Climate of Ghana
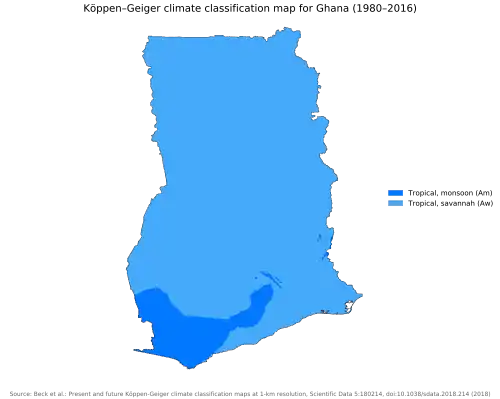
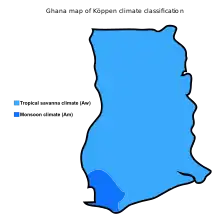
The climate of Ghana is tropical.[1] The eastern coastal belt is warm and comparatively dry, the south-west corner of Ghana is hot and humid, and the north of Ghana is hot and dry.[2] Ghana is located on the Gulf of Guinea, only a few degrees north of the Equator, giving it a warm climate.[3]
Climate
The climate of Ghana is tropical and there are two main seasons: the wet and the dry seasons.[4] North Ghana experiences its rainy season from April to mid-October while South Ghana experiences its rainy season from March to mid-November.[4] The tropical climate of Ghana is relatively mild for its latitude.[4] The harmattan, a dry desert wind, blows in north-east Ghana from December to March, lowering the humidity and causing hotter days and cooler nights in northern part of Ghana.[4]
Average daily temperatures range from 30°C (86°F) during the day to 24°C (75°F) at night with a relative humidity between 77 percent and 85 percent.[5] In the southern part of Ghana, there is a bi-modal rainy season: April through June and September through November.[5] Squalls occur in the northern part of Ghana during March and April, followed by occasional rain until August and September, when the rainfall reaches its peak.[5] Rainfall ranges from 78 to 216 centimeters (31 to 85 inches) a year.[5]
| Climate data for Ghana | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 30.1 (86.2) |
31.2 (88.2) |
31.6 (88.9) |
31.0 (87.8) |
30.0 (86.0) |
28.3 (82.9) |
27.1 (80.8) |
26.8 (80.2) |
27.4 (81.3) |
28.6 (83.5) |
30.0 (86.0) |
29.5 (85.1) |
29.2 (84.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 24.5 (76.1) |
25.8 (78.4) |
26.2 (79.2) |
26.2 (79.2) |
25.4 (77.7) |
24.6 (76.3) |
23.5 (74.3) |
23.2 (73.8) |
23.6 (74.5) |
24.2 (75.6) |
24.3 (75.7) |
24.1 (75.4) |
24.6 (76.3) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 13.6 (0.54) |
40.3 (1.59) |
88.2 (3.47) |
115.7 (4.56) |
160.7 (6.33) |
210.4 (8.28) |
121.3 (4.78) |
88.9 (3.50) |
133.0 (5.24) |
128.1 (5.04) |
56.5 (2.22) |
24.6 (0.97) |
1,184.1 (46.62) |
| Average rainy days | 2 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 11 | 14 | 7 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 4 | 2 | 77 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 79 | 77 | 77 | 80 | 82 | 85 | 85 | 83 | 82 | 83 | 80 | 79 | 85 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 214 | 204 | 223 | 213 | 211 | 144 | 142 | 155 | 171 | 220 | 240 | 235 | 2,372 |
| Source: weatherbase.com[5] | |||||||||||||
Climate change in Ghana
Climate change in Ghana will have wide-reaching impacts on the country. Because Ghana sits at the intersection of three hydro-climatic zones, the climate of Ghana is expected to become quite variable.[6] Based on a 20-year baseline climate observation, it is forecasted that maize and other cereal crop yields will reduce by 7% by 2050. Available data also shows a sea level rise of 2.1 mm per year over the last 30 years, indicating a rise of 5.8 cm, 16.5 cm and 34.5 cm by 2020, 2050 and 2080.
Changes in rainfall, other extreme weather conditions, sea-level rise, and the salinity of coastal waters are expected to negatively affect food security, in both farming and fisheries.[7] The national economy stands to suffer from the impacts of climate change because it is dependent on climate sensitive-sectors such as agriculture, energy, forestry, etc. Moreover, access to freshwater is expected to create challenges for both sanitary water, and hydropower which provides 54% of the country's electric capacity.[7] Additionally, Ghana will likely see certain diseases, like malaria and cholera exacerbated by changing weather conditions.[8]

References
- Igawa, Momoko; Kato, Makoto (2017-09-20). "A new species of hermit crab, Diogenes heteropsammicola (Crustacea, Decapoda, Anomura, Diogenidae), replaces a mutualistic sipunculan in a walking coral symbiosis". PLOS ONE. 12 (9): e0184311. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0184311. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 5606932. PMID 28931020.
- "Ghana high plains". photius.com. Retrieved 24 June 2013.
- "Ghana: Geography Physical". photius.com. Retrieved 24 June 2013., "Ghana: Location and Size". photius.com. Retrieved 24 June 2013.
- "UNDP Climate Change Country Profile: Ghana". ncsp.undp.org. Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 24 June 2013.
- "Ghana Travel Weather Averages (Weatherbase)". Retrieved 1 June 2013.
- "Ghana". Climatelinks. Retrieved 2020-04-22.
- "Climate Risk Profile: Ghana". Climatelinks. USAID. January 2017. Retrieved 2020-04-22.
- Lipp, Erin K.; Huq, Anwar; Colwell, Rita R. (October 2002). "Effects of Global Climate on Infectious Disease: the Cholera Model". Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 15 (4): 757–770. doi:10.1128/CMR.15.4.757-770.2002. ISSN 0893-8512. PMID 12364378.