Geography of Mauritius
Mauritius is an island of Africa's southeast coast located in the Indian Ocean, east of Madagascar. It is geologically located within the Somali plate.
| Native name: Moris Nickname: The Star and Key of the Indian Ocean | |
|---|---|
 Location of Mauritius | |
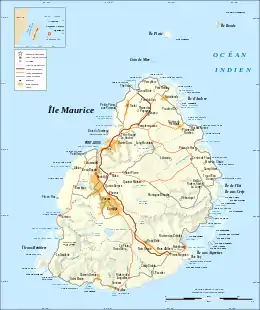 | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Indian Ocean |
| Coordinates | 20°17′S 57°33′E |
| Archipelago | Mascarene Islands |
| Area | 2,011 km2 (776 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 828 m (2717 ft) |
| Highest point | Piton de la Petite Rivière Noire |
| Administration | |
| Largest settlement | Port Louis (pop. 147,688) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 1,264,866 (2007) |
| Pop. density | 616/km2 (1595/sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | Indo-Mauritian 68%, Mauritian Creole people 27%, Sino-Mauritian 3%, Franco-Mauritian 2% |
Statistics

Area (includes Agaléga, Cargados Carajos (Saint Brandon), and Rodrigues):
total:
2,011 km²
land:
2,030 km²
water:
10 km²
note: includes Agalega Islands, Cargados Carajos Shoais (Saint Brandon), and Rodrigues.
Coastline: 177 km
Maritime claims:
territorial sea:
12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi)
continental shelf:
200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi) or to the edge of the continental margin
exclusive economic zone:
200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi)
Elevation extremes:
lowest point:
Indian Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Piton de la Petite Rivière Noire 828 m
Natural resources: arable land, fish
Land use:
arable land:
38.24%
permanent crops:
1.96%
other:
59.80% (2011)
Irrigated land: 212.2 km² (2003)
Total renewable water resources: 2.75 km3 (2011)
Environment - current issues: water pollution, degradation of coral reefs
Environment - international agreements:
party to:
Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
Geography - note: The main island is from which the country derives its name, former home of the dodo, a large flightless bird related to pigeons, driven to extinction by the end of the 17th century through a combination of hunting and the introduction of predatory species.
Table of Islands
| Island | Capital | Other Cities | Area (km²) | Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agalega Islands | Vingt Cinq | La Fourche, St Rita, Port St James | 26.0 | 290 |
| Agalega Islands | Vingt Cinq | La Fourche, St Rita, Port St James | 26.0 | 290 |
| Cargados Carajos | Raphael | Avocare, Ile du Sud, Coco Island | 3.2 | 63 |
| Cargados Carajos | Raphael | Avocare, Ile du Sud, Coco Island | 3.2 | 63 |
| Islets of Mauritius | Port Louis | 1871 | 1252980 | |
| Ile aux Benitiers | Ile aux Benitiers | 0.7 | 10 | |
| Ile Aux Cerfs | Le Touessrok Resort | 1.2 | 0 | |
| Ile des deux Cocos | deux Cocos resort | 0.04 | 2 | |
| Mouchoir Rouge | Mouchoir Rouge resort | 0.01 | 3 | |
| Mauritius Island | Port Louis | Beau-Bassin Rose-Hill, Quatre Bornes, Vacoas-Phoenix, Curepipe | 1860 | 1252964 |
| More Mauritius Islands | Ile aux Aigrettes | Ronde Island, Ile de la Passe, Coin du Mire, Ile D’Ambre, Ile Plate, Ilot Gabriel, Grand Port Islets, Ile aux Serpents, Ile de L’Est | 8.8 | 1 |
| Islets of Rodrigues | Port Mathurin | 111 | 38167 | |
| Ile Crabe Rodrigues | Port Crabe | 0.4 | 2 | |
| Rodrigues Island | Port Mathurin | Gabriel, Riviere Cocos, port south east | 109 | 38164 |
| More Rodrigues Islands | Ile aux Cocos | Ile Fregate, Ile aux Sables, Ile aux Chats, le Hermitage, Ile Gombrani | 1.36 | 1 |
| Mauritius | Port Louis | 2011 | 1291500 |
notes: excludes Tromelin and other îles éparses
Climate
The local climate is tropical, modified by southeast trade winds; there is a warm, dry winter from May to November and a hot, wet, and humid summer from November to May. Anti-cyclones affect the country during May to September.
Cyclones affect Mauritius or Mauricio during November–April. Hollanda (1994) and Dina (2002) were the worst two last cyclones to have affected the island.
Terrain
The country's landscape consists of a small coastal plain rising to discontinuous mountains encircling a central plateau. Mauritius is almost completely surrounded by reefs that may pose maritime hazards. The main island is of volcanic origin.
The mountains with the greatest prominence include:
Piton de la Petite Rivière Noire, 828m, the highest point of the island[1]
Le Morne Brabant, 556m
Tourelle de Tamarin, 563m[2]
Corps de Garde, 720m, prominence 382m[3]
Le Pouce, 820m, prominence 352m[4]
Pieter Both, 820m, prominence 229m[5]
Montagne Cocotte, 780m
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of Mauritius, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northernmost point – Tappe à Terre, North Island, Agalega Islands
- Easternmost point – Trou d’Argent, Rodrigues Island
- Southernmost point - Le Gris Gris, Savanne District, Mauritius
- Westernmost point - North West Point, North Island, Agalega Islands
See also
References
- "Piton de la Petite Rivière Noire - Peakbagger.com". www.peakbagger.com. Retrieved 2020-12-01.
- "Tourelle du Tamarin". peakery.com. Retrieved 2020-12-01.
- "Corps de Garde - Peakbagger.com". www.peakbagger.com. Retrieved 2020-12-01.
- "Le Pouce". peakery.com. Retrieved 2020-12-01.
- "Pieter Both - Peakbagger.com". www.peakbagger.com. Retrieved 2020-12-01.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook website https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/.
This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook website https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/.
External links
- Mauritius Travel Information (English)
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Geography of Mauritius. |

.svg.png.webp)