Jiading District
Jiading is a suburban district of Shanghai. It had a population of 1,471,100 in 2010.
Jiading
嘉定区 Kiating | |
|---|---|
 Shanghai International Circuit | |
| |
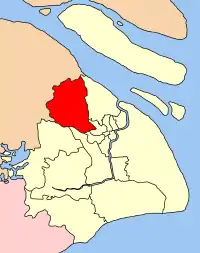 Jiading in Shanghai | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Municipality | Shanghai |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Jiading District | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 嘉定区 | ||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 嘉定區 | ||||||||||
| Postal | Kahding | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
History
Historically Jiading was a separate municipality/town until it was under the administration of Shanghai in 1958. In 1993 it was changed from a county to a district of Shanghai.[1]
In early Qing dynasty, which overlapped with Southern Ming, the municipality was infamously known for "Jiading Massacre", a mass murder by the invading Qing force led by defected northern Chinese bandit general Li Chengdong.[2][3] In late Qing (in 1853), Jiading city [sic] was also known for bandit activities that once captured the city and then Shanghai, as a rebellion of taxation.[4]
In 2005 Jiading District government invested RMB 10 million to build the Shanghai Museum of the Imperial Examination System.[5]
Geography
Jiading District is located in the northwestern part of Shanghai. It stretches across 463.9 square kilometers (179.1 sq mi). It is located about 20 kilometers (12 mi) from downtown Shanghai. Jiading District is connected to downtown Shanghai by the Hujia Expressway, the first expressway in China. Jiading District is near Shanghai's Hongqiao Airport but across town from the Pudong International Airport.
Administration
Jiading administers several towns including Jiading, Anting, Nanxiang, Huating, Xuhang, Waigang, Huangdu, Malu Town and Jiangqiao.
Subdistricts and towns
| Name | Chinese (S) | Hanyu Pinyin | Shanghainese Romanization | Population (2010)[6] | Area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xincheng Road Subdistrict | 新成路街道 | Xīnchénglù Jiēdào | sin zen lu ka do | 55,223 | 5.14 |
| Zhenxin Subdistrict | 真新街道 | Zhēnxīn Jiēdào | tzen sin ka do | 106,164 | 5.09 |
| Jiadingzhen Subdistrict | 嘉定镇街道 | Jiādìngzhèn Jiēdào | ka din tzen ka do | 81,854 | 4.10 |
| Nanxiang town | 南翔镇 | Nánxiáng Zhèn | neu zian tzen | 139,845 | 33.31 |
| Anting town | 安亭镇 | Āntíng Zhèn | eu din tzen | 232,503 | 89.29 |
| Malu town | 马陆镇 | Mǎlù Zhèn | mau loq tzen | 172,864 | 57.16 |
| Xuhang town | 徐行镇 | Xúháng Zhèn | zi raon tzen | 165,452 | 39.91 |
| Huating town | 华亭镇 | Huátíng Zhèn | rau din tzen | 46,355 | 39.57 |
| Waigang town | 外冈镇 | Wàigāng Zhèn | nga kaon tzen | 80,896 | 50.95 |
| Jiangqiao town | 江桥镇 | jiāng qiáo Zhèn | kaon djio tzen | 256,218 | 42.37 |
| Jiading Industrial Zone | 嘉定工业区 | Jiādìng Gōngyèqū | ka din kon gniq chiu | 72,933 | 78.10 |
| Juyuan New Area Administrative Committee | 菊园新区管委会 | Yúyuán Xīnqū Guǎn Wěihuì | cioq yeu sin chiu kueu we | 60,924 | 18.61 |
Landmarks
Shanghai University has a campus in downtown Jiading, which is where SILC is based.
The Shanghai International Circuit is located in Jiading. Each year in April the Shanghai International Circuit holds the Chinese Grand Prix.
The Jiading Confucian Temple is one of the best conserved Confucian temples in China. It has gone through several repairs in the past 800 years.
The Fahua Pagoda located in central Jiading is a tetragonal brick-wooden pagoda with seven floors and a height of 40.85 meters (134.0 ft).
The Bamboo Carving Museum, covering bamboo carving over the past 400 years since the mid-Ming Dynasty.
Sports
Shanghai Jiading F.C. is the local football club of the district.
Accommodation
There are numerous international hotels within the Jiading district. Among the most famous are Sheraton Shanghai Jiading Hotel and the Crowne Plaza Shanghai Anting, the latter one being the first five star international hotel in Jiading.
Notable people
- Yang Yongliang (b. 1980), artist
- James S.C. Chao (b. ~1935), merchant mariner, business leader, and philanthropist. He is the founder of Foremost Group.
- Wellington Koo (b. ~1888), a Chinese statesman of the Republic of China.
Transportation
Metro
Jiading is currently served by two metro lines operated by Shanghai Metro:
References
- 国务院关于上海市销嘉定县设立嘉定区的批复 (PDF). 国务院公报 (in Chinese). State Council of the People's Republic of China. 1993 (31): 1390. 1 February 1993.
- Lary, Diana; MacKinnon, Stephen (November 2011). Scars of War: The Impact of Warfare on Modern China. p. 30. ISBN 9780774841986.
- Struve, Lynn A. (1993). Voices from the Ming-Qing Cataclysm: China in Tigers' Jaws. p. 18. ISBN 0300075537.
- Burg, David F. (2004). "Nineteenth Century". A World History of Tax Rebellions. New York City; London: Routledge (Taylor & Francis Books). p. 353. ISBN 0-415-92498-7. Retrieved 11 March 2019 – via Google book preview.
- "Shanghai Museum of the Chinese Imperial Examination System". Administration of Jiading District, Shanghai. 11 July 2013. Retrieved 13 June 2019.
- Census Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China; Population and Employment Statistics Division of the National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China (2012). 中国2010人口普查分乡、镇、街道资料 (1 ed.). Beijing: China Statistics Print. ISBN 978-7-5037-6660-2.
Further reading
- "Jiading District". Encyclopedia of Shanghai. Shanghai Municipal Government. 2010. Archived from the original on 2013-03-02.
- James S.C. Chao
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Jiading District. |