Arque Province
Arque is a rural province in Cochabamba Department in the eastern cordillera of the South American state of Bolivia.
Arque | |
|---|---|
Province | |
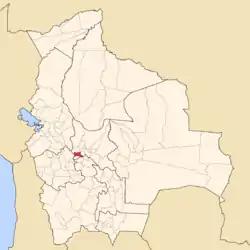 Location of the Arque Province within Bolivia | |
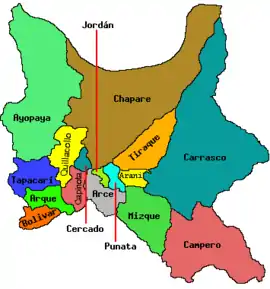 Provinces of the Cochabamba Department | |
| Coordinates: 17°50′S 66°55′W | |
| Country | |
| Department | Cochabamba Department |
| Municipalities | 2 |
| Cantons | 4 |
| Capital | Arque |
| Area | |
| • Total | 416 sq mi (1,077 km2) |
| Population (2001) | |
| • Total | 23,464 |
| • Density | 56/sq mi (21.8/km2) |
| • Ethnicities | Quechua |
| Area code(s) | BO.CB.AQ |
Geography
The province is surrounded by the provinces of Tapacarí in the northwest, Quillacollo in the northeast, Capinota in the east, Bolívar in the south and the departments of Oruro in the west and Potosí in the southeast.
It is located in the Bolivian Andes at an elevation between 3,000 and 4,500 metres and about 250 km west of Cochabamba, the capital of the department. The landscape is deeply fissured. Some of the highest mountains of the province are listed below:[1][2][3]
- Apachita
- Awila Chukuña
- Chullpa Ch'utu
- Chuymani
- Ch'uñawi
- Inka Pukara
- Jach'a Qullu
- Janq'u Jaqhi
- Juch'uy Sayari
- Kuntur Sayana
- Kuntur Wachana
- Mik'ayani
- Millu Wiqu
- Murmuntani
- Pichaqani
- Puka Puka
- Pukara
- P'ujru P'ujruni
- Qala Pampa
- Sayari
- Silla Q'asa
- Siwinqani
- Wila Ch'utu
- Yanakuna
- Yaritani
Arque, the capital of the province, is situated on the northern bank of the Arque River, an affluent of the Río Grande.
Climate
The rainy season covers the months from December to April. The precipitation can occur in the form of devastating hailstorms which may even destroy the planted seeds of field crops and the harvests.
Subdivision
Arque Province is divided into two municipalities (Spanish: municipio, sección or sección municipal): Arque Municipality (first section) and Tacopaya Municipality (second section). The two municipalities with one mayor each are further subdivided into four cantons and supervised each of them by a corregidor: Arque Canton and Colcha Canton in Arque Municipality and Tacopaya Canton and Ventilla Canton within Tacopaya Municipality. The province is managed by a sub-prefect (subprefecto).
| Section | Municipality | Inhabitants [4] | Capital | Inhabitants [5] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | Arque | 11,806 | Arque | 487 |
| 2nd | Tacopaya | 11,658 | Tacopaya | 137 |
Arque Municipality is situated in the eastern part of the province and Tacopaya Municipality is located in the west.
The People
Arque Province has the lowest Index on Human Development (0.311) [6] within Bolivia. Of all the 314 municipalities in Bolivia Arque was on the last position (HDI 0.311) in the year 2001 and Tacopaya was on rank 308 (HDI 0.361). However, in recent years many measures particularly done in the field of education and health have been taken in order to improve the social situation. In 2005 92% of the population of Arque including larger and smaller communities had access to potable water according to reports from Arque Municipality. Only seven communities still remained without water supply at that time.[7]
The province has a rural character. Most families rely on subsistence farming for their livelihood. The peasants cultivate maize, wheat, barley and potatoes on the stark, steep slopes. The population with a high number of indigenous citizens of Quechuan and Aymara descent [8][9] mostly lived or still lives in humble houses with earthen floor, adobe walls, roofed with thatched material. Often these houses only consist of one single room where the meals are prepared on open fire so that the smoke can cause infections of the eyes. The roofs bear a deadly danger which comes overnight: the blood-sucking winchuka[10] bugs (vinchuca), common to the zone, which can cause the Chagas disease. During the day the insects hide in crevices in the walls and roofs made of straw. The bugs emerge at night, when the inhabitants are sleeping. One measure to reduce the risk of acquiring the disease is the renovation of houses by using tiles and the construction of houses that are resistant to the entry of the bug.
Some data:[6]
| Arque Province | ||
|---|---|---|
| Municipality | Arque | Tacopaya |
| Nacional ranking (out of 314) | 314 | 308 |
| Human Development Index (2001) | 0.311 | 0.361 |
| Index of life expectancy | 0.412 | 0.428 |
| Index of education | 0.338 | 0.473 |
| Life expectancy (years) | 49.7 | 50.7 |
| Literacy of adults (% of 15 years old and more) | 42.7 | 57.4 |
| Average years of schooling | 1.7 | 2.1 |
| Population 2001 | 11,496 | 11,968 |
| Percentage of rural population | 100.0% | 100.0% |
The latest results about the ethnic-linguistic composition of the population are as follows:
| Ethnic group | Arque Municipality (%) | Tacopaya Municipality (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Quechua | 93.5 | 95.4 |
| Aymara | 0.9 | 1.7 |
| Guaraní, Chiquitos, Moxos | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Not indigenous | 5.4 | 2.8 |
| Other indigenous groups | 0.1 | 0.1 |
Ref.: obd.descentralizacion.gov.bo
Languages
The languages spoken in the Arque Province are mainly Quechua and Spanish. The following table shows the number of those belonging to the recognized group of speakers.[11]
| Language | Arque Municipality | Tacopaya Municipality |
|---|---|---|
| Quechua | 10.793 | 10.766 |
| Aymara | 107 | 123 |
| Guaraní | 3 | 3 |
| Another native | 2 | 132 |
| Spanish | 2.185 | 3.309 |
| Foreign | 13 | 9 |
| Only native | 8.778 | 7.552 |
| Native and Spanish | 2.052 | 3.236 |
| Only Spanish | 134 | 74 |
References
- Bolivia 1:100,000 Tarata 3635, Map prepared and published by the Defense Mapping Agency, Hydrographic/Topographic Center, Bethesda, MD
- "Arque". INE, Bolivia. Archived from the original on April 7, 2016. Retrieved March 30, 2016.
- "Tacopaya". INE, Bolivia. Archived from the original on April 7, 2016. Retrieved March 30, 2016.
- www.ine.gov.bo Archived August 25, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- "world-gazetteer.com". Archived from the original on 2008-10-24.
- Informe sobre Desarollo Humano Archived 2009-01-19 at the Wayback Machine (Spanish)
- Arque apuesta por revertir calidad de vida de poblados Archived May 12, 2008, at the Wayback Machine (Spanish)
- Statistical Data: Arque Municipality
- Statistical Data: Tacopaya Municipality
- Teofilo Laime Ajacopa, Diccionario Bilingüe Iskay simipi yuyayk'ancha, La Paz, 2007 (Quechua-Spanish dictionary)
- obd.descentralizacion.gov.bo Archived February 18, 2009, at the Wayback Machine (Spanish)