Door breaching
Door breaching is a process used by military, police, or emergency services to force open closed and/or locked doors. A wide range of methods are available, one or more of which may be used in any given situation.[1] Regarding the use of specified tools for forcible entry, there are several other methods of door breaching. These methods may be divided up into mechanical breaching, ballistic breaching, hydraulic breaching, explosive breaching, and thermal breaching.[2]
Common methods

Where no tools are available, it is usually possible to force open most inward-opening doors with a strong kick that breaks through the door frame. This can be a common method of entry for many trained police officers who are conducting searches, most interior doors can be forced by kicking. Converse to most movies, the safest method to kick a door is back kicking, with your back to the door. This method reduces the chance of injury to the breacher. Kicking in a locked door is also sometimes attempted or performed by neighbors and ordinary passers-by who witness an emergency situation such as a house that is on fire (though the first step should always be to call emergency services) in order to ensure that everyone is out of the house or to notify/assist anyone who is not. Kicking in doors is less commonly used in burglary attempts since the process requires a great deal of energy and makes a lot of noise.
Types
Mechanical

Mechanical breaching can be minimally destructive, through the use of lock picks.[3] This method is relatively slow and requires a trained operator, but does not damage the lock or door. Using specialized tools (i.e.: A-tool, K-tool), a lock cylinder can also be quickly dismantled and unlocked without removing it from the door; this method also allows the door to be closed and re-locked. Mechanical breaching also includes hydraulic breaching, which uses a special hydraulic ram to overcome the lock. The hydraulic ram may be powered manually, pneumatically, or electrically. More dynamic methods (kinetic breaching) use force to break the lock or door. The common methods are to use a lever, such as a Halligan bar or crowbar, or to use a tool to concentrate a large amount of force on the door, such as a sledgehammer, hydraulic jack, or battering ram.[4][5]
Ballistic
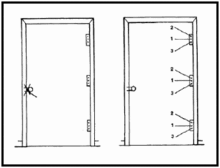
Ballistic breaching uses a projectile weapon to breach an opening. Weapons used can range from small arms to the 120 mm cannon of a main battle tank with a HEAT round, which will breach most obstacles easily, though the force involved may violate the rules of engagement.[6] A less damaging ballistic breach needs to destroy either the latch and lock, or the hinges of the door, and the ideal choice for this is the shotgun. While in theory other firearms can be used, handguns are usually underpowered[7] and rifles are less effective than the shotgun and pose a far higher risk of ricochet and collateral injury.[6] Most shotgun ammunition can be used for breaching, though the risk of injury varies with type. Of the available shotgun ammunition, shotgun slugs pose the highest risk, as they will retain significant energy to cause lethal wounds well after they have penetrated the door. Buckshot is far safer and birdshot even more so, as the multiple small projectiles disperse quickly after penetration, reducing the chances of causing a lethal wound. The safest option is a frangible round such as the TESAR or Hatton round, which turns to dust upon penetrating the door, and disperses completely upon exit.[2]
Breaching a door with the fewest shots possible both is faster and reduces the chance of collateral damage. Attacking the latch and lock is easiest, as it requires fewer shots and is easiest to target, whereas attacking the hinges requires more shots, and the hinges may be hidden from the outside. Careful aim is required; shots to the lock side are fired at a point halfway between the lock or handle and the door frame in order to hit the bolt holding the door shut. According to US urban warfare doctrine, the breaching operation is performed with the muzzle in contact with the door, or as close as possible, and angled downwards at a 45 degree angle. This process provides the best chance of hitting the desired point, while minimizing risk to occupants of the room being breached. Muzzle attachments are available on some specialized breaching shotguns to facilitate this operation, by holding the barrel securely in place while providing a slight standoff to allow powder gases to escape.[2][8]
Magazine capacity and operating mechanism are also important considerations in a breaching shotgun, because to quickly breach a door requires the ability to quickly fire multiple shots. For a breach on the latch side, US doctrine calls for two shots to be fired, and then an attempt made to open the door. If the door cannot be opened, the process would need to be quickly repeated. If the hinges must be breached, then doctrine calls for a total of three shots, one per hinge followed by an attempt to open the door.[2]
Hydraulic
Hydraulic breaching is mostly relevant when mechanical breaching fails to operate or explosive entry solutions cannot be used. The main advantages of the hydraulic breaching are: The operation is controlled. The operation is safe and intuitive. Furthermore, the systems require zero maintenance.
Nowadays the hydraulic breaching area offers compact tiny and yet very strong tools. The tools can breach doors and different objects, lifting, spreading, cutting and other tasks. Hydronoa has developed this area and has a variety of tools. The evolution started with manual hydraulic tools, Afterwards due to the need of speedy operating hydro pneumatic pumps were introduced, providing fast operation and portability. With the latest developments with battery cells technology all over the world electric pump was introduced. Providing speed portability and lighter systems HN pump speed was almost half from the pneumatic pump, which can breach any type of door within 8 sec.
Different types of hydraulic tools: door busters, cutters, spreaders, rams, manual pumps, electric hydraulic pumps and many other unique tools.
The systems can be used for rescue task as well as for breaching. Hydraulic breaching tools are being used by: Fire services, military; police Special Forces, antinarcotic, rescue teams and etc.
Explosive
Explosive breaching can be the fastest method, though it is also the most dangerous, to both the breachers and the room occupants. Depending on the situation, explosive breaching is potentially slower than a ballistic breach due to the large standoff required when using explosives, if there is no cover available.[6] Breaching can be performed with a specially formed breaching charge placed in contact with the door, or with various standoff breaching devices, such as specialized rifle grenades like the SIMON breach grenade.[9]
Breaching using explosives is primarily an operation performed by highly trained explosives experts. Explosive breaching charges can range from highly focused methods, such as detcord, plastic explosives, or strip shaped charges that explosively cut through doors or latches, to large satchel charges, containing 20 pounds (9 kg) of C-4, that can breach even reinforced concrete bunkers.[10]
Explosive method of entry can be a safe and effective tool in the hands of qualified breachers. It is the mission of the explosive breacher to use the least amount of explosive needed to secure penetration to a target. This can often be accomplished using less than a quarter of a pound of explosives when used correctly.
In addition to the tactical use, explosives have been used for search and rescue or other critical access situations.
Thermal
Thermal breaching is one of the least common techniques and also one of the slowest. It involves the use of a cutting torch to cut through metal doors.[11]
Examples of tools and operations
- Mechanical breaching
 The adze and pick end of a typical Halligan bar
The adze and pick end of a typical Halligan bar A manually operated hydraulic spreader-cutter of a type used by rescue workers to force open doors
A manually operated hydraulic spreader-cutter of a type used by rescue workers to force open doors An externally powered spreader-cutter tool
An externally powered spreader-cutter tool A Halligan tool and an axe, both common tools used by firefighters to breach doors to fight a fire
A Halligan tool and an axe, both common tools used by firefighters to breach doors to fight a fire
- Ballistic breaching
 A U.S. Marine performs a ballistic breach of a padlocked door using a combat shotgun
A U.S. Marine performs a ballistic breach of a padlocked door using a combat shotgun A ballistic breach at night of a padlocked door; this shotgun has a pistol grip rather than a full stock to make it more compact
A ballistic breach at night of a padlocked door; this shotgun has a pistol grip rather than a full stock to make it more compact The breaching shotgun can be carried on a long sling, to allow easy transition to a primary weapon
The breaching shotgun can be carried on a long sling, to allow easy transition to a primary weapon KAC Masterkey is a system that consists of a Remington 870 12 gauge pump-action shotgun mounted on a M16 or M4 assault rifle in an underbarrel configuration. This removes the need to carry a separate breaching shotgun.
KAC Masterkey is a system that consists of a Remington 870 12 gauge pump-action shotgun mounted on a M16 or M4 assault rifle in an underbarrel configuration. This removes the need to carry a separate breaching shotgun.
- Hydraulic Breaching
 Push door with hydraulic door breaker
Push door with hydraulic door breaker Hydraulic cutter
Hydraulic cutter SAN Ltd Tactical breaching electro-hydraulic gear
SAN Ltd Tactical breaching electro-hydraulic gear Hydraulic tactical breach
Hydraulic tactical breach
- Explosive breaching
 U.S. Marines place an explosive breaching charge on a door, positioned to separate the door from its hinges
U.S. Marines place an explosive breaching charge on a door, positioned to separate the door from its hinges U.S. Marines take cover behind a protective shield during an explosive breach of a door
U.S. Marines take cover behind a protective shield during an explosive breach of a door
 A US M100 Grenade Rifle Entry Munition (a SIMON derivative) detonates against a door
A US M100 Grenade Rifle Entry Munition (a SIMON derivative) detonates against a door
- Thermal breaching
 Crewmembers from a U.S. Coast Guard cutter practice exothermal breaching techniques
Crewmembers from a U.S. Coast Guard cutter practice exothermal breaching techniques A member of the U.S. Coast Guard Maritime security Response Team uses a torch to cut through a ship's watertight door
A member of the U.S. Coast Guard Maritime security Response Team uses a torch to cut through a ship's watertight door
References
- west, phil (2014). Survival Weapons: Optimizing Your Arsenal. Lulu.com. ISBN 978-1-291-46098-8.
- "Section 3-20, Breaching". FM 3-06-11. US Army.
- Haris, Hofelner (2019-12-05). "Door Knobs in 2019 Guide and Review". Household Professor. Retrieved 2019-12-07.
- Don Munson. "Action Target's Tactical Breach Door". Tactical Response Magazine.
- LaFemina, Fred. "Back to Basics: Forcible Entry". FireRescue1. Retrieved 11 September 2016.
- US Army. FM 7-8 INFANTRY RIFLE PLATOON AND SQUAD. Chapter 6, Urban Operations
- See Mythbusters Special 9
- The "Mossberg 500 Tactical Cruiser". Archived from the original on 2008-02-16.is equipped with a standoff door breaching barrel
- Scott R. Gourley (April 2007). "M100 Grenade Rifle Entry Munition" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-02-18. Retrieved 2015-05-15. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - FM 3-06-11. US Army. Table 8-7, Summary of breaching charges
- "Special Ops Breaching". Tactical Life Gun Magazine: Gun News and Gun Reviews. 2008-03-01. Retrieved 2019-12-07.