Aqua (satellite)
Aqua (EOS PM-1) is a NASA scientific research satellite in orbit around the Earth, studying the precipitation, evaporation, and cycling of water. It is the second major component of the Earth Observing System (EOS) preceded by Terra (launched 1999) and followed by Aura (launched 2004).
 Aqua (EOS PM-1) | |
| Mission type | Earth observation |
|---|---|
| Operator | NASA |
| COSPAR ID | 2002-022A |
| SATCAT no. | 27424 |
| Website | aqua.nasa.gov |
| Mission duration | 6 years (planned) Elapsed: 18 years, 9 months |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Bus | T330 (AB-1200) |
| Manufacturer | TRW |
| Launch mass | 3,117 kilograms (6,872 lb) |
| Dimensions | 4.81 m × 16.7 m × 8.04 m (15.8 ft × 54.8 ft × 26.4 ft) |
| Power | 4.444 kilowatts |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | May 4, 2002, 09:54:58 UTC |
| Rocket | Delta II 7920-10L |
| Launch site | Vandenberg SLC-2W |
| Contractor | Boeing |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Low Earth |
| Semi-major axis | 7,080.6 kilometers (4,399.7 mi) |
| Eccentricity | 0.0000979 |
| Perigee altitude | 702 kilometers (436 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 703 kilometers (437 mi) |
| Inclination | 98.1987° |
| Period | 99 minutes |
| RAAN | 95.2063° |
| Argument of perigee | 120.4799° |
| Mean anomaly | 351.4268° |
| Mean motion | 14.57116559 |
| Epoch | 02 June 2016, 10:25:37 UTC |
| Revolution no. | 74897 |
 Logotype of the mission. | |
The name "Aqua" comes from the Latin word for water. The satellite was launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base on May 4, 2002, aboard a Delta II rocket. Aqua is on a Sun-synchronous orbit. It flies as the third in the satellite formation called the "A Train" with several other satellites (OCO-2, the Japanese GCOM W1, CALIPSO, CloudSat, and Aura).
Mission
Aqua is one of NASA's missions for Earth science operating in the A-Train constellation. It has demonstrated a very high level of precision in making the primary long-term measurements of the mission. These highly calibrated climate quality measurements of radiance, reflectance, and backscatter have been used to cross-calibrate past and present sensors launched by NASA, as well as a variety of sensors launched from other agencies and the international community. Thousands of scientists and operational users from around the world have made use of the Aqua data to address NASA's six interdisciplinary Earth science focus areas: Atmospheric Composition, Weather, Carbon Cycle and Ecosystems, Water and Energy Cycle, Climate Variability and Change, and Earth Surface and Interior.
Aqua has experienced some minor, non-mission ending anomalies.
Because of a 2007 anomaly with the Solid State Recorder (SSR) it can only hold two orbits worth of data. A series of solar array and array regulator electronics anomalies starting in 2010 has led to the loss of 13 strings of solar cells out of a total of 132 strings. A 2005 short circuit within a battery cell led to a partial loss of cell capacity. In 2009, a solar panel thermistor failed and an error in the Solar Array offset was detected. The offset issue has been corrected periodically since then. On September 8, 2007, the Dual Thruster Module (DTM-2) Heater experienced an anomaly.[1] On August 16, 2020, The Formatter Multiplexer Unit (FMU) experienced an anomaly, corrupting some data in the SSR and stopping all data streams until it was recovered on September 2, 2020.[2]
The current end of mission plan has Aqua leaving the "A-Train" constellation in March 2022, with the mission continuing at a lower orbit until 2025. Aqua's life could be extended with a possible re-fueling mission. Worst-case scenario would result in a re-entry by 2046.[3]
Instruments
Aqua carries six instruments for studies of water on the Earth's surface and in the atmosphere, of which four are still operating:
- Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer-EOS (AMSR-E) — measures cloud properties, sea surface temperature, near-surface wind speed, radiative energy flux, surface water, ice and snow. Furnished by the National Space Development Agency of Japan. The AMSR-E instrument had over 480 pounds of spinning mass, and the lubricant in the bearing assembly gradually deteriorated over the course of the mission. By 2007, there was a noticeable increase in motor current. This led to the development of new contingency procedures in case of high current or torque, which were put in place in 2011. In October 2011, the instrument began to cause yaw vibrations in the spacecraft that exceeded torque limits and on October 4, 2011 was automatically slowed to 4 rpm from the normal 40 rpm and then, because it could not maintain 4 rpm, was slowed to a stop.[4] A recovery procedure was developed and tested through 2012, culminating with a December 4, 2012 successful acceleration to 2.0767 rpm to allow for cross-calibration with the AMSR-2 instrument launched in 2012 aboard the GCOM-W1 satellite.[5] On December 4, 2015 AMSR-E was slowed to a stop and then on March 3, 2016 it was turned off.[6]
- Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) — also measures cloud properties and radiative energy flux, also aerosol properties; land cover and land use change, fires and volcanoes. An identical MODIS instrument is also aboard Terra. As of 2017, some degradation of channels in the MODIS short wave visible bands has been observed by the Ocean Biology Processing Group (OBPG).[7]
- Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit (AMSU-A) — measures atmospheric temperature and humidity. Since launch, AMSU has lost 5 of 15 channels.[8][9] Power to the AMSU-A2 microwave instrument was lost at 19:47 UT September 24, 2016. This caused the loss of Channels 1 and 2. All recovery attempts were unsuccessful and no further recovery attempts are planned.[1]
- Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) — measures atmospheric temperature and humidity, land and sea surface temperatures. Cooler A telemetry became frozen on March 24, 2014, but this had no impact on science gathering.[10] On September 25, 2016, Cooler-A experienced a shut down anomaly. Anomaly recovery occurred two days later and also cleared a condition that had disabled Cooler-A telemetry since the 2014 Cooler-A anomaly.[9]
- Humidity Sounder for Brazil (HSB) — VHF band equipment measuring atmospheric humidity. Furnished by Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais of Brazil. The HSB instrument has been in survival mode, and thus non-operational, since February 5, 2003, when the scan mirror motor failed.[10]
- Clouds and the Earth's Radiant Energy System (CERES) — Flying Modules 3 and 4, measure broadband radiative energy flux. CERES' shortwave channel on module 4 failed on March 30, 2005, but its two other channels remain operational.[10]
The Aqua spacecraft has a mass of about 2,850 kilograms (6,280 lb), plus propellant of about 230 kilograms (510 lb) at launch. Stowed for launch, the satellite fit in a volume of 2.68 m x 2.49 m x 6.49 m. Deployed, Aqua is 4.81 m x 16.70 m x 8.04 m.
 Aqua instruments
Aqua instruments Aqua satellite
Aqua satellite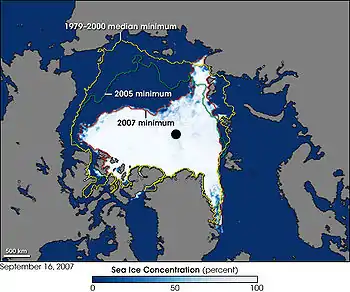 Image of Arctic shrinkage from Aqua observations
Image of Arctic shrinkage from Aqua observations
References
- Guit, Bill. "EOS Aqua Mission Status at the Earth Science Constellation Mission Operations Working Group (MOWG) Meeting at GSFC" (PDF). Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- "Case PM_MYD_20229_NRT". Retrieved 24 August 2020.
- Guit, Bill. "EOS Aqua: 2017 Mission Status at the Earth Science Constellation (ESC) Mission Operations Working Group (MOWG) Meeting at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC)" (PDF). Retrieved 6 April 2018.
- Spencer, Roy W. "AMSR-E Ends 9+ Years of Global Observations". drroyspencer.com. Retrieved 16 October 2017.
- Guit, Bill. "AMSR-E Recovery" (PDF). Retrieved 16 October 2017.
- MIURA, Satoko Horiyama. "AMSR-E Spun Down on Dec. 2015" (PDF). Retrieved 16 October 2017.
- Vandemark, Douglas. "NASA Earth Science Senior Review Subcommittee Report — 2017" (PDF). Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- Liu, Guosheng (22 June 2015). "NASA Earth Science Senior Review 2015" (PDF). Retrieved 17 October 2017. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "Aqua Summary August 31, 2017" (PDF). Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- Parkinson, Claire. "2015 Aqua Update" (PDF). Retrieved 16 October 2017.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Aqua (satellite). |