Hyundai Ioniq
The Hyundai Ioniq is a compact five door liftback manufactured and marketed by Hyundai.[2][3] The nameplate Ioniq is a portmanteau of ion and unique.[4] It is the first automobile to be offered in hybrid, plug-in hybrid, and all-electric variants with no "standard" internal combustion engine only version.[5]
| Hyundai Ioniq (AE) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Hyundai |
| Production | 2016–present |
| Model years | 2017–present |
| Assembly | South Korea: Ulsan Malaysia: Kulim (Hyundai-Sime Darby Motors, hybrid only) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Compact car (C) |
| Body style | 5-door liftback |
| Layout | Front-engine or motor, front-wheel-drive |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,700 mm (106.3 in)[1] |
| Length | 4,470 mm (176.0 in) |
| Width | 1,820 mm (71.7 in) |
| Height | 1,450 mm (57.1 in) |
The Ioniq Hybrid debuted in South Korea in January 2016, with all three variants debuting at 2016 Geneva and New York auto shows.[6][3] The hybrid variant launched in its home market in February 2016, followed by the electric model in July 2016.[6][7] The plug-in hybrid version followed in February 2017.[8]
From its first model year (2017) through the 2019 model year, the Ioniq Electric had been the EPA's most efficient vehicle with a rated fuel economy of 136 miles per gallon gasoline equivalent (mpg-e) (1.7 L/100 km).[9][10] The Ioniq Blue hybrid version has been rated at 58 miles per gallon, making it the most fuel efficient hybrid vehicle that is mass produced.[11]
Ioniq Hybrid
| Ioniq Hybrid | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.6 L Kappa II GDI HEV I4 |
| Electric motor | 32 kW (43 bhp)[12] |
| Power output | 105 PS (77 kW; 104 hp) (petrol engine)[12] |
| Transmission | 6-speed DCT |
| Hybrid drivetrain | Series hybrid |
| Battery | 1.56 kWh lithium-ion polymer battery[12] |
| Dimensions | |
| Curb weight | 1,359–1,469 kg (2,996–3,239 lb) |
The Ioniq is Hyundai's first automobile built from the ground up and specifically available as a hybrid or electric powered.
The hybrid version competes with, and surpasses in fuel economy, the previous mileage leader in the Toyota Prius.[11] Sharing the same powertrain with the Kia Niro hybrid crossover, the Ioniq is powered by a 1.6 litre Kappa four cylinder Atkinson-cycle engine with 40% thermal efficiency capable of delivering 78 kW (105 hp) and an estimated 109 lb⋅ft (148 N⋅m) of torque alone.
The Ioniq Hybrid's electric motor additionally delivers an estimated 32 kW (43 bhp) with an estimated maximum torque of 125 lb⋅ft (169 N⋅m), powered by a lithium-ion polymer battery with 1.56 kWh capacity.
The battery is positioned under the rear passenger seats.[12] In combination with the 1.6 litre direct injection engine, the Ioniq Hybrid offers an estimated total system output of 139 bhp (104 kW) and 195 lb⋅ft (264 N⋅m).[13] This engine is combined with a shifting six speed dual-clutch transmission.[12] Like many hybrids and electric cars, neither the Ioniq Hybrid nor Electric are suitable for towing a trailer.[14]
The Ioniq uses aluminium in the hood and tailgate, reducing weight by 27 lb (12 kg) compared with conventional steel with no measurable disadvantages in noise or vibration.[12] With a higher usage of lightweight components and a more compact build, the cargo screen cover is about 25% lighter than the types used in other Hyundai models.

Its aerodynamic design helped lower the drag coefficient of the Ioniq down to 0.24.[13] Excessive weight is reduced by utilization of high strength steel for the structure and aluminium for non structural components.[6]
Hyundai expects the model with 15 inch wheels to obtain an EPA rated combined fuel economy between 57 mpg‑US (4.1 L/100 km; 68 mpg‑imp) and 58 mpg‑US (4.1 L/100 km; 70 mpg‑imp), just ahead of the 2016 Toyota Prius Eco (56 mpg‑US (4.2 L/100 km; 67 mpg‑imp)).[15] The Ioniq is also available with a 17" alloy rim option and trims that include the alloy rims produce approximately 5 MPG less overall fuel economy on the highway.
The Ioniq Hybrid was released in South Korea in February 2016.[6] The hybrid was launched in Malaysia in November 2016. Two Ioniq Hybrid trims are available, HEV and HEV Plus.[16] Many parked Ioniqs appeared in the early scenes in Johnny English Strikes Again, starring Johnny English, played by Rowan Atkinson.
Ioniq Electric
| Ioniq Electric | |
|---|---|
.JPG.webp) | |
| Powertrain | |
| Electric motor | Front-engine rear-battery Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor |
| Power output | 120 hp (120 PS; 89 kW); 295 N⋅m (30.1 kg⋅m; 218 lb⋅ft) (2016–2019) 134 hp (136 PS; 100 kW); 295 N⋅m (30.1 kg⋅m; 218 lb⋅ft) (2020–present) |
| Transmission | 1-speed automatic |
| Battery | 28 kWh lithium-ion polymer battery[2] (2016–2019) 38.3 kWh lithium-ion polymer battery (2020–present) |
| Electric range | 2016–2019:- 200 km (124 mi) (EPA)[17] 280 km (174 mi) (NEDC)[2] 169 km (105 mi) (South Korea)[2] 2020–present:- 274 km (170 mi) (EPA) 310 km (193 mi) (WLTP) 200 km (124 mi) (South Korea) |
| Plug-in charging | 6.6 kW (2016–2019) 7.2 kW (2020–present) |
| Dimensions | |
| Curb weight | 1,420–1,575 kg (3,131–3,472 lb) |
The Hyundai Ioniq Electric is a mid-2010s limited-production all-electric version of the Ioniq that is sold only in select countries and US states. It features a 28 kWh lithium-ion polymer battery (LiPo) that delivers an EPA-rated all-electric range of 124 mi (200 km).[2][17] Hyundai originally expected the Ioniq to deliver a range of 110 mi (180 km).[18]
At the 2016 LA Auto Show, Hyundai announced that they are planning to extend the electric range of the Ioniq EV to more than 200 mi (320 km) by 2018.[19] However, the increase in battery size did not happen until 2019[20] and has an 193 mile range WLTP rated.[21] The Ioniq Electric has an 88 kW (120 PS) electric motor with 295 Nm of torque, and can be charged up to 80% in 33 minutes at 50 kW or in 24 minutes at 100 kW with a DC fast charging station.[22]
An integrated In-Cable Control Box (ICCB) also allows drivers to charge their Ioniq at a regular household outlet, but this is recommended only for use in emergencies in countries with 110 volt standard outlets.[23] In most countries, with 220-240 volt standard household outlets, 100% range can be added with an overnight charge.[24]
The charging plug of the car is located in a position where gas fillers are normally located.[2] The Ioniq features paddle shifters to allow drivers to choose from one of four levels of regenerative braking.[18] As of 2019, Hyundai USA sells the Ioniq Electric only in select states.[25] It is sold by Hyundai in other countries as well, which as of December 2018 included Canada,[26] Norway,[27] Netherlands, Portugal or Switzerland.[28] As of 2020, the car remains listed on the Hyundai website.[29]
Range and efficiency

Under the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) four cycle test, the 2017 Ioniq Electric combined fuel economy rating is 136 miles per gallon gasoline equivalent (mpg-e) (1.7 L/100 km), with an energy consumption of 25 kW·h/100 mi (15.7 kW⋅h/100 km).
The fuel economy rating for city is 150 mpg-e (1.6 L/100 km) and 122 mpg-e (1.9 L/100 km) in highway.[17]
With these ratings, the Ioniq Electric became in November 2016 the most efficient EPA certified vehicle considering all fuels and of all years, surpassing the 2014–2016 model year BMW i3, and also the 2017 Toyota Prius Prime, the most energy efficient plug in hybrid in EV mode.[9][10] Similarly electric Ioniq was praised by the Green NCAP for high energy efficiency, even under high-load highway test.
| Green NCAP test results | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hyundai Ioniq (2019)[30] 4x2 electric automatic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Test | Points | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overall: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
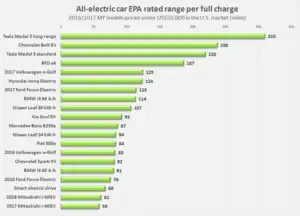
The 2017 Ioniq Electric has a combined EPA rated range of 124 mi (200 km).[17] Charging time is rated at 4 hours on a Level 2 fast charger (240 V).[31] The range under the New European Driving Cycle (NEDC) standard is 280 km (170 mi),[32] and 169 km (105 mi) under the South Korean cycle.[2]
Ioniq Plug-in
| Ioniq Plug-in | |
|---|---|
.JPG.webp) | |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.6 L Kappa II GDI HEV I4 |
| Electric motor | 60.5 PS (44.5 kW; 59.7 hp)[2] |
| Power output | 105 PS (77 kW; 104 hp) (petrol engine)[12] |
| Transmission | 6-speed DCT |
| Hybrid drivetrain | Plug-in hybrid |
| Battery | 8.9 kWh lithium-ion polymer battery[2] |
| Electric range | 50 km (31 mi) (claimed)[2] |
| Dimensions | |
| Curb weight | 1,495–1,551 kg (3,296–3,419 lb) |
The plug-in hybrid variant was released in February 2017.[35] It has an 8.9 kWh lithium-ion polymer battery (LiPo) capable of delivering 50 km (31 mi) in all-electric mode (18 miles in real world highway use).[36] The Ioniq Plug-in combines a 45 kW (61 PS) electric motor and 1.6-L GDI four cylinder Kappa engine with 40% thermal efficiency capable of delivering 78 kW (105 hp).[2][12]
Hyundai expects the Ioniq Plug-in to achieve a combined EPA rating of 125 mpg‑e (28 kW⋅h/100 mi; 17.1 kW⋅h/100 km) in all-electric mode.[12] EPA all electric range is 29 miles.[37]


The Ioniq Plug-in has the same dual-clutch transmission as the hybrid variant. This is an important differentiator for Hyundai from the majority of other hybrid and plug-in hybrid cars that use a continuously variable transmission.
Enhancing the Ioniq Plug-in fuel efficiency and dynamic driving characteristics, the driver can select either SPORT or ECO modes. The SPORT function holds lower gears longer and combines power from the engine and electric motor for maximum performance.
In ECO mode, the dual clutch transmission optimizes gear selection for efficiency, upshifting earlier to achieve better fuel economy.[12]

Sales
By January 2018, the Ioniq had surpassed 106,300 units sold worldwide, including over 73,800 conventional hybrids and nearly 25,000 purely electric cars, as well as over 5,500 plug-in hybrid variants (which had been on sale for three months).[38]
See also
References
- "Hyundai IONIQ (facelift 2019) 1.6 GDI (141 Hp) Plug-in Hybrid DCT Specifications from auto-data.net".
- Kane, Mark (2016-03-02). "Hyundai IONIQ Electric & IONIQ Plug-in At The Geneva Motor Show (Gallery, New Stats)". InsideEVs. Retrieved 2016-03-02. See more details in the official press release.
- Park Jin-hai (2016-01-14). "Hyundai launches Ioniq hybrid compact". Korea Times. Archived from the original on 2016-03-06. Retrieved 2016-03-02.
- Cobb, Jeff (2016-02-01). "Who Else Besides Toyota Will The Hyundai Ioniq Threaten?". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2016-02-20.
- 2017 Hyundai Ioniq first drive review: hybrid, EV, plug-in, no gas-only engines, accessed January 9, 2019
- Joseph, Noah (2016-01-14). "Hyundai Ioniq launches in Korea before challenging Prius in US [w/video]". Autoblog.com. Retrieved 2016-02-20.
- "Hyundai's Ioniq EV sales top 1,000 units". Yonhap News Agency. 2016-09-12. Retrieved 2016-09-22.
- Szostech, Michael. "Hyundai IONIQ Availability". My Electric Car Forums. Retrieved 28 January 2017.
- U. S. Environmental Protection Agency and U.S. Department of Energy (2019-11-15). "Extreme MPG: Most Efficient EPA Certified Vehicles". fueleconomy.gov. Retrieved 2019-11-23. The 2014–15 BMW i3 BEV was the most efficient EPA certified vehicles considering all fuels and of all years until November 2016, when it was surpassed by the Hyundai Ioniq Electric.
- Edelstein, Stephen (2016-11-21). "Hyundai Ioniq Electric beats Prius Prime, BMW i3 on energy efficiency". Green Car Reports. Retrieved 2016-11-21.
- Fuel Economy: 2019 Ioniq vs. 2019 Insight vs. 2019 Prius c, accessed January 9, 2019
- Mike Millikin (2016-03-24). "Hyundai unveils Ioniq HEV, PHEV and EV for US market at New York show". Green Car Congress. Retrieved 2016-03-24.
- Cobb, Jeff (2016-01-14). "Hyundai Ioniq Hybrid Gets Better Fuel Economy Than A 2015 Toyota Prius – In Korea". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2016-02-20.
- "Review: Hyundai Ioniq Hybrid". Car Buyer UK. Retrieved 2017-01-07.
- Cobb, Jeff (2016-03-23). "Hyundai Ioniq Hybrid Projected To Achieve 57 or 58 mpg". HybridCars.com. Retrieved 2016-03-24.
- "Hyundai Ioniq Hybrid in Malaysia: CKD, 7 airbags, from RM100k; RM111k with AEB and Smart Cruise Control". Paul Tan's Automotive News. 2016-11-29. Retrieved 2016-12-01.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency and U.S. Department of Energy (2016-11-16). "Compare Side-by-Side: 2017 Hyundai Ioniq Electric". fueleconomy.gov. Retrieved 2016-11-19.
- Voelcker, John (2016-03-21). "2017 Hyundai Ioniq Electric to offer 110 miles of range: company". Green Car Reports. Retrieved 2016-03-21.
- Szostech, Michael. "Hyundai IONIQ next-gen EV to come with 200-mile range in 2018". My Electric Car Forums. Retrieved 2016-11-18.
- "2019 Hyundai Ioniq: prices, specs and release date". buyacar.
"Order books are open now with deliveries expected to begin in early September".
- "Hyundai IONIQ Electric". Electric Vehicle Database.
- Szostech, Michael. "Hyundai IONIQ Electric Specifications". My Electric Car Forums. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
- "Hyundai Ioniq and Kia Niro review: Korean tanks parked on Japan's lawn".
- "Hyundai IONIQ Electric Charger - Pod Point".
- "2019 Ioniq Electric". Hyundai USA. Retrieved 2019-10-12.
- "Ioniq Electric". Hyundai Canada. Retrieved 2019-06-04.
- "Ioniq Electric". Hyundai Norway. Retrieved 2018-12-23.
- "Ioniq Electric". Hyundai Switzerland. Retrieved 2018-12-23.
- . Hyundai https://www.hyundaiusa.com/us/en/vehicles/ioniq-electric. Retrieved 4 March 2020. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - "Green NCAP assessment of the Hyundai Ioniq". greenncap.com. 2019.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency and U.S. Department of Energy (2016-11-16). "Model Year 2017 Fuel Economy Guide - Electric vehicles & Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles" (PDF). fueleconomy.gov. Retrieved 2016-11-19. pp. 32–36.
- "Hyundai Prices IONIQ Electric". 2016-06-22. Retrieved 2017-01-22.
- Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy, U.S. Department of Energy and U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (2016-09-14). "Find a car - Years: 2016–2017 - Vehicle Type: Electric". fueleconomy.gov. Retrieved 2017-03-26.
- Krok, Andrew (2017-07-29). "By the numbers: Tesla Model 3 vs. Chevrolet Bolt EV". CNET. Retrieved 2017-07-29.
- "Hyundai's Ioniq surpasses 30,000 in global sales". Yonhap News Agency. 2017-03-05. Retrieved 2017-03-26.
- <url=https://www.caranddriver.com/reviews/a19484142/2018-hyundai-ioniq-plug-in-hybrid-test-review/>
- "Hyundai IONIQ Plug-In Hybrid Gets EPA Range Rating Of 29 Miles Combined". insideevs.com.
- Hyundai IONIQ surpasses 100.000 units sold worldwide, accessed January 9, 2019
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hyundai Ioniq. |
- Official website (Electric)
- Official website (Hybrid)
- Official website (Plug-in Hybrid)