Hague Service Convention
The Convention on the Service Abroad of Judicial and Extrajudicial Documents in Civil or Commercial Matters, more commonly called the Hague Service Convention, is a multilateral treaty which was adopted in The Hague, The Netherlands, on 15 November 1965 by member states of the Hague Conference on Private International Law. It came into existence to give litigants a reliable and efficient means of serving the documents on parties living, operating or based in another country. The provisions of the convention apply to service of process in civil and commercial matters but not criminal matters. Also, Article 1 states that the Convention shall not apply if the address of the person to be served with the document is not known.
Long name:
| |
|---|---|
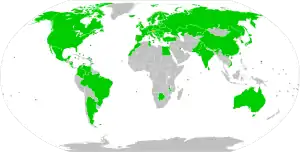 State party to the Convention State ratified, not yet in force | |
| Signed | 15 November 1965 |
| Location | |
| Effective | 10 February 1969 |
| Condition | 3 ratifications |
| Parties | 75 |
| Depositary | Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Kingdom of the Netherlands |
| Languages | English and French |
Diplomatic service via letters rogatory
For states which are not party to the Hague Service Convention, diplomatic channels are generally used for the service of legal documents. It is generally effected by a letter rogatory, which is a formal request to issue a judicial order from a court in the state where proceedings are underway to a court in another state. This procedure generally requires transmission of the document to be served from the originating court to the foreign ministry in the state of origin. The foreign ministry in the state of origin forwards the request to the foreign ministry in the destination state. The foreign ministry then forwards the documents to the local court. The local court then makes an order to allow for the service. Once service is made, a certificate of service would then pass through the same channels in reverse. Under a somewhat more streamlined procedure, courts can sometimes forward service requests to the foreign ministry or the foreign court directly, cutting out one or more steps in the process.
Procedure
The Hague Service Convention established a more simplified means for parties to effect service in other contracting states. Under the convention, each contracting state is required to designate a central authority to accept incoming requests for service. A judicial officer who is competent to serve process in the state of origin is permitted to send request for service directly to the central authority of the state where service is to be made. Upon receiving the request, the central authority in the receiving state arranges for service in a manner permitted within the receiving state, typically through a local court. Once service is effected, the central authority sends a certificate of service to the judicial officer who made the request. Parties are required to use three standardized forms: a request for service, a summary of the proceedings (similar to a summons), and a certificate of service.
The main benefits of the Hague Service Convention over letters rogatory is that it is faster (requests generally take two to four months rather than six months to one year), it uses standardized forms which should be recognized by authorities in other states, and it is cheaper (in most cases) because service can be effected by a local attorney without hiring a foreign attorney to advise on foreign service procedures.
The Hague Service Convention does not prohibit a receiving state from permitting international service by methods otherwise authorized by domestic law. For example, a state could allow for service directly by mail or by personal service. States which permit parties to use these alternative means of service make a separate designation in the documents they file upon ratifying or acceding to the Convention.
Alternate methods of service
The Hague Convention provides various modes of process service of documents such as by postal channel or by diplomatic/consular agents, judicial officers, officials or other competent persons. These provisions are covered under Articles 8 to 10 and may or not be allowed by member countries as a valid mode of serving the documents in their territory. The method of serving the documents through a central agency (Article 5) is not optional but is binding on all the member countries. Service through a central agency usually takes a long time: 4 to 12 months. The convention gives relief to the litigants if they have not received certificate of service or delivery from the central agency even after waiting for six months. In such cases, the court may, if it considers that a reasonable time has elapsed, give its judgment. Also, in case of urgency, the court may issue a provisional order or protective measure even before six-month waiting period.
Central authority
Although the service is free, it may take 4 to 12 months for the central authority to process. The central authority decides which method is to be used. In many cases, a bailiff will be assigned by a local court to serve the documents and mail back the proof of service, but service by mail is also possible.[1]
Service by mail
Service by mail is possible only in states that have not objected to that method under Article 10(a) of the convention and if the jurisdiction where the court case takes place allows it under its applicable law. It is therefore possible in France and the Netherlands but not in Germany, Switzerland, and South Korea, where incoming service is to be effected exclusively through the state's central authority.[2]
In the United States, the interpretation of a provision in Article 10(a) has long been controversial, as the judiciary in some of its jurisdictions contended that service by mail was impossible because the word "send" rather than "serve" was used in the English-language version of the convention. The matter was finally resolved in May 2017 by the US Supreme Court in Water Splash, Inc. v. Menon, bringing the interpretation in line with parties in other US jurisdictions and the rest of the world.
Relation with other instruments
Under the convention, states may conclude different agreements between them that take precedence over the convention. Thus, in the European Union (except for Denmark) other rules are applied instead of the Convention.
State parties
As of July 2020, 78 states are contracting parties of the Hague Service Convention. They include 64 of the 82 Hague Conference on Private International Law member states in addition to 14 other states.[2]
| State party | Signed | Ratified or acceded | Entry into force |
|---|---|---|---|
| — | 1 November 2006 | 1 July 2007 | |
| — | 26 April 2017 | 1 December 2017 | |
| — | 1 May 1985 | 1 November 1981 | |
| — | 2 February 2001 | 2 December 2001 | |
| — | 27 June 2012 | 1 February 2013 | |
| — | 15 March 2010 | 1 November 2010 | |
| 22 November 2019 | 14 July 2020 | 12 September 2020 | |
| — | 17 June 1997 | 1 February 1998 | |
| — | 10 February 1969 | 1 October 1969 | |
| — | 6 June 1997 | 1 February 1998 | |
| 21 January 1966 | 19 November 1970 | 18 January 1971 | |
| — | 8 September 2009 | 1 May 2010 | |
| — | 16 June 2008 | 1 February 2009 | |
| — | 10 February 1969 | 1 September 1969 | |
| — | 1 November 2018 | 1 June 2019 | |
| — | 23 November 1999 | 1 August 2000 | |
| — | 26 September 1998 | 1 May 1999 | |
| — | 6 May 1991 | 1 January 1992 | |
| — | 10 April 2013 | 1 November 2013 | |
| — | 16 March 2016 | 1 October 2016 | |
| — | 28 February 2006 | 1 November 2006 | |
| — | 26 October 1982 | 1 June 1983 | |
| — | 28 January 1993 | 1 January 1993 | |
| 7 January 1969 | 2 August 1969 | 1 October 1969 | |
| 1 March 1966 | 12 December 1968 | 10 February 1969 | |
| — | 2 February 1996 | 1 October 1996 | |
| 15 November 1965 | 11 November 1969 | 10 November 1969 | |
| 12 January 1967 | 3 July 1972 | 1 September 1972 | |
| 15 November 1965 | 27 April 1979 | 26 June 1979 | |
| 20 July 1983 | 20 July 1983 | 18 September 1983 | |
| — | 13 July 2004 | 1 April 2005 | |
| — | 10 November 2008 | 1 July 2009 | |
| — | 23 November 2006 | 1 August 2007 | |
| 20 October 1989 | 5 April 1994 | 4 June 1994 | |
| 25 November 1965 | 14 August 1972 | 13 October 1972 | |
| 25 January 1979 | 25 November 1981 | 24 January 1982 | |
| 12 March 1970 | 28 May 1970 | 27 July 1970 | |
| — | 15 October 2015 | 1 June 2016 | |
| — | 13 January 2000 | 1 August 2000 | |
| — | 8 May 2002 | 1 December 2002 | |
| — | 28 March 1995 | 1 November 1995 | |
| — | 2 August 2000 | 1 June 2001 | |
| 27 October 1971 | 9 July 1975 | 7 September 1975 | |
| — | 24 April 1972 | 1 December 1972 | |
| — | 1 February 2011 | 1 October 2011 | |
| — | 29 July 2020 | 1 February 2021 | |
| — | 2 November 1999 | 1 June 2000 | |
| — | 4 July 2012 | 1 February 2013 | |
| — | 1 March 2007 | 1 November 2007 | |
| — | 16 January 2012 | 1 September 2012 | |
| — | 24 March 2011 | 1 November 2011 | |
| 15 November 1965 | 3 November 1975 | 2 January 1976 | |
| — | 24 July 2019 | 1 February 2020 | |
| — | 23 December 2008 | 1 September 2009 | |
| 15 October 1968 | 2 August 1969 | 1 October 1969 | |
| — | 7 December 1988 | 1 August 1989 | |
| — | 3 March 2020 | 1 October 2020 | |
| — | 13 February 1996 | 1 September 1996 | |
| 5 July 1971 | 27 December 1973 | 25 February 1974 | |
| — | 21 August 2003 | 1 April 2004 | |
| — | 1 May 2001 | 1 December 2001 | |
| — | 6 January 2005 | 27 October 1979 | |
| — | 15 April 2002 | 1 November 2002 | |
| — | 2 July 2010 | 1 February 2011 | |
| — | 18 November 1980 | 1 July 1981 | |
| — | 15 March 1993 | 1 January 1993 | |
| — | 18 September 2000 | 1 June 2001 | |
| 21 October 1976 | 4 June 1987 | 3 August 1987 | |
| — | 31 August 2000 | 1 June 2001 | |
| 4 February 1969 | 2 August 1969 | 1 October 1969 | |
| 21 May 1985 | 2 November 1994 | 1 January 1995 | |
| — | 10 July 2017 | 2 February 2018 | |
| 11 June 1968 | 28 February 1972 | 28 April 1972 | |
| — | 1 February 2001 | 1 December 2001 | |
| 10 December 1965 | 17 November 1967 | 10 February 1969 | |
| 15 November 1965 | 24 August 1967 | 10 February 1969 | |
| — | 29 October 1993 | 1 July 1994 | |
| — | 16 March 2016 | 1 December 2016 |
Notes
- The Convention entered into force on 1 November 2010 for all of Australia's external territories.[3]
- The Convention entered into force on 27 July 1986 for Aruba.[4]
- The Convention entered into force on 19 July 1970 for Bermuda, the British Virgin Islands, the Cayman Islands, the Falkland Islands, Gibraltar, Guernsey, the Isle of Man, Jersey, Montserrat, the Pitcairn Islands, Saint Helena, and the Turks and Caicos Islands.[5] It entered into force on 2 October 1982 for Anguilla.[5]
- The Convention entered into force for the Northern Mariana Islands on 30 May 1994.[6]
References
- "International Service of Process in Hong Kong". www.plexus-pi.com. Plexus Investigative Solutions. Archived from the original on 8 August 2016. Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- "Convention of 15 November 1965 on the Service Abroad of Judicial and Extrajudicial Documents in Civil or Commercial Matters: Status table". Hague Conference on Private International Law. Retrieved 26 September 2014.
- "Extension of Application of the Convention of 15 November 1965 on the Service Abroad of Judicial and Extrajudicial Documents in Civil or Commercial Matters to Australian External Territories". Hague Conference on Private International Law. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- "Extension of Application of the Convention of 15 November 1965 on the Service Abroad of Judicial and Extrajudicial Documents in Civil or Commercial Matters to Aruba". Hague Conference on Private International Law. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- "Extension of Application of the Convention of 15 November 1965 on the Service Abroad of Judicial and Extrajudicial Documents in Civil or Commercial Matters to British Territories". Hague Conference on Private International Law. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- "Extension of Application of the Convention of 15 November 1965 on the Service Abroad of Judicial and Extrajudicial Documents in Civil or Commercial Matters to the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands". Hague Conference on Private International Law. Retrieved 22 April 2015.