Eastern Desert
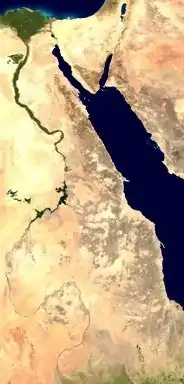
The Eastern Desert is the part of the Sahara desert that is located east of the Nile river, between the river and the Red Sea.[1][2] It extends from Egypt in the north to Eritrea in the south, and also comprises parts of Sudan and Ethiopia. The Eastern Desert is also known as the Red Sea Hills, the Arabian Desert, and the Arabian Mountain Ranges because to the east it is bordered by the Red Sea and because it was originally inhabited by Arabs in Pre-Islamic Egypt, respectively.[3][4][5]
Features
The Eastern Desert's main geographic features are the western Red Sea coastline—with the "Red Sea Riviera"—and the Eastern Desert mountain range that runs along the coast, the highest peak of which is Shaiyb al-Banat (2,187 m). Other notable ecological areas are Wadi Gamal National Park, Gebel Elba and the Wadi Dib ring complex. The Eastern Desert is a popular setting for safaris and other excursions.
Gallery


 Early morning with the Eastern Desert mountain range on the horizon
Early morning with the Eastern Desert mountain range on the horizon Tourist bus in the Eastern Desert
Tourist bus in the Eastern Desert_3.jpg.webp) Lunar landscape
Lunar landscape
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Eastern Desert. |
References
- Hobbs, Joseph J. (2007). Egypt. New York: Chelsea House. p. 26.
- Zahran, M. A.; Willis, A. J. (2009). The Vegetation of Egypt. Berlin: Springer. p. 101.
- Bard, Kathryn A. (2005). Encyclopedia of the Archaeology of Ancient Egypt. Routledge. p. 46. ISBN 1134665245. Retrieved 27 September 2017.
- Flora Aegyptiaca, Volume 1, Issue 1. Palm Press. 2000. p. 5. ISBN 9775089344. Retrieved 27 September 2017.
- Rawlinson, George. The History of Herodotus. p. 9.