Jones Glacier
Jones Glacier (66°36′S 91°30′E) is a channel glacier, 5 nautical miles (9 km) wide and 6 nautical miles (11 km) long, flowing north from the continental ice to the coast close east of Krause Point. It was delineated from aerial photographs taken by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump, 1946–47, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Ensign Teddy E. Jones, U.S. Navy Reserve, a photo interpreter with the Naval Photographic Interpretation Center, who served as recorder and assistant with the U.S. Navy Operation Windmill parties which established astronomical control stations along Wilhelm II Coast, Knox Coast and Budd Coast in 1947–48.[1]
| Jones Glacier | |
|---|---|
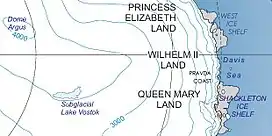 Kaiser Wilhelm II Land | |
 Location of Jones Glacier in Antarctica | |
| Type | channell |
| Location | Kaiser Wilhelm II Land |
| Coordinates | 66°36′S 91°30′E |
| Length | 5 nmi (9 km; 6 mi) |
| Width | 6 nmi (11 km; 7 mi) |
| Thickness | unknown |
| Terminus | east of Krause Point |
| Status | unknown |
References
- "Jones Glacier". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2013-04-05.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the United States Geological Survey document: "Jones Glacier". (content from the Geographic Names Information System)
This article incorporates public domain material from the United States Geological Survey document: "Jones Glacier". (content from the Geographic Names Information System)
| Types | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anatomy | |||||||
| Processes | |||||||
| Measurements | |||||||
| Volcanic relations | |||||||
| Landforms |
| ||||||
| |||||||
Glaciers of Kaiser Wilhelm II Land | |
|---|---|