Australian property bubble
The Australian property bubble is the economic theory that the Australian property market has become or is becoming significantly overpriced and due for a significant downturn (also called a correction or collapse). Since the early 2010s, various commentators, including one Treasury official,[1] have claimed the Australian property market is in a significant bubble.
Various industry professionals have argued that it is not a bubble and that house prices have the potential to keep rising in line with income growth. Some commentators have blamed rising property prices on state governments' restrictions on land supply, driving up the cost of land, lots, and thus homes.[2] Some have also blamed planning rules as acting to restrain supply of housing.
A property bubble is a form of economic bubble normally characterised by a rapid increase in market prices of real property until they reach unsustainable levels relative to incomes and rents, and then decline. Australian house prices rose strongly relative to incomes and rents during the late 1990s and early 2000s; however, from 2003 to 2012 the price to income ratio and price to rent ratio have both remained fairly steady, with house prices tracking income and rent growth during that decade. Since 2012 prices have once again risen strongly relative to incomes and rents. In June 2014, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) reported that house prices in several developed countries are "well above the historical averages" and that Australia had the third highest house price-to-income ratio in the world.[3] In June 2016, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) reported that Australia's housing boom could end in 'dramatic and destabilising' real estate hard landing.[4] As of December 2018, Sydney and Melbourne along with some regional cities have experienced price declines of up to 10% over the year, with a further 10-20% forecast in the near future. Declines were largely triggered by the significant tightening of lending standards following the Royal Commission into Misconduct in the Banking, Superannuation and Financial Services Industry that revealed mortgage fraud aka subprime 'liar loans' and widespread irresponsible lending practices. Combined with the significant declines in Western Australia since 2014 due to the drop in global resource prices, there is mounting evidence that the housing bubble is entering the correction phase.[5]
Australian property market
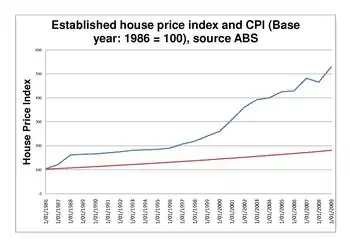
The Australian property market saw an average real price increase of around 0.5% per annum from 1890 to 1990, approximately matching CPI. Since the 1990s, however, prices have risen faster resulting in an elevated price to income ratio.[6]
In the late 2000s, house prices in Australia, relative to incomes, were at elevated levels similar to many comparable countries, prompting speculation that Australia was experiencing a real estate bubble like other comparable countries. Since then, several comparable countries have experienced property crashes.
Rising house prices
All capital cities have seen strong increases in property prices since about 1998. Sydney and Melbourne have seen the largest price increases, with house prices rising 105% and 93.5% respectively since 2009. These massive increases in house prices coincide with record low wage growth, record low interest rates and record household debt equal to 130% of GDP. This indicates unsustainable growth in property, driven by ever higher debt levels fuelled by the RBA's then chief, Glenn Stevens who began cutting rates beginning in 2011.
The Housing Affordability in Australia - Good house is hard to find report stated that "the average house price in the capital cities is now equivalent to over seven years of average earnings; up from three in the 1950s to the early 1980s.[7] Some factors that may have contributed to the increase in property prices include:
- greater availability of credit due to financial deregulation.
- low interest rates since 2008, increasing borrowing capacity to borrow due to lower repayments.
- limited government release of new land (reducing supply).[8]
- the average floor area of new houses has increased by up to 53.8% in the 18 years from 1984–85 to 2002–03.[9]
- a tax system that favours investors and existing home owners, with policies such as negative gearing and capital gain tax discounts.
- government restrictions on the use of land preventing higher density land use.
- government restrictions on greenfield development designed to encourage "urban densification".
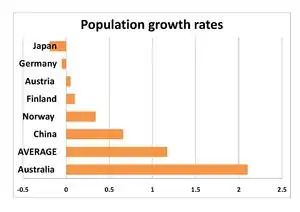
- high population growth (about double the world average in 2010- see Population growth rates chart).[10] [11]
- 2008 foreign investment rule changes for temporary visa holders.[12]
- introduction by local councils of upfront infrastructure levies in the early 2000s.
Influence of planning laws
Beginning in the 1980s, Australian states (who under the Constitution have control of environmental and land use issues) started progressively implementing more rigid planning laws that regulated the use of land.[13] Planning laws often concentrated, after the 1990s, on restricting greenfield development in favour of "urban densification", or infill development.[14][15] Land rationing is a system of banning development in all but designated areas, and can lead to extreme land price inflation if insufficient land is designated as allowed to be developed.[15] The restrictive planning laws in Australia have used land rationing systems as part of the goal of restricting greenfield development in favour of infill development, but this inevitably lead to land prices, and thus house prices, rising significantly.[16] There is good evidence to suggest that the price of a new unit of housing is the ultimate anchor of all housing in an area, so when planning laws that implemented land rationing severely drove up the cost of new homes, all other homes followed suit.
Influence of tax system
The Reserve Bank of Australia has noted that there are "a number of areas in which the taxation treatment in Australia is more favourable to investors than is the case in other countries."[17] The main tax incentives include tax deductions for losses on investment properties, even those that have been negatively geared, and the 50% discount on capital gains on sale of investments properties.
Investors using their superannuation for property investments have a tax advantage compared to 'savers' who are effectively taxed up to 45% (the top marginal taxation rate) on income from bank interest or bonds, as superannuation contributions are normally only taxed at around 15%.
Influence of banking system
The influence of interest rates and banking policy on property prices has been noted. The financial deregulation has led to greater availability of credit and a variety of financial products and options. Presently the Reserve Bank of Australia has maintained for some time a low cash interest rate policy which has also reduced the cost of financing property purchase. In addition, the easy availability of interest-only loans has also made possible for property investors to borrow to purchase a property and compounding the benefits of negative gearing.
Land price inflation is a story of housing debt
Debt growth averaged 15% per annum compounding (1998–2009). During the same period national economic growth was less than 3% with debt stripped out.[18]
Between 1998 and 2008 inflation was about 36%[19] and property prices increased by more than 300% in all capital cities except Melbourne (up 280%) and Sydney (up 180%).[20]
Housing costs excluded from the CPI
One of the market distortions in the housing market relates to the calculation of the Consumer Price Index [CPI]. One senior economist noted "The index ignores price changes in the single biggest purchase a person (or household) is likely to make in their lifetime – a dwelling″. This implies that Australia's main official cost of living measure is failing to represent young Australians by excluding home purchase costs. [21]
Immigration to Australia
A number of economists, such as Macquarie Bank analyst Rory Robertson, assert that high immigration and the propensity of new arrivals to cluster in the capital cities is exacerbating the nation's housing affordability problem.[22] According to Robertson, Federal Government policies that fuel demand for housing, such as the currently high levels of immigration, as well as capital gains tax discounts and subsidies to boost fertility, have had a greater impact on housing affordability than land release on urban fringes.[23]
The Productivity Commission Inquiry Report No. 28 First Home Ownership (2004) also stated, in relation to housing, "that Growth in immigration since the mid-1990s has been an important contributor to underlying demand, particularly in Sydney and Melbourne."[24] This has been exacerbated by Australian lenders relaxing credit guidelines for temporary residents, allowing them to buy a home with a 10 percent deposit.
The RBA in its submission to the same PC Report also stated "rapid growth in overseas visitors such as students may have boosted demand for rental housing".[24] However, in question in the report was the statistical coverage of resident population. The "ABS population growth figures omit certain household formation groups – namely, overseas students and business migrants who do not continuously stay for 12 months in Australia."[24] This statistical omission lead to the admission: "The Commission recognises that the ABS resident population estimates have limitations when used for assessing housing demand. Given the significant influx of foreigners coming to work or study in Australia in recent years, it seems highly likely that short-stay visitor movements may have added to the demand for housing. However, the Commissions are unaware of any research that quantifies the effects."[24]
Some individuals and interest groups have also argued that immigration causes overburdened infrastructure.[25]
However, higher house prices caused by immigration do not necessarily lead to lower housing affordability, particularly in the longer-term, because immigration in Australia has contributed to higher incomes, it has increased net government revenue, and it has contributed to economies of scale in many goods and services, such as public transport and mobile networks. Immigration in Australia has contributed to higher incomes due to higher economic growth due to migrants tending to be of working age, highly educated, and less entitled to welfare than citizens in some cases before they obtain citizenship. Immigration in Australia has increased net government revenue due to immigrants having a higher workforce participation rate and tending to be in a higher tax bracket; and due to immigration fees; and due to some non-citizen residents having to pay higher rates of income tax than citizens; and due to some non-citizens having to pay more than citizens for university units and medical care. Without the net revenue it has received from migrants, the Australian government would have been forced to increase the cost of living or to reduce incomes (possibly by raising taxes, possibly by not granting pay-rises to government staff, or possibly by offering less generous welfare and services).
Foreign investment in residential property
In December 2008, the federal government introduced legislation relaxing rules for foreign buyers of Australian property. According to FIRB (Foreign Investment Review Board) data released in August 2009, foreign investment in Australian real estate had increased by more than 30% year to date. One agent said that "overseas investors buy them to land bank, not to rent them out. The houses just sit vacant because they are after capital growth."[26]
In April 2010, the government announced amendments to policies to "ensure that foreign non-residents can only invest in Australian real estate if that investment adds to the housing stock, and that investments by temporary residents in established properties are only for their use whilst they live in Australia."[27][28]
Under the rules, temporary residents and foreign students will be:
- Screened by the Foreign Investment Review Board to determine if they will be allowed to buy a property.
- Forced to sell property when they leave Australia.
- Punished if they do not sell by a government-ordered sale plus confiscation of any capital gain.
- Required to build on vacant land within two years of purchase to stop "land banking".
Failure to do this would also lead to a government-ordered sale.[29]
Several Australian Banks and lenders provide home loans to non-residents for the purchase of Australian real estate. This is also thought by some to have contributed to the increases in Australia's property prices.
Government inquiries related to housing
In 2002, the government initiated a Productivity Commission Inquiry into the homes ownership in Australia. The Commission's Report titled 'First Home Ownership'[30] observed inter alia that "general taxation arrangements [capital gains tax, negative gearing, capital works deductions and depreciation provisions] have lent impetus to the recent surge in investment in rental housing and consequent house price increases."
The government's response to the report stated that "There is no conclusive evidence that the tax system has had a significant impact on house prices."[31]
In 2008, another study was commissioned – the 2008 Senate Select Committee on Housing Affordability in Australia.[32] The report noted that "On some measures, housing affordability is at a record low.
'Australia's Future Tax System' (AFTS) review, more commonly known as the 'Henry Tax Review', made a number of recommendations that would have impacted on the housing market, including:
- introduction of land tax "on all land . . removing disincentives for institutional investment in rental property",
- that "transfer taxes on property should be reduced, and ultimately removed",
- a move to "more neutral personal income tax treatment of private residential rental investment . . through a 40 per cent discount on all net residential rental income and losses, and capital gains."[33]
In regard to recommendations of changes to tax policy that might impact the housing market, the Government advised "that it will not implement the following policies at any stage" (excerpt of list):
- include the family home in means tests (see Rec 88c),
- introduce land tax on the family home – this is a state tax and thus an issue for the states (see Rec 52 & 53),
- reduce the CGT discount, apply a discount to negative gearing deductions, or change grandfathering arrangements for CGT (see Rec 14 & 17c)[34]
In May 2015, the House of Representatives Standing Committee on Economics started an Inquiry into Home Ownership. Almost two years later the announcement was made that the Inquiry had made no recommendations whatsoever.[35]
In 2017, a Royal Commission into Misconduct in the Banking, Superannuation and Financial Services Industry was established. Hearings into banking misconduct began on 13 March.
Effect of inflated housing prices on the greater economy
Diverting capital away from the rest of the economy
Increased residential housing costs can cause excessive lending to the residential housing sector, at the expense of businesses. This can lead to "a banking system which allocated capital away from the most productive areas of the economy — business — is ultimately bad for growth, bad for competition, bad for jobs, bad for business and in the end, bad for Australia."[36]
Research conducted in overseas markets confirms that "in areas with high housing appreciation, banks increase the amount of mortgage lending and decrease the amount of commercial lending as a fraction of their total assets. This allocation results in firms receiving reduced loan amounts, paying higher interest rates, and reducing investment."[37]
Mortgage and rent stress
Increased housing prices and therefore increased borrowings can lead to difficulty in meeting housing payments. According to Ratings agency Standard & Poor's (S&P), "Arrears for sub-prime loans backing RMBS [residential mortgage-backed securities] jumped 126 basis points to 11.45 per cent"[38]
Australian specific market factors
The Australian market had several features either singly or together are not typical in other housing markets, being;
- Very constricted land supply and extremely onerous planning approval processes
- Unusually high stamp duties
- High proportion of variable rate mortgage loans compares to past housing bubbles outside of Australia, making borrowers more vulnerable to rising interest rates
- Income Tax relief through negative gearing
- Social security (Centrelink) that offers payment including rent assistance that is calculated on the amount of rent paid
- Only recourse loans
- One of the most highly urbanised populations
- Large areas of rural and remote Australia can not secure loans from banks against land in those areas.
Timeline
1980s–2009
- 1985: Australian government quarantines interest expenses, so that interest can only be claimed against rental income, not other income.[39]
- 1987: Negative gearing is reintroduced.[39]
- 1998 to 2008: real net national disposable incomes increase by 2.8% a year on average from about $32,000 to about $42,000 per year.[40] There is a rise in the number of two-income households, relaxation of lending standards, active promotion of real estate as an investment, population growth creating demand that was not matched by supply, planning and land release issues and a tax system that was skewed in favour of property investors.
- 1999: Property sale proceeds subject to Capital Gains Tax reduced from 100 to 50 percent (for property held at least one year), while 100 percent of costs remained deductible.
- 2000: July - The Federal government introduces the First Home Owners Grant of $7,000 for established homes, and $14,000 for newly built homes.[41]
- 2002: Urban Growth Boundary introduced for Melbourne, severely limiting land supply.[42]
- 2003: Significant amendments to Queensland's planning law, the Integrated Planning Act, are made by state government.[43] These amendments aimed to better protect the environment by stopping "urban sprawl", and lead to massive land price inflation.[44] Queensland's property prices start to rise quickly at this point.
- 2004: The Productivity Commission Inquiry on 'First Home Ownership' published its findings (No. 28, 31 March 2004). It identified several factors that had contributed to the rapid increase in real estate prices, including overall fairness of the tax system, lending regulations, lower interest rates and planning issues.[30]
- 2008: A Senate Select Committee on Housing Affordability was established. Its final report 'A good house is hard to find' included dozens of recommendations.[45]
- 2008: October - The First Home Owners Grant Boost is introduced as an addition to the First Home Owners Grant. This consisted of an extra $14000 available to first home owners buying or building a new home, as well as an extra $7000 made available for established homes. First Home Saver Accounts are also introduced, where the Federal Government will contribute up to $850 per annum towards savings for a deposit to purchase housing.
- 2008: December - FIRB rules allow temporary visa holders including students, to more easily buy up 'second-hand dwellings'. Changes did not require notification of sales be made to the FIRB and the $300,000 cap on price was removed.[46]
- 2009: October - First Home Owners Grant Boost is withdrawn. The UNSW City Futures Research Centre director said "the boost has resulted in inflated prices" and had created "a bit of a mini-bubble". A senior economist of Housing Industry Association (HIA) said the boost has not pushed prices up significantly.[47]
- 2009: November - "capital city house prices . . climbed average 10 per cent" in 2009. Melbourne led the "house price boom, with values up 14.9 per cent in the 10 months . . to an average of $481,247."[48]
- 2009: December - Reporting of RE data was questioned by one source: "AVERAGE house prices have been overstated by up to 18 per cent by the real estate industry . . . In September the average house price quoted by the Real Estate Institute of Victoria was $67,000 higher than the official figure, based on preliminary valuer-general data . . "[49]
2010
- January - The removal of First Home Owners Grant Boost. Mortgage applications reduce by 21.2%.[50] First-home buyers account for 13.1 per cent of new loan applications in December, whereas nine months previously they were at 28.1 per cent.
- March: ABS declares that house prices "soared 20 per cent in the 12 months to March" - a rate that was described as the "fastest ever recorded" in Australian history. The Head of Australian economics at National Australia Bank admits "This is a shocker".[51]
- April - Rules allowing foreign investment in real estate that were introduced in 2008 are withdrawn. Temporary residents are required to sell their Australian property when they leave Australia.[52]
- May - 'Australia's Future Tax System' (AFTS) Review (aka 'Henry Tax Review') makes a number of recommendations on policies that could affect the housing market.[53]
- The government responds to the AFTS review findings with a report 'Stronger, Fairer, Simpler: A Tax Plan for our Future'.[34]
2011
- February - New housing loans approved by Australian banks fall 5.6 per cent to a 10-year low in February.[54]
2012
- October - The RBA cuts interest rates to 3.25%.
- December - The RBA cuts interest rates to 3.00%.
2013
- April - Glenn Stevens is re-appointed as RBA Governor for 3 more years.
- May - The RBA cuts interest rates to 2.75%.
- August - The RBA cuts interest rates to 2.50%.
- November - Statistics released by the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority revealed that the total amount of residential term loans to households held by all ADIs (authorised deposit taking institutions) was $1.15 trillion. This was an increase of 1.7% on 30 June 2013 and an increase of 7.5 on September 2012. Furthermore, investment loans accounted for 33.1 per cent of the loans. Major banks held $933 billion of these loans.[55]
2014
- 1 January - RP Data reveals that national residential prices increased by 9.8% in 2013, with Sydney increasing by 15.2%.[56]
- 13 January - Housing Finance statistics released by the Australian Bureau of Statistics shows the value of outstanding home loans financed by the ADIs was $1.27 trillion. $849 billion of that amount was for owner occupied housing and $419 billion was for investment housing loans.[57]
- Data released by RP Data, APM, Residex and ABS in 2014 showed that Australian house prices continued to rise strongly throughout 2013 and 2014.[58]
2015
- The International Monetary Fund sends an economic team to Australia to examine "the risks posed by property speculation and record-high household debt as part of a broad health check-up of the sagging domestic economy."[59]
- The head of the Federal Treasury Department, and the Federal government's most senior economic adviser, John Fraser publicly warned that Sydney and more expensive parts of Melbourne were experiencing a bubble. This was disputed by members of the government including the Prime Minister and Assistant Treasurer.[60]
- June - APRA 10% investment credit growth limit introduced.
- October - Macquarie Bank, a major Australian investment bank forecasted an end to property prices with "quarter-on-quarter house prices to fall from the March 2016 quarter before beginning to recover from June 2017, with a 7.5 per cent fall from peak to trough".[61] Westpac Bank independently raised the rates on its standard variable mortgage by 20 basis points against the Australian Reserve Bank. This was the first rate rise by an Australian bank in five years.[62][63]
2016
- May - From 1 July, "Foreign buyers will have to provide citizenship and visa details, as well as Foreign Investment Review Board clearance, through the stamp duty process." "The ATO will match data to ensure foreign buyers have paid a $5000 fee for any property sold for less than $1 million, and $10,000 for properties over $1 million."[64]
- June - "In NSW, foreign buyers will be hit with a 4 per cent stamp duty surcharge from 21 June and 0.75 per cent land tax surcharge starting in 2017. Victoria will raise its existing 3 per cent stamp duty surcharge and 0.5 per cent land tax surcharge to 7 per cent and 1.5 per cent respectively on 1 July, while Queensland's 3 per cent stamp duty surcharge kicks in on 1 October."[65]
- 3 August - The Official cash rate drops to 1.5%, the lowest cash rate on record.[66] The cash rate remains at 1.5% as of 1 July 2018.
2017
- March - APRA limits interest only lending to 30% of new loans.
- March - The four major banks, NAB, Westpac, ANZ and Commonwealth Bank increase home loan rates despite Reserve bank rates citing the rising costs and regulatory responsibilities. These four banks controls more than 80 per cent of the $1.6 trillion mortgage market. Owner-occupier customers repaying principal and interest experiences the smallest rise while investors with interest-only loans get the largest hike. The changes effective in April–May.[67]
- April - The governor of the Reserve Bank of Australia Phil Lowe states that increasing debt and rising house prices were risking the future health of the Australian economy. He noted that slow wage growth was making it harder for people to pay down their debt and attacked banks for lending to people with too little income buffer after interest.[68]
- July - Stamp duty abolished for first home buyers in Victoria, Queensland and Western Australia. Investor tax deductions for depreciation and travel abolished.
- September - The market reached its most recent peak in September 2017, according to Corelogic data.[69]
- 14 December - Royal Commission into Misconduct in the Banking, Superannuation and Financial Services Industry established.
2018
- 13 March - hearings into the Royal Commission into Misconduct in the Banking, Superannuation and Financial Services Industry begin.
- 1 July - Since the previous peak in September 2017, the combined capital 5 city property market has declined by -1.3% according to Corelogic.[69]
- 11 July - It is estimated by Digital Finance Analytics that there are approximately 1 million households in mortgage stress. These households risk defaulting on their mortgages in the event of interest rate rises of as little as 0.15%.[70] APRA chairman Wayne Byres announced that the "heavy lifting on lending standards has largely been done", and that there was unlikely to be any further tightening of macroprudential policy.[71]
- 16 July - Pressure is growing on the big four banks to follow smaller lenders (including ME, AMP, Suncorp, Bendigo Bank, Macquarie Bank, Bank of Queensland, ING, Pepper Group, IMB, Auswide and Teachers Mutual Bank) who have been raising interest rates on mortgage products from April 2018 onwards.[72] This is due to a rise in the inter-bank Bank Bill Swap Rate (BBSW). It is speculated that the causes for BBSW changes include the US Federal reserve's increases in US rates and poor returns on Australian deposits drawing funds away to international markets and Australian equities for better returns, as well as income repatriation of large American companies following tax changes of Donald Trump.[73] The funding gap between deposits and funds lent in Australia is estimated to have grown to A$457 billion in the first quarter of 2018.[74] This is putting pressure on bank wholesale lending and profit margins, raising the likelihood of interest rate rises independently of the Reserve Bank of Australia by the big four banks, despite the ongoing Royal Commission.
2019
- January 2019 - RBA releases a research discussion paper 'A Model of the Australian Housing Market', which concludes that the lower interest rates explain much of the rapid growth in housing prices and construction over the past few years.[75]
- 7 February - Home prices across Sydney and Melbourne continue to fall as the RBA keeps rates on hold at 1.5 percent for a record 29th month.
- 4 June - The RBA drops interest rates to a record low of 1.25 percent, suggesting further cuts were to come later in the year[76]
- 2 July - RBA drops rates to another low of 1 percent.[77]
- 1 October - The RBA announces interest rate cut to 0.75%
2020
4 November - The RBA announces interest rate cut to 0.1% from previous 0.25% of April 2020
30 November Homebuilder grants scheme extended until march 2021 at the lower rate of $15000.
References
- "Treasury Warning on Home Price Bubble". The Australian. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- Matthewson, Paula (21 June 2012). "House prices must be allowed to fall - The Drum (Australian Broadcasting Corporation)". Abc.net.au. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- ABC News, 12 June 2014: Australia has third highest house price-to-income ratio in the world: IMF
- ABC News, 3 June 2016: Housing boom could end in a 'dramatic and destabilising' real estate hard landing: OECD
- "This property downturn is a different beast from the big one in 1989". ABC News. 12 December 2018.
- Stapledon, Nigel. A History of Housing Prices in Australia 1880-2010. School of Economics Discussion Paper: 2010/18. Sydney, Australia: The University of New South Wales Australian School of Business. ISBN 978-0-7334-2956-9. SSRN 1711224.
- "Executive Summary - Parliament of Australia". aph.gov.au. Retrieved 7 June 2020.
- "Housing industry accuses state government of dragging its feet over releasing land". Seek Estate. 2 June 2014. Archived from the original on 2 June 2014. Retrieved 1 June 2014.
- "1301.0 - Year Book Australia, 2005". Abs.gov.au. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- "Australia Population (2020) - Worldometer". worldometers.info. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- "World Population Growth - Our World In Data". ourworldindata.org. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- "Parliament of Australia: Senate Committees Affordability in Australia: A good house is hard to find: Housing affordability in Australia - Chapter 4 - Factors influencing the demand for housing". Archived from the original on 15 March 2011. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- http://ro.uow.edu.au/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1542&context=lawpapers
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 October 2016. Retrieved 4 March 2016.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 October 2016. Retrieved 4 March 2016.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 8 March 2016. Retrieved 4 March 2016.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Productivity Commission Inquiry on First Home Ownership". Rba.gov.au. 14 November 2003. Archived from the original on 5 August 2012. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- Don't mention the debt Michael West, Sydney Morning Herald, 19 February 2009
- "Inflation Calculator". Rba.gov.au. 14 February 1966. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- "Residex - Australian Property Market Experts - Residex". Residex. Archived from the original on 29 August 2008.
- Inflation data 'very poor' cost of living measure due to house price exclusion Michael Janda "ABC News", 20 April 2017
- Klan, A. (17 March 2007) Locked out Archived 22 October 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- Wade, M. (9 September 2006) PM told he's wrong on house prices
- "Microsoft Word - prelims.doc" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 June 2011. Retrieved 14 July 2011.
- "A good house is hard to find: Housing affordability in Australia". aph.gov.au. June 2008.
- "Foreign buyers blow out the housing bubble". Crikey.com.au. 21 September 2009. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- Colebatch, Tim (24 April 2010). "Foreign home buyers backflip The Age 23 April 2010". Melbourne.
- "Government Tightens Foreign Investment Rules for Residential Housing". Ministers.treasury.gov.au. 24 April 2010.
- "Prime Minister Kevin Rudd Slams Door in Asian Raiders". Heraldsun.com.au. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- First Home Ownership - Productivity Commission Inquiry Report (PDF). 31 March 2004. ISBN 1740371437. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 June 2011. Retrieved 14 July 2011.
- Peter Costello, Treasurer of Australia. "Government response to the productivity commission inquiry report on first home ownership". Archived from the original on 26 October 2009. Retrieved 7 February 2010.
- "Parliament of Australia: Senate Select Committee on Housing Affordability in Australia". Archived from the original on 13 March 2011. Retrieved 10 April 2011.
- "Australia's future tax system - Final Report - Part 1 (consolidated version)" (PDF). treasury.gov.au. December 2009.
- "Former Australian Government Department of Education, Employment and Workplace Relations | Australian Government Shared Services Centre" (PDF). Deewr.gov.au. 18 September 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 April 2012. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- "Housing Affordability: No Recommendations". Henry Belot, ABC News. 16 December 2016.
- "Residential lending may hurt us in the long run". Crikey. 12 February 2010.
- "Do Asset Price Bubbles have Negative Real Effects?" (PDF). University of Pennsylvania. November 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 December 2013. Retrieved 29 December 2013.
- "Mortgage holders showing stress". News.com.au. 5 April 2011. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- O’Donnell, Jim (July 2005). "Quarantining Interest Deductions for Negatively Geared Rental Property Investments". eJournal of Tax Research. Sydney: Atax, University of New South Wales. 3 (1). Retrieved 2 May 2011.
- "1383.0.55.001 - Measures of Australia's Progress: Summary Indicators, 2009". Abs.gov.au. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- "First Home Owners Scheme". Firsthome.gov.au. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- "Melbourne's Green wedge history - Peninsula Speaks Inc". Peninsulaspeaks.org. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- "INTEGRATED PLANNING AND OTHER LEGISLATION AMENDMENT BILL 2003 Explanatory Notes". Austlii.edu.au. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- "House Affordability : Australia : Markets : 1981-2010" (JPG). Macrobusiness.com.au. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- "Parliament of Australia: Affordability in Australia: A god house is hard to find: Housing affordability in Australia". Archived from the original on 19 February 2009. Retrieved 2 June 2009.
- Archived 6 March 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- "Home grant boost rolled back - ABC News (Australian Broadcasting Corporation)". Abc.net.au. 1 October 2009. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- "Prices rise as new home sales fall - ABC News (Australian Broadcasting Corporation)". Abc.net.au. 30 November 2009. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- "Victorian home prices overstated". Heraldsun.com.au. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- Uren, David (6 January 2010). "Housing sector hit by rate rises, end of grant". The Australian.
- "Asia Inflation Fears Point to Likely Rate Rises". 4 May 2010.
- Colebatch, Tim (24 April 2010). "Foreign home buyers backflip". Melbourne: The Age.
- "Executive summary" (PDF). Taxreview.treasury.gov.au. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- Uren, David (7 April 2011). "Buyer retreat spells slump in home prices". The Australian.
- "Quarterly Authorised Deposit-taking Institution Property Exposures" (PDF). 26 November 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 February 2014. Retrieved 26 January 2014.
- "News & Research | CoreLogic". RPData. Archived from the original on 19 February 2014.
- "Main Features - Summary of Findings". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 12 March 2014.
- "Worries over property boom, dollar - RN Breakfast - ABC Radio National (Australian Broadcasting Corporation)". Abc.net.au. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- Kehoe, John (2 May 2015). "IMF to probe Australia's record property and debt levels". Australian Financial Review.
- Daniel Hurst. "Josh Frydenberg disputes top Treasury adviser's advice on housing bubble risk | Australia news". The Guardian. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- "Property prices: House prices to fall in March 2016: Macquarie". News.com.au. 12 October 2015. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- Elizabeth Knight (14 October 2015). "Westpac rate rise ushers in end of the property boom". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- "Westpac's raising will hit economy but ward off hedge fund attack". Afr.com. 14 October 2015. Retrieved 20 January 2016.
- Kirsty Needham (15 May 2016). "Foreign buyer crackdown as new identity rules applied to Sydney property market". SMH. Retrieved 6 July 2016.
- Larry Schlesinger (15 June 2016). "New foreign buyer taxes cast their net far and wide: Frasers Property boss". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 6 July 2016.
- Sydney, Build. "When will the Australian Housing Bubble Burst?". Retrieved 16 January 2017.
- "www.theaustralian.com.au/business/financial-services/anz-hikes-mortgage-rates-following-westpac-and-nab/news-story/28b7303207fb95037d11d3801478cbb9". Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- "Negative gearing fuelling unhealthy appetite for interest-only home loans: RBA governor". ABC News. 4 April 2017.
- "Australian Dwelling Values Continue To Trend Lower In June Amidst Tight Credit Conditions And Less Investment Activity". Corelogic.
- "Nearly a million households 'on the edge' of mortgage default, analyst warns". ABC News. 10 July 2018.
- "APRA's Wayne Byres says there is no evidence of a mortgage credit crunch". Australian Financial Review. 11 July 2018.
- Yeates, Clancy (13 July 2018). "Bendigo Bank raises mortgage rates, blames funding costs". The Sydney Morning Herald.
- "How long before the big banks join in the rate hike party?". Australian Financial Review. 16 July 2018.
- "'No strong case' for near-term interest rate hike: RBA". Australian Financial Review. 17 July 2018.
- Tulip, Peter; Saunders, Trent. "Research Discussion Paper – RDP 2019-01 A Model of the Australian Housing Market". Reserve Bank of Australia. Retrieved 28 September 2019.
- Letts, Stephen; Janda, Michael. "RBA cuts interest rates to a fresh record low". ABC News (Australia). Retrieved 4 June 2019.
- Zhou, Naaman; Farrer, Martin (2 July 2019). "Reserve Bank interest rates cut to historic low of 1% – as it happened". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 18 July 2019.