Broadcasting-satellite service
Broadcasting-satellite service (short: BSS | also: broadcasting-satellite radiocommunication service ) is – according to Article 1.39 of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR)[1] – defined as «A radiocommunication service in which signals transmitted or retransmitted by space stations are intended for direct reception by the general public. In the broadcasting-satellite service, the term “direct reception” shall encompass both individual reception and community reception.»
- See also
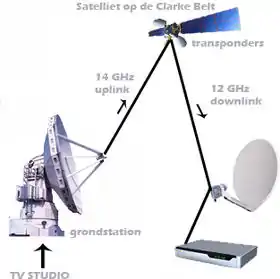
* earth station / feeder link (uplink)
* space station
* satellite dish, LNB, and receiver
Classification
This radiocommunication service is classified in accordance with ITU Radio Regulations (article 1) as follows:
Broadcasting service (article 1.38)
- Broadcasting-satellite service (article 1.32)
- Hardware broadcasting-satellite service
Broadcasting studio in Springfield, 2011 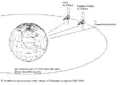
Broadcasting-satellites on geostationary orbit position 
Broadcasting-satellite footprints 
"INSAT 3E" broadcastin-satellite, solar panels fully extended 
"TV-SAT" German broadcasting-satellite 
Offset satellite dish 
"Kathrein UFD 08" analogue satellite TV receiver, 1986 
Earth station BSS
Frequency allocation
The allocation of radio frequencies is provided according to Article 5 of the ITU Radio Regulations (edition 2012).[2]
In order to improve harmonisation in spectrum utilisation, the majority of service-allocations stipulated in this document were incorporated in national Tables of Frequency Allocations and Utilisations which is with-in the responsibility of the appropriate national frequency administration.
- Example of frequency allocation
| Allocation to services | ||
| Region 1 | Region 2 | Region 3 |
| 1 452–1 492 MHz FIXED MOBILE except aeronautical mobile BROADCASTING BROADCASTING-SATELLITE |
1 452–1 492
| |
| 2 520–2 655 FIXED MOBILE except aeronautical mobile BROADCASTING-SATELLITE |
2 520–2 655 FIXED FIXED-SATELLITE (space-to-Earth) MOBILE except aeronautical mobile BROADCASTING-SATELLITE |
2 520–2 535 FIXED FIXED-SATELLITE (space-to-Earth) MOBILE except aeronautical mobile BROADCASTING-SATELLITE |
| 2 535–2 655 FIXED MOBILE except aeronautical mobile BROADCASTING-SATELLITE | ||
| 2 655–2 670 FIXED MOBILE except aeronautical mobile BROADCASTING-SATELLITE Earth exploration-satellite (passive) Radio astronomy Space research (passive) |
2 655–2 670 FIXED FIXED-SATELLITE (Earth-to-space/space-to-Earth) MOBILE except aeronautical mobile BROADCASTING-SATELLITE Earth exploration-satellite (passive) Radio astronomy Space research (passive) |
2 655–2 670 FIXED FIXED-SATELLITE (Earth-to-space) MOBILE except aeronautical mobile BROADCASTING-SATELLITE Earth exploration-satellite (passive) Radio astronomy Space research (passive) |
| 11.7–12.5 GHz FIXED MOBILE except aeronautical mobile BROADCASTING BROADCASTING-SATELLITE |
12.2-12.7 FIXED MOBILE except aeronautical mobile BROADCASTING BROADCASTING-SATELLITE |
11.7-12.2 FIXED MOBILE except aeronautical mobile BROADCASTING BROADCASTING-SATELLITE |
| 12.5-12.75 FIXED FIXED-SATELLITE (space-to-Earth) MOBILE except aeronautical mobile BROADCASTING-SATELLITE | ||
| 17.3-17.7 BROADCASTING-SATELLITE and other services | ||
| 17.7-17.8 BROADCASTING-SATELLITE and other services | ||
| 21.4-22 BROADCASTING-SATELLITE and other services | 21.4-22 BROADCASTING-SATELLITE and other services | |
40.5-41
| ||
41-42.5
| ||
See also
References / sources
- ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Systems – Article 1.39, definition: broadcasting-satellite service / broadcasting-satellite radiocommunication service
- ITU Radio Regulations, CHAPTER II – Frequencies, ARTICLE 5 Frequency allocations, Section IV – Table of Frequency Allocations