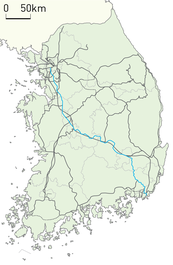
Gyeongbu Line
The Gyeongbu Line (Gyeongbuseon) is a railway line in South Korea and is considered to be the most important and one of the oldest ones in the country. It was constructed in 1905, connecting Seoul with Busan via Suwon, Daejeon, and Daegu. It is by far the most heavily travelled rail line in South Korea.
| Gyeongbu Line | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overview | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Native name | 경부선(京釜線) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Owner | Korea Rail Network Authority | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line number | 302 (KR) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Termini | Seoul Busan | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stations | 90 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Service | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Type | Passenger/freight rail | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operator(s) | Korail | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Opened | January 1, 1905 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line length | 441.7 km (274.5 mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of tracks | 6 (Seoul–Guro) 4 (Guro–Cheonan) 2 (Cheonan–Busan) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrification | 25 kV/60 Hz Catenary | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating speed | 150 km/h (93 mph) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gyeongbu Line | |
| Hangul | |
|---|---|
| Hanja | |
| Revised Romanization | Gyeongbuseon |
| McCune–Reischauer | Kyŏngbusŏn |
All types of high-speed, express, local, and freight trains provide frequent service along its entire length.
History

The Gyeongbu Line was originally constructed as a vehicle of colonialism.[1] In 1894-1895, Imperial Japan and Qing Dynasty China fought the First Sino-Japanese War for influence over Korea. Following the war, in competition with Russia's rail expansion across China, Japan sought the right from the Korean Empire to build a railway from Busan to Seoul, the Gyeonbu Line.[1] Surveying began in 1896, and in spite of local protests, the Korean Empire gave Japan the right to build the line in 1898.[2] Construction of the Gyeongbu Line started on August 20, 1901, with a ceremony at Yeongdeungpo, Seoul.[2] Construction was done by locals commanded to do forced labour, and paid with coupons.[2]
Japan also sought to gain control of the Gyeongui Line project that was to continue tracks further north, recognising the trunk route as a means to keep Korea under its influence.[1] The line was also advanced for military considerations in expectation of a confrontation with Russia, which came in 1904 as the Russo-Japanese War.[1] At the start of the war, Japan ignored Korea's declaration of neutrality and transported troops to Incheon, and forced the Korean government to sign an agreement that gave Japan's military control of the railway. Troop bases were established in connection with the railway, the biggest of them next to Yongsan station in Seoul.[1]
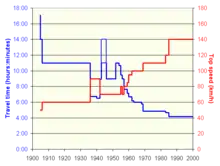
Construction of the Gyeongbu Line was completed on January 1, 1905.[2] The first trains travelled the line in 17 hours 4 minutes.[3] By April 1906, travel time was reduced to 11 hours,[3] while top speed was 60 km/h (37 mph).[4] The line developed into the backbone of transport in Korea under Japanese rule. Following the Japanese invasion of Manchuria, from April 1, 1933, the line was traversed by direct trains from Busan to Andong (today Dandong) across the border.[5] From December 1, 1936, the Akatsuki luxury express trains ran on the line with a maximum speed of 90 km/h (56 mph), and achieved the shortest pre-war travel time of 6 hours 30 minutes[3] in the timetable valid from November 1, 1940.[6]
Travel times increased greatly while the line was used for transport in World War II.[6] Following World War II, the Seoul–Busan express train re-established on May 20, 1946,[6] was named Chosun Liberator.[5] During the Korean War, the line transported troops and refugees.[7] The line remained the backbone of transport in South Korea after the war,[8] when diesel locomotives[5] and the cross-country Mugunghwa-ho train class was introduced.[3] Following the 1961 coup, the Supreme Council for National Reconstruction started South Korea's first five-year plan, which included a construction program to complete the railway network, to foster economic growth.[9] On the Gyeongbu Line, the effort was advertised with a new class of express trains named Jaegeon-ho, (Reconstruction train) introduced on May 15, 1962.[5] These trains reduced travel times below the best pre-WWII travel times for the first time, connecting Seoul and Busan in 6 hours 10 minutes at a top speed of 100 km/h (62 mph).[3]
From the 1960s, road construction began to make road transport more attractive and faster. Although top speed rose to 110 km/h (68 mph) and the Seoul–Busan travel time along the Gyeongbu Line was reduced to 4 hours 50 minutes by June 10, 1969,[3] on the parallel Gyeongbu Expressway, completed in 1970, travel time was only 4 hours to 4 hours 30 minutes.[8] Korean National Railroad responded by introducing the Saemaul-ho class of elevated-comfort express trains on August 15, 1974.[3] with the introduction of new streamlined diesel locomotives and then diesel multiple units in Saemaul-ho service,[5] top speed was raised to 140 km/h (87 mph) and travel time was reduced to 4 hours 10 minutes with the timetable valid from November 16, 1985.[3]
Upgrade
The Gyeongbu Line was extensively upgraded in parallel with the development of the Seoul Metropolitan Subway urban rapid transit system and the Korea Train Express (KTX) high-speed rail system from the 1970s.
The Gyeongbu Line is six-tracked from Seoul to Guro, four-tracked from Guro to Cheonan,[10] and double-tracked from Cheonan all the way to Busan. The entire line is electrified.[10]
Relationship with the KTX project
The Seoul-Busan axis is Korea's main traffic corridor. In 1995, it housed 73.3% of Korea's population, and conducted 70% of the freight traffic and 66% of the passenger traffic. With both the Gyeongbu Expressway and Korail's Gyeongbu Line congested, the government saw the need to develop railways.[8] The first proposals for a second Seoul-Busan railway line originated from a study prepared between 1972 and 1974 by experts of France's SNCF and Japan Railway Technical Service (JARTS) on a request from the IBRD.[8][11] A more detailed 1978-1981 study by KAIST, focusing on the needs of freight transport, also came to the conclusion that the necessary capacity for freight transport on the existing Gyeongbu Line could best be released by separating off long-distance passenger traffic on a parallel high speed passenger railway, which was then taken up in Korea's next Five Year Plan.[8]
Following the 1997 Asian Financial Crisis, the government decided to finish the Gyeongbu High Speed Railway (Gyeongbu HSR) in two phases, and upgrade and electrify the conventional Gyeongbu Line for KTX services on the sections paralleling the parts of the high-speed line not completed in the first phase.[8][12]
Plans foresaw the development of the Gyeongbu Line into a high-capacity freight corridor after the completion of the second phase of the Gyeongbu HSR.[13] At the time of the opening of the Daegu–Busan section of the high-speed line on November 1, 2010, capacity available for freight trains on the conventional line was expected to increase by a factor of 7.7, while the capacity for passenger transport in the entire corridor increased by a factor of 3.4.[14]
Electrification
The line was electrified in stages from 1974 to 2006:[10]
| Section | Length | Start of electric operation | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seoul–Suwon | 41.5 km | August 15, 1974 | Integration into Seoul Subway Line 1 |
| Yeongdeungpo–Suwon | 32.3 km | December 23, 1981 | Second pair of tracks |
| Yongsan–Guro | 8.5 km | December 30, 1996 | Third pair of tracks |
| Suwon–Byeongjeom | 7.2 km | April 30, 2003 | Four tracks; extension of Seoul Subway Line 1 |
| Byeongjeom–Cheonan | 48.4 km | January 20, 2005 | Four tracks |
| Cheonan–Jochiwon | 32.7 km | March 30, 2005 | |
| Jochiwon–Daejeonjochajang | 34.9 km | July 1, 2005 | |
| Daejeonjochajang–Daejeon–Okcheon | 20.7 km | April 1, 2004 | For KTX trains |
| Okcheon–Sangdong | 125.3 km | Dec 8, 2006 | |
| Sangdong–Daegu–Busan | 132.8 km | April 1, 2004 | For KTX trains |
For KTX trains and new electric locomotives, top speed was also raised to up to 150 km/h.[10][15]
Services
The Gyeongbu Line is the major route out of Seoul and Yongsan stations and, in addition to regular departures for Busan, trains travel along the Gyeongbu Line en route to Janghang, Gwangju, Mokpo, Suncheon, Yeosu, Pohang, Ulsan, Haeundae, Masan, and Jinju. Trains for Jecheon, Andong, and Yeongju also operate along sections of the Gyeongbu Line.
On the section between Seoul station, Guro (where roughly half of the trains leave the Gyeongbu Line to head out to Incheon via the Gyeongin Line), Suwon, and Byeongjeom, Seoul Subway Line 1 provides frequent commuter services.
The Gyeongbu Line is served along its entire length by frequent intercity Saemaul-ho and cross-country Mugunghwa-ho trains. Some trains run along the entire length of the line, others only on some sections, including trains diverging to the connected lines. As of October 2010, direct Saemaul day trains connect Seoul to Busan in a minimum 4 hours 50 minutes, and Mughungwa trains in a minimum 5 hours 28 minutes.[16]
KTX
Korail launched KTX high-speed services with the opening of the first phase of the Gyeongbu HSR on April 1, 2004.[8] The Seoul–Busan travel distance was shortened to 408.5 km, the shortest travel time was 2 hours 40 minutes.[8]
All KTX services use the conventional Gyeongbu Line between Seoul and the start of the Siheung Interconnection at a junction after Geumcheon-gu Office station, until the Siheung Interconnection diverges in a tunnel towards the present start of the Gyeongbu HSR. The terminal for most Gyeongbu KTX services is Seoul station, for most Honam KTX services, Yongsan station.[8][16] In addition, some trains continue beyond Seoul station for 14.9 km along the Gyeongui Line to terminate at Haengsin station,[16] next to which KTX trains have a depot.[17] An additional stop at Yeongdeungpo station was proposed in 2004, however, the plans were dropped in face of opposition from locals living around Gwangmyeong station along the Gyeongbu HSR, who feared that Yeongdeungpo would draw away passengers from the new station and force its closing.[18] However, the November 1, 2010, timetable change made Yeongdeungpo a KTX stop, for newly introduced trains that also use the Gyeongbu Line on the entire Seoul–Daejeon section, to serve Suwon.[16][19]
From its opening, the Gyeongbu KTX service also returned to the Gyeongbu Line for two short sections crossing Daejeon and Daegu, where local disputes about the high-speed line alignment across urban areas held up construction;[20] and all the way from Daegu to Busan. Consequently, all but two of the stations of the Gyeongbu KTX service were on the conventional Gyeongbu Line: after the two stations on the high-speed line, Gwangmyeong and Cheonan-Asan, stops were at Daejeon, Dongdaegu (East Daegu), Miryang, Gupo and Busan.[8] Some Gyeongbu KTX services maintained service on this relation after the November 1, 2010, opening of the second phase of the Gyeongbu HSR, with the daily number of halts in Miryang and Gupo increased.[16] Korail met local demands by introducing additional KTX services between Seoul and Dongdaegu in June 2007, which used the conventional Gyeongbu Line between Daejeon and Dongdaegu to serve Gimcheon and Gumi.[21] However, these services were discontinued with the opening of the Gimcheon–Gumi station on the high-speed line.[21]
The section between Daegu and Samnangjin, the junction with the Gyeongjeon Line, is also used by the Gyeongjeon KTX services, which connect Seoul to Masan on the Gyeongjeon Line since December 15, 2010,[22] and will be extended to Jinju by 2012.[23] Stops along the Gyeongbu Line will be at Dongdaegu and Miryang.
Evolution of long-distance passenger traffic
Between Seoul and Cheonan, the Mugunghwa and Saemaul express trains on the Gyeongbu Line gave rail around a fifth of the modal share before the launch of KTX services. Due to the short distance and the location of the KTX station outside the city, the conventional line could retain most of its passengers, and the increase in the total modal share of rail was modest.[8] On the medium-distance relation from Seoul to Daejeon, KTX gained market share mostly at the expense of normal express services on the Gyeongbu Line, which decreased by half in the first year, while the total share of rail increased to a third.[8] On the long-distance relations from Seoul to Daegu and Busan, the total share of rail increased from around two-fifths to a market dominating three-fifths, with the bulk of that traffic taken by the KTX. For intercity passenger traffic on the conventional Gyeongbu Line, that translates to a sharp drop on the Daejeon-Daegu section (bypassed by KTX trains) and a sharp increase on the Daegu-Busan section.[8]
| Seoul to... | Cheonan | Daejeon | Daegu | Busan | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period | Total | Without KTX | Total | Without KTX | Total | Without KTX | Total | Without KTX | |||
| 2003/4 | 21.1% | 21.1% | 27.5% | 27.5% | 40.5% | 40.5% | 38.0% | 38.0% | |||
| 2004/5 | 24.2% | 19.2% | 33.9% | 14.0% | 63.6% | 11.4% | 60.9% | 10.6% | |||
Station list
| ● | Stops at the station |
| | | Does not stop at the station |
| ○ | Limited service |
| Station | Hangul | Hanja | Connecting lines and services |
Station distance |
Line distance |
Location | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km | |||||||||
| Seoul | 서울 | - | 0.0 | Seoul | Jung-gu | ||||
| Namyeong | 남영 | 南營 | - | 1.7 | Yongsan-gu | ||||
| Yongsan | 용산 | 龍山 | Gyeongwon Line ( Yongsan Line Honam Line |
1.5 | 3.2 | ||||
| Noryangjin | 노량진 | 鷺梁津 | 2.6 | 5.8 | Dongjak-gu | ||||
| Daebang | 대방 | 大方 | - | 1.5 | 7.3 | Yeongdeungpo-gu | |||
| Singil | 신길 | 新吉 | 0.8 | 8.1 | |||||
| Yeongdeungpo | 영등포 | 永登浦 | 1.0 | 9.1 | |||||
| Sindorim | 신도림 | 新道林 | Sinjeong Branch (Seoul Subway Line 2) |
1.5 | 10.6 | Guro-gu | |||
| Guro | 구로 | 九老 | Gyeongin Line (Seoul Subway Line 1) |
1.1 | 11.7 | ||||
| Gasan Digital Complex | 가산디지털단지 | 加山디지털團地 | 2.4 | 14.1 | Geumcheon-gu | ||||
| Doksan (Haan-dong) |
독산 (하안동입구) |
禿山 (下安洞入口) |
- | 2.0 | 16.1 | ||||
| Geumcheon-gu Office | 금천구청 | 衿川區廳 | Gwangmyeong Line (Seoul Subway Line 1) |
1.2 | 17.3 | ||||
| Seoksu | 석수 | 石水 | - | 2.3 | 19.6 | Gyeonggi-do | Anyang | ||
| Gwanak | 관악 | 冠岳 | 1.9 | 21.5 | |||||
| Anyang | 안양 | 安養 | 2.4 | 23.9 | |||||
| Myeonghak (Sungkyul University) |
명학 성결대앞 |
鳴鶴 (聖潔大앞) |
2.2 | 26.1 | |||||
| Geumjeong | 금정 | 衿井 | (Seoul Subway Line 4) (Seoul Subway Line 4) |
1.4 | 27.5 | Gunpo | |||
| Gunpo | 군포 | 軍浦 | - | 2.2 | 29.7 | ||||
| Dangjeong (Hansei University) |
당정 (한세대앞) |
堂井 (韓世大앞) |
1.6 | 31.3 | |||||
| Uiwang (Korea National University of Transportation) |
의왕 (철도대학) |
義王 (鐵道大學) |
Nambu Hwamulgiji Line |
4.2 | 33.9 | Uiwang | |||
| Sungkyunkwan Univ. | 성균관대 | 成均館大 | - | 2.9 | 36.8 | Suwon | |||
| Hwaseo | 화서 | 華西 | 2.6 | 39.4 | |||||
| Suwon | 수원 | 水原 | 2.1 | 41.5 | |||||
| Seryu | 세류 | 細柳 | - | 2.9 | 44.4 | ||||
| Byeongjeom (Hanshin University) |
병점 (한신대) |
餅店 (韓神大) |
Byeongjeomgiji Line (Seoul Subway Line 1) |
4.3 | 48.7 | Hwaseong | |||
| Sema | 세마 | 洗馬 | - | 2.4 | 51.1 | Osan | |||
| Osan College (Mulhyanggi Arboretum) |
오산대 (물향기수목원) |
烏山大 (물香気樹木園) |
2.7 | 53.8 | |||||
| Osan | 오산 | 烏山 | 2.7 | 56.5 | |||||
| Jinwi | 진위 | 振威 | 4.0 | 60.5 | Pyeongtaek | ||||
| Songtan | 송탄 | 松炭 | 3.8 | 64.3 | |||||
| Seojeong-ri (Kookje College) |
서정리 (국제대학) |
西井里 (國際大學) |
2.2 | 66.5 | |||||
| Jije | 지제 | 芝制 | 4.8 | 71.3 | |||||
| Pyeongtaek | 평택 | 平澤 | 3.7 | 75.0 | |||||
| Seonghwan (Namseoul University) |
성환 (남서울대) |
成歡 (南서울大) |
9.4 | 84.4 | Chungcheongnam-do | Cheonan | |||
| Jiksan | 직산 | 稷山 | 5.4 | 89.8 | |||||
| Dujeong | 두정 | 斗井 | 3.8 | 93.6 | |||||
| Cheonan | 천안 | 天安 | Janghang Line Anseong Line (Closed) |
3.0 | 96.6 | ||||
| Sojeong-ri | 소정리 | 小井里 | No Seoul Subway Line 1 Service | - | 10.8 | 107.4 | Sejong City | ||
| Jeonui | 전의 | 全義 | 7.5 | 114.9 | |||||
| Jeondong | 전동 | 全東 | 7.7 | 122.6 | |||||
| Seochang | 서창 | 瑞倉 | Osong Line | 3.5 | 126.1 | ||||
| Jochiwon | 조치원 | 鳥致院 | Chungbuk Line | 3.2 | 129.3 | ||||
| Naepan | 내판 | 內板 | - | 5.6 | 134.9 | ||||
| Bugang | 부강 | 芙江 | 4.9 | 139.8 | |||||
| Maepo | 매포 | 梅浦 | 4.6 | 144.4 | |||||
| Sintanjin | 신탄진 | 新灘津 | 7.5 | 151.9 | Daejeon | Daedeok-gu | |||
| Hoedeok | 회덕 | 懷德 | 5.6 | 157.5 | |||||
| Daejeonjochajang | 대전조차장 | 大田操車場 | Honam Line | 4.1 | 161.6 | ||||
| Daejeon | 대전 | 大田 | Daejeon Line ● Daejeon Subway Line 1 |
4.7 | 166.3 | Dong-gu | |||
| Secheon | 세천 | 細川 | - | 7.6 | 173.6 | ||||
| Jeungyak (Closed) |
증약 | 增若 | - | Chungcheongbuk-do | Okcheon-gun | ||||
| Okcheon | 옥천 | 沃川 | 8.0 | 182.5 | |||||
| Gapung (Closed) |
가풍 | 加豊 | - | ||||||
| Iwon | 이원 | 伊院 | 8.3 | 190.8 | |||||
| Jitan | 지탄 | 池灘 | 5.6 | 196.4 | |||||
| Simcheon | 심천 | 深川 | 4.4 | 200.8 | Yeongdong-gun | ||||
| Gakgye | 각계 | 覺溪 | 3.8 | 204.6 | |||||
| Yeongdong | 영동 | 永同 | 7.0 | 211.6 | |||||
| Mireuk (Closed) |
미륵 | 彌勒 | - | ||||||
| Hwanggan | 황간 | 黃澗 | 14.6 | 226.2 | |||||
| Chupungnyeong | 추풍령 | 秋風嶺 | 8.5 | 234.7 | |||||
| Sinam | 신암 | 新岩 | 6.0 | 240.7 | Gyeongsangbuk-do | Gimcheon | |||
| Jikjisa | 직지사 | 直指寺 | 5.5 | 246.2 | |||||
| Gimcheon | 김천 | 金泉 | Gyeongbuk Line | 7.6 | 253.8 | ||||
| Daesin | 대신 | 大新 | - | 9.7 | 263.5 | ||||
| Apo | 아포 | 牙浦 | 5.7 | 269.2 | |||||
| Gumi | 구미 | 龜尾 | 7.5 | 276.7 | Gumi | ||||
| Sagok | 사곡 | 沙谷 | 4.6 | 281.3 | |||||
| Yangmok | 약목 | 若木 | 8.2 | 289.5 | Chilgok-gun | ||||
| Waegwan | 왜관 | 倭館 | 6.5 | 296.0 | |||||
| Yeonhwa | 연화 | 蓮花 | 6.2 | 302.2 | |||||
| Sindong | 신동 | 新洞 | 3.7 | 305.9 | |||||
| Jicheon | 지천 | 枝川 | 7.4 | 313.3 | |||||
| Daegu | 대구 | 大邱 | 9.8 | 323.1 | Daegu | Buk-gu | |||
| Dongdaegu | 동대구 | 東大邱 | Daegu Line |
3.2 | 326.3 | Dong-gu | |||
| Gomo | 고모 | 顧母 | - | 5.5 | 331.8 | Suseong-gu | |||
| Gacheon | 가천 | 佳川 | Daegu Line | 1.6 | 333.4 | ||||
| Gyeongsan | 경산 | 慶山 | - | 5.2 | 338.6 | Gyeongsangbuk-do | Gyeongsan | ||
| Samseong | 삼성 | 三省 | 7.1 | 345.7 | |||||
| Namseonghyeon | 남성현 | 南省峴 | 7.4 | 353.1 | Cheongdo-gun | ||||
| Cheongdo | 청도 | 淸道 | 8.7 | 361.8 | |||||
| Singeo | 신거 | 新巨 | 5.6 | 367.4 | |||||
| Sangdong | 상동 | 上東 | 4.8 | 372.2 | Gyeongsangnam-do | Miryang | |||
| Miryang | 밀양 | 密陽 | 9.4 | 381.6 | |||||
| Muwol (Closed) |
무월 | 無月 | - | - | |||||
| Mijeon | 미전 | 美田 | Mijeon Line | 11.0 | 392.6 | ||||
| Samnangjin | 삼량진 | 三浪津 | Gyeongjeon Line | 1.5 | 394.1 | ||||
| Wondong | 원동 | 院洞 | - | 9.1 | 403.2 | Yangsan | |||
| Mulgeum | 물금 | 勿禁 | 9.2 | 412.4 | |||||
| Hwamyeong | 화명 | 華明 | 9.4 | 421.8 | Busan | Buk-gu | |||
| Gupo | 구포 | 龜浦 | 3.4 | 425.2 | |||||
| Sasang | 사상 | 沙上 | Gaya Line |
5.1 | 430.3 | Sasang-gu | |||
| Busanjin | 부산진 | 釜山鎭 | Donghae Line |
9.6 | 439.9 | Busanjin-gu | |||
| Busan | 부산 | 釜山 | 1.8 | 441.7 | Dong-gu | ||||
See also
References
- "Korea's Railway Network the Key to Imperial Japan's Control". The Asia-Pacific Journal: Japan Focus. Retrieved 2010-10-28.
- "[책갈피 속의 오늘]1901년 경부선 철도 기공 ". The Dong-a Ilbo. 2007-08-20. Retrieved 2010-10-28.
- "열차속도의 변천" (in Korean). Korail. Archived from the original on 2011-10-03. Retrieved 2011-01-14.
- 차량 기술현황 (in Korean). Woosong University. Archived from the original on 2012-03-17. Retrieved 2011-01-07.
- "History of train operation". Korea Railway Industry information Center. Archived from the original on March 31, 2012. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- 한국철도 열차운전속도 변천사 (in Korean). Rail Safety Information System. Retrieved 2011-01-07.
- "History". Korea Railway Industry information Center. Archived from the original on July 22, 2011. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- Cho, Nam-Geon; Chung, Jin-Kyu (2008). "High Speed Rail Construction of Korea and Its Impact" (PDF). KRIHS Special Report Series (in Korean). Korea Research Institute for Human Settlements. 12. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-05-29. Retrieved 2010-08-30.
- "철마 110년, 영고의 자취 [12] 경제개발과 철도" (in Korean). Silvernet News. 2010-03-20. Retrieved 2010-11-16.
- "Electricity Almanac 2009" (PDF). Korea Electric Association. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-03-14. Retrieved 2010-10-23.
- "Major Projects Overseas - I-K". JARTS. Archived from the original on 2011-07-22. Retrieved 2010-08-26.
- D. Suh, Sunduck (2000). "RISK MANAGEMENT IN A LARGE-SCALE NEW RAILWAY TRANSPORT SYSTEM PROJECT ─ Evaluation of Korean High Speed Railway Experience ─" (PDF). IATSS Research. IATSS. 24 (2). Retrieved 2010-08-30.
- "South Korea's growing network". Railway Gazette International. 2008-09-08. Archived from the original on 2012-12-05. Retrieved 2010-08-29.
- "KTX 경부선 개통 - 에어부산 취항 2주년" (in Korean). The Dong-a Ilbo. 2010-10-28. Retrieved 2010-11-01.
- "One year later, KTX faces rider shortfalls, complaints". JoongAng Daily. 2005-03-25. Retrieved 2010-10-21.
- "Booking". Korail. Archived from the original on 2011-07-13. Retrieved 2010-10-28.
- Lee, Kyung Chul (August 2007). "Launch of Korean High-Speed Railway and Efforts to Innovate Future Korean Railway" (PDF). Japan Railway & Transport Review (48): 30–35. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-03-13. Retrieved 2010-10-23.
- 광명역은 이렇게 죽으라고? (in Korean). Pride of Gwang Myeong. 2010-10-08. Retrieved 2010-11-03.
- 경부고속철도 2단계 개통에 따른 열차운행 알림 (in Korean). Korail. 2010-10-06. Archived from the original on 2011-07-22. Retrieved 2010-10-31.
- "Bullet trains coming to a town near you by 2020". JoongAng Daily. 2010-09-02. Retrieved 2010-10-23.
- "'KTX가 뭐기에'…김천·구미 끝없는 대립". JoongAng Ilbo. 2010-07-18. Archived from the original on 2011-07-13. Retrieved 2010-10-23.
- "[오늘의 세상] 서울~부산 KTX 22분 단축" (in Korean). The Chosun Ilbo. 2010-10-07. Retrieved 2010-10-19.
- "KTX ready for big expansion in 2010". JoongAng Daily. 2009-12-31. Retrieved 2010-08-29.