Hendrik-Ido-Ambacht
Hendrik-Ido-Ambacht (Dutch: [ˈɦɛndrɪk ido ɑmbɑxt] (![]() listen)) (population: 30,966 in 2019) is a town and municipality in the western Netherlands. It is located on the island of IJsselmonde, and borders with Zwijndrecht, Ridderkerk, and the Noord River (with Alblasserdam and Papendrecht on the other side).
listen)) (population: 30,966 in 2019) is a town and municipality in the western Netherlands. It is located on the island of IJsselmonde, and borders with Zwijndrecht, Ridderkerk, and the Noord River (with Alblasserdam and Papendrecht on the other side).
Hendrik-Ido-Ambacht | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
.svg.png.webp) Location in South Holland | |
| Coordinates: 51°51′N 4°38′E | |
| Country | Netherlands |
| Province | South Holland |
| Government | |
| • Body | Municipal council |
| • Mayor | Jan Heijkoop (CDA) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 11.90 km2 (4.59 sq mi) |
| • Land | 10.61 km2 (4.10 sq mi) |
| • Water | 1.29 km2 (0.50 sq mi) |
| Elevation | −1 m (−3 ft) |
| Population (January 2019)[4] | |
| • Total | 30,966 |
| • Density | 2,919/km2 (7,560/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Ambachter |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postcode | 3340–3344 |
| Area code | 078 |
| Website | www |
The jurisdiction of the municipality covers an area of 11.90 km2 (4.59 sq mi) of which 1.29 km2 (0.50 sq mi) is water. The municipality comprises no other population centres.
Name
Until 1855, the town was known as Hendrik-Ido-Schildmanskinderen-Ambacht en de Oostendam. Then it merged with Sandelingen-Ambacht and its full name for a period of time was said to be Hendrik-Ido-Oostendam-Schildmanskinderen-Groot-en-Klein-Sandelingen-Ambacht. This used to be the longest name of any town in the Netherlands.
Topography
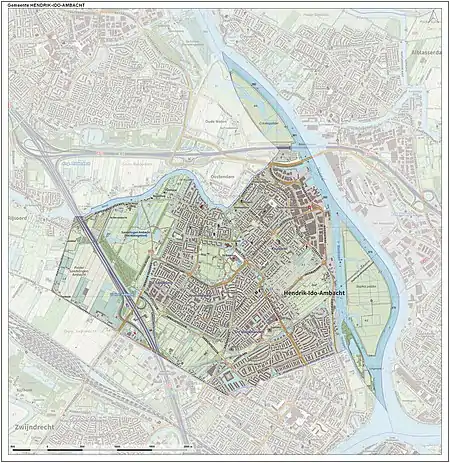
Dutch topographic map of the municipality of Hendrik-Ido-Ambacht, June 2015
History
The area has been populated from circa the year 1000 CE. Agriculture and animal husbandry were the only means of existence for many centuries. All lands were owned by or in control of the nobility of Dordrecht. Not until the Eighty Years' War some industrial activities began to appear along the river dike. Furthermore, horticulture and flax growing also developed.
Because of the rapid industrial growth in Germany and the daily tides, two citizens of Hendrik-Ido-Ambacht started a ship breaking yard which grew into an industry resulting in the town becoming worldwide known as the "ship breaking village".
The establishment of industries in the region changed the centuries-old seasonal labour to permanent work opportunities with higher wages. Only a few monumental farms and buildings, including the 14th century Reformed Church, remain as a reminder of its historic past.[5]
Notable people

- Cornelis Ekkart (1892 – 1975 in H.I. Ambacht) a Dutch fencer, competed at the 1924 and 1928 Summer Olympics
- Flor Silvester (1923–2008) a Dutch graphic designer, illustrator, painter, sculptor and trombonist; lived in H.I. Ambacht
- Henk van Lijnschooten (1928 - 2006 in H.I. Ambacht) a Dutch composer
- Bart Berman (born 1938) a Dutch-Israeli pianist and composer
- Marco Janssen (born 1969) a Dutch econometrician and academic
- Roeland Pruijssers (born 1989) a Dutch chess grandmaster
Gallery
References
- "college: samenstelling, taken en functies" [Board: Members, tasks and functions] (in Dutch). Gemeente Hendrik-Ido-Ambacht. Archived from the original on 2014-07-28. Retrieved 30 July 2013.
- "Kerncijfers wijken en buurten 2020" [Key figures for neighbourhoods 2020]. StatLine (in Dutch). CBS. 24 July 2020. Retrieved 19 September 2020.
- "Postcodetool for 3342XA". Actueel Hoogtebestand Nederland (in Dutch). Het Waterschapshuis. Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 30 July 2013.
- "Bevolkingsontwikkeling; regio per maand" [Population growth; regions per month]. CBS Statline (in Dutch). CBS. 1 January 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
- Hendrik-Ido-Ambacht Official Website