Dinard
Dinard (Breton: Dinarzh, Gallo: Dinard) is a commune in the Ille-et-Vilaine department in Brittany in northwestern France.
Dinard
Dinarzh | |
|---|---|
 Pointe de la Malouine | |
 Flag .svg.png.webp) Coat of arms | |
Location of Dinard 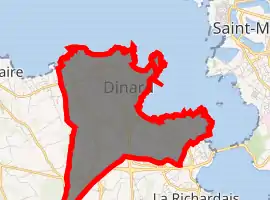
| |
 Dinard  Dinard | |
| Coordinates: 48°38′00″N 2°03′37″W | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Brittany |
| Department | Ille-et-Vilaine |
| Arrondissement | Saint-Malo |
| Canton | Saint-Malo-2 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2014–2020) | Martine Craveïa |
| Area 1 | 8 km2 (3 sq mi) |
| Population (2017-01-01)[1] | 10,027 |
| • Density | 1,300/km2 (3,200/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 35093 /35800 |
| Elevation | 0–56 m (0–184 ft) (avg. 28 m or 92 ft) |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
Dinard is on the Côte d'Émeraude of Brittany. Its beaches and mild climate make it a holiday destination, and this has resulted in the town having a variety of famous visitors and residents. The towns of Pleurtuit and Saint-Malo are nearby and the Dinard Pleurtuit Saint-Malo airport is about 4 km south of Dinard.
With its international film festival, villas, sumptuous hotels and casino, Dinard is regarded as one of the most prestigious seaside resorts in all of France.
History
In modern history Dinard was first settled by Saint-Malo's shipping merchants who built some of the town's larger houses, very few of which survive. In the late 19th century American and British aristocrats made Dinard a fashionable summer resort, and they built stunning villas on the cliff tops and exclusive hotels such as the 'Le Grand Hotel' on the seafront during the French "Belle Époque".
The name Dinard comes from the words "Din" ("hill"/"fort") and Ard/Art ("fortified"). It has been claimed, probably erroneously, that the second element means "bear"/"Arthur"); the bear in Celtic mythology is a symbol of sovereignship. The town council is in the process of removing the bear from the municipal flag, a decision disputed by the former mayor.
Originally, Dinard was part of the parish of Saint-Énogat. In the late 19th century, the resort became popular with the British wealthy who built villas on the coast. Dinard rapidly expanded. It started declining in the 1930s when the fashionable social set started preferring the Côte d'Azur. Today, Dinard is considered as one of the most "British" of sea resorts in France, however it has retained its French charm. There are 407 listed villas.
The official name of the town was Saint-Énogat until 1879 when the name was changed to Dinard-Saint-Énogat. The name was changed once more in 1921 to become simply Dinard. Saint-Énogat is now just the name for the western area of the town.
The town was liberated by American forces in August 1944 during the Battle of Saint-Malo.
Population
Inhabitants of Dinard are called Dinardais in French.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1962 | 8,834 | — |
| 1968 | 9,052 | +2.5% |
| 1975 | 9,234 | +2.0% |
| 1982 | 9,590 | +3.9% |
| 1990 | 9,918 | +3.4% |
| 1999 | 10,430 | +5.2% |
| 2006 | 10,644 | +2.1% |
| 2008 | 11,033 | +3.7% |
| 2009 | 10,724 | −2.8% |
| 2011 | 10,230 | −4.6% |
Climate
Dinard lies on the Gulf Stream which means it enjoys a warm climate, several degrees warmer than the surrounding areas. The Yacht club has fine examples of tropical palms and plants, which stretch round the coast on the Promenade du Clair de Lune.
| Climate data for Dinard / 1981–2010 normals, extremes 1950–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 16.4 (61.5) |
20.9 (69.6) |
23.2 (73.8) |
27.1 (80.8) |
29.2 (84.6) |
33.8 (92.8) |
37.6 (99.7) |
39.4 (102.9) |
33.1 (91.6) |
28.9 (84.0) |
20.6 (69.1) |
17.6 (63.7) |
39.4 (102.9) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 8.8 (47.8) |
9.3 (48.7) |
11.9 (53.4) |
13.7 (56.7) |
17.0 (62.6) |
19.8 (67.6) |
21.9 (71.4) |
22.0 (71.6) |
20.0 (68.0) |
16.3 (61.3) |
12.0 (53.6) |
9.2 (48.6) |
15.2 (59.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.1 (43.0) |
6.2 (43.2) |
8.3 (46.9) |
9.8 (49.6) |
13.0 (55.4) |
15.6 (60.1) |
17.7 (63.9) |
17.8 (64.0) |
15.9 (60.6) |
12.8 (55.0) |
9.1 (48.4) |
6.5 (43.7) |
11.6 (52.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 3.4 (38.1) |
3.1 (37.6) |
4.8 (40.6) |
5.9 (42.6) |
9.0 (48.2) |
11.5 (52.7) |
13.5 (56.3) |
13.6 (56.5) |
11.7 (53.1) |
9.4 (48.9) |
6.1 (43.0) |
3.7 (38.7) |
8.0 (46.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −13.7 (7.3) |
−11.7 (10.9) |
−6.2 (20.8) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
−0.2 (31.6) |
3.6 (38.5) |
6.7 (44.1) |
5.0 (41.0) |
2.3 (36.1) |
−4.2 (24.4) |
−5.9 (21.4) |
−9.6 (14.7) |
−13.7 (7.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 67.0 (2.64) |
57.6 (2.27) |
53.5 (2.11) |
53.0 (2.09) |
63.6 (2.50) |
49.1 (1.93) |
49.7 (1.96) |
49.4 (1.94) |
62.2 (2.45) |
86.8 (3.42) |
86.8 (3.42) |
80.0 (3.15) |
758.7 (29.87) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1 mm) | 12.6 | 10.8 | 11.1 | 10.7 | 10.3 | 7.8 | 7.6 | 8.0 | 9.7 | 13.6 | 13.8 | 13.4 | 129.5 |
| Average snowy days | 1.7 | 2.5 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 1.4 | 7.9 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 84 | 81 | 79 | 79 | 79 | 81 | 81 | 81 | 82 | 85 | 84 | 85 | 81.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 69.5 | 84.3 | 127.5 | 164.1 | 188.4 | 206.4 | 206.4 | 198.6 | 167.1 | 112.6 | 77.8 | 64.0 | 1,666.6 |
| Source: Meteo France[2][3] Infoclimat.fr (humidity, snowy days 1961–1990),[4] and Meteociel [5] | |||||||||||||
Hotels

The most exclusive hotels are the Grand Hôtel Barrière (5-star) which overlooks the Rance Estuary, and Castelbrac (5-star), the former Villa "Bric à Brac". Other notable hotels are the Royal, which sits next to the Casino above the main Esplanade, and the Hotel de la Reine Hortense, with a direct view on the Ecluse beach and Saint Malo. Further round the coast in the Saint-Énogat area of Dinard is the Thalassa Dinard and Villas de La Falaise. This exclusive seawater therapy centre is one of only a few throughout Europe. The architecture of this building is sympathetic with the coastline, and from some angles becomes at one with the cliffside.
In the summer, the population swells to over 40,000 with the influx of holiday makers.
Visitors
Dinard's reputation as the "Cannes of the North" has attracted a wide variety of stars. Joan Collins is a frequent visitor, and Winston Churchill enjoyed holidaying on the River Rance. It is claimed locally that Alfred Hitchcock visited Dinard and based the house used in his most famous movie Psycho on a villa standing over the Plage de l'Écluse, but no evidence has been produced. T.E. Lawrence (Lawrence of Arabia) lived in Dinard as a small child, long before his Arabian exploits, and Picasso painted here in the 1920s. Debussy is supposed to have had the idea for "La Mer" during a visit to Saint-Énogat in 1902. In 1996 Éric Rohmer filmed parts of Conte d'été in Dinard. Oscar Wilde also visited the place and mentions it in his De Profundis.
The Wales national football team used Dinard as its base during UEFA Euro 2016.
Attractions
Dinard cannot boast much nightlife, but many bars and fine restaurants fill the town's streets. The abundance of beaches coupled with a consistently sunny weather, however, attracts many visitors during the summer holidays. The attractions include a casino with a restaurant facing the sea and a hall which hosts many expositions. The nearby towns of Saint-Briac-sur-Mer and Saint-Lunaire also feature respectively a fairly large golf course and the beach of Longchamp, renowned as a "surfers' spot".
Dinard holds every year a Festival of British Cinema in the first days of October.[6]
Educational facilities
Many educational facilities may be found in Dinard, most of them elementary and primary schools, though there are two secondary schools. The most popular, the Collège Le Bocage, is a state school (the other being private) and has an estimated 700 pupils from Dinard and its vicinity. From there onward, children go to lycée, the closest being the Lycée Jacques Cartier in Saint-Malo.
Beaches
The town has several beaches, all of which are sandy, clean and large. The main beach is Plage de l'Écluse and the second largest are Saint-Énogat and Prieuré beaches.
International relations
Dinard is twinned with:
Notable residents
- Captain Philippe Koenigswerther, French Resistance fighter, Chevalier de la Légion d'Honneur, executed by the Nazis, born in Dinard in 1918,[7]
- Virginia d'Albert-Lake, French Resistance fighter
- Robert W. Service – Scottish poet and writer of the Klondike Gold Rush spent winter seasons in Dinard from 1913 until 1929.[8]
- Florence Delaage, classical pianist, was born in Dinard.
Gallery
 Saint-Énogat's beach, one of Dinard's four main beaches
Saint-Énogat's beach, one of Dinard's four main beaches Plage de L'Écluse
Plage de L'Écluse Saint Énogat church
Saint Énogat church
References
- "Populations légales 2017". INSEE. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- "Données climatiques de la station de Dinard" (in French). Meteo France. Retrieved December 11, 2014.
- "Climat Bretagne" (in French). Meteo France. Retrieved December 11, 2014.
- "Normes et records 1961-1990: Dinard - St Malo (35) - altitude 58m" (in French). Infoclimat. Retrieved December 11, 2014.
- "Normales et records pour Dinard (35)". Meteociel. Retrieved 14 September 2020.
- Official website of the festival
- https%3A%2F%2Fmaitron.fr%2Fspip.php%3Farticle178799
- "Biography". Robert W Service Estate. Retrieved 3 May 2013.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dinard. |
- Official website (in French)
- Dinard's homepage (in French)
- Amis de Dinard Saint-Enogat, association for the protection of the site and of the environment of Dinard (in French)
- Unofficial Guide to the Dinard Airport (in English)
- Base Mérimée: Search for heritage in the commune, Ministère français de la Culture. (in French)
