct species of the Amiiformes can be found fossilized in Asia and Europe, but the bowfin is the last living species in the order.
| Amiiformes | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Amia calva | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Subclass: | Neopterygii |
| Infraclass: | Holostei |
| Order: | Amiiformes O. P. Hay, 1929[1] |
| Families | |
|
See text | |
Characteristics of Amiiformes are a cylindrical body with a long dorsal fin, single gular plate, heterocercal caudal fin, 10 to 13 flattened branchiostegal rays, maxilla included in gape, and prominent ocellus near upper base of caudal fin.
Taxonomy
- Order Amiiformes Hay 1929[2][3][4]
- Genus †Guizhouamia Liu, Yin & Wang 2002
- Genus †Stromerichthys Weiler 1935
- Superfamily †Caturoidea
- Family †Liodesmidae Jordan 1905
- Genus †Paraliodesmus Dunkle 1969
- Genus †Liodesmus Wagner 1859 [Lophiurus Vetter 1881]
- Family †Caturidae Owen 1860 corrig.
- Genus ?†Allolepidotus (Deecke 1889) [Heterolepidotus (Allolepidotus) Deecke 1889; Plesiolepidotus Schlosser 1923]
- Genus ?†Catutoichthys Gouiric-Cavalli 2016
- Genus ?†Ditaxiodus Owen 1866
- Genus ?†Eoeugnathus Brough 1939
- Genus ?†Guizhoueugnathus Liu 2004
- Genus ?†Harpactira Egerton 1876 [Harpactes Egerton 1876 non Swainson 1833 non Templeton 1834 non Menetries 1848]
- Genus ?†Plesiofuro Su 1993
- Genus ?†Sinoeugnathus Su 1959
- Genus ?†Thlattodus Owen 1866
- Genus ?†Xingyia Liu et al. 2003
- Genus †Amblysemius Agassiz 1844
- Genus †Caturus Agassiz 1834 [Uraeus Agassiz 1832 non Wagler 1830; Strobilodusss Wagner 1851; Endactis Egerton 1858 non Rafinesque 1820; Conodus Woodward 1895 non Gervais 1869; Conodus Agassiz 1841 nomen nudum]
- Genus †Furo Gistl 1848 [Eugnathus Agassiz 1844 non Schönherr 1833; Eugnathus Agassiz 1836 nomen nudum; Isopholis Zittel 1887]
- Genus †Heterolepidotus Egerton 1872 [Eulepidotus Egerton 1868 non Herrich-Schaeffer 1850-1856; Brachyichthys Winkler 1862]
- Genus †Neorhombolepis Woodward 1888
- Genus †Osteorachis Egerton 1868
- Genus †Otomitla Felix 1891
- Family †Liodesmidae Jordan 1905
- Superfamily Amioidea Bonaparte 1838
- Genus ?†Amiidarum Lange 1968 [Otolith]
- Genus ?†Ferganamia Kaznyshkin 1990
- Genus ?†Lehmanamia Casier 1966
- Family Amiidae Bonaparte 1837
- Subfamily †Siamamiinae Berg 1940
- Genus †Siamamia Cavin, Suteethorn, Buffetaut, Claude, Cuny, Le Loeuff and Tong 2007
- Subfamily Amiinae Bonaparte 1837 sensu Grande & Bemis 1998
- Genus Amia Linnaeus 1766 non Browne 1756 ex Browne 1789 non Gronow 1763 ex Gray 1854 non Meuschen 1781; Amiatus Rafinesque 1815; Hypamia (Leidy 1873); Amia (Hypamia) Leidy 1873; Kindleia Jordan 1927; Protamia (Leidy 1873); Amia (Protamia) Leidy 1873; Stylomyleodon Russell 1928]
- Genus †Cyclurus Agassiz 1839 [Notaeus Agassiz 1843]
- Genus †Pseudamiatus Whitley 1954 [Pseudamia Lehman 1951 non Bleeker 1865]
- Subfamily †Amiopsinae Grande and Bemis 1998
- Genus †Amiopsis Kner 1863 [Urocles]
- Subfamily †Solnhofenamiinae Grande and Bemis 1998
- Genus †Solnhofenamia Grande and Bemis 1998 (type)
- Subfamily †Vidalamiinae Grande and Bemis 1998
- Tribe †Calamopleurini Grande and Bemis 1998
- Genus †Calamopleurus Agassiz 1841 [Enneles Jordan & Branner 1908]
- Genus †Maliamia Patterson and Longbottom 1989
- Tribe †Vidalamiini Grande and Bemis 1998
- Genus †Melvius Bryant 1987
- Genus †Pachyamia Chalifa and Tchernov 1982
- Genus †Vidalamia White and Moy-Thomas 1941 [Vidalia le Sauvage1903 non Robineau-Desvoidy 1830 non Lamouroux ex Agardh 1863]
- Genus †Nipponamia Yabumoto 1994
- Tribe †Calamopleurini Grande and Bemis 1998
- Subfamily †Siamamiinae Berg 1940
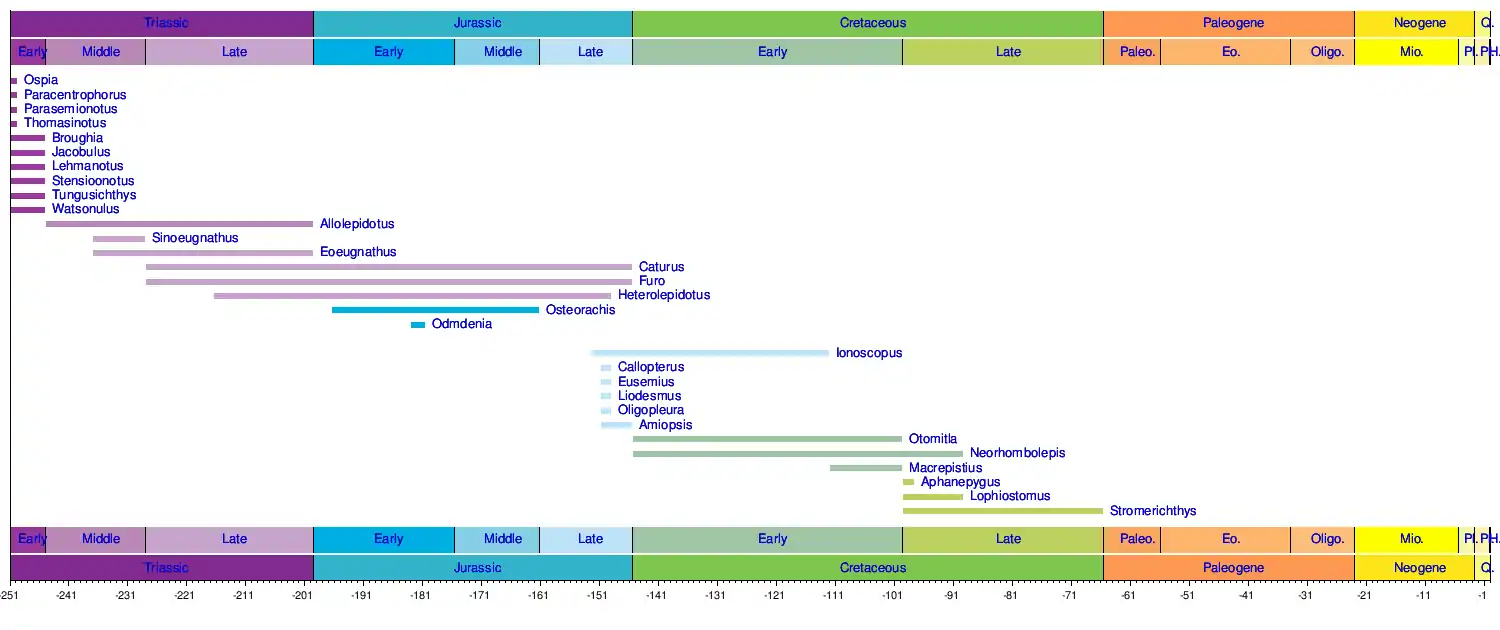
Timeline of genera
References
- "Amiiformes". Paleobiology Database. Retrieved November 15, 2012.
- Haaramo, Mikko (2007). "Amiiformes – bowfin and relatives". Mikko's Phylogeny Archive. Retrieved 30 December 2016.
- Nelson, Joseph S.; Grande, Terry C.; Wilson, Mark V. H. (2016). Fishes of the World (5th ed.). John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781118342336.
- van der Laan, Richard (2016). "Family-group names of fossil fishes". Cite journal requires
|journal=(help)
External links
| Wikispecies has information related to Amiidae. |
