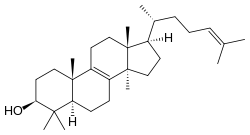
Lanosterol
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
lanosta-8,24-dien-3-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.105 |
| MeSH | Lanosterol |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H50O | |
| Molar mass | 426.71 g/mol |
| Melting point | 138 to 140 °C (280 to 284 °F; 411 to 413 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Role in biosynthesis of other steroids
Elaboration of lanosterol under enzyme catalysis leads to the core structure of steroids. 14-Demethylation of lanosterol by CYP51 eventually yields cholesterol.
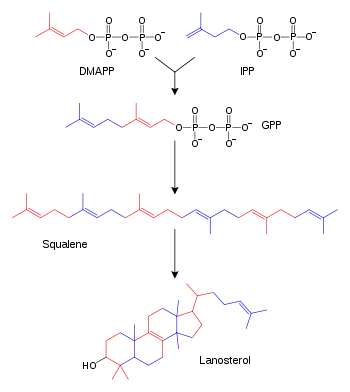
Simplified version of the lanosterol synthesis pathway with the intermediates isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP), dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP), and squalene shown. Some intermediates are omitted.
Biosynthesis
| Description | Illustration | Enzyme |
| Two molecules of farnesyl pyrophosphate condense with reduction by NADPH to form squalene | squalene synthase | |
| Squalene is oxidized to 2,3-oxidosqualene (squalene epoxide) | 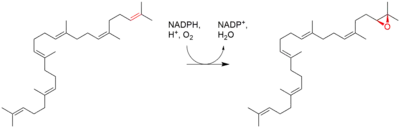 | squalene monooxygenase |
| 2,3-Oxidosqualene is converted to a protosterol cation and finally to lanosterol | 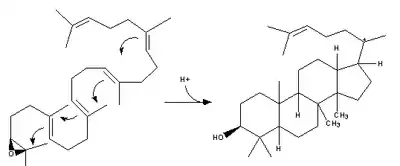 | lanosterol synthase |
| (step 2) | 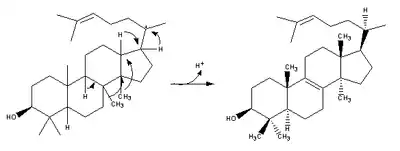 | (step 2) |
See also
References
- Schaller, Hubert (May 2003). "The role of sterols in plant growth and development". Progress in Lipid Research. 42 (3): 163–175. doi:10.1016/S0163-7827(02)00047-4.
- E. J. Corey, W. E. Russey, P. R. Ortiz de Montellano (1966). "2,3-Oxidosqualene, an Intermediate in the Biological Synthesis of Sterols from Squalene". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 88 (20): 4750–4751. doi:10.1021/ja00972a056. PMID 5918046.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- I. Abe; M. Rohmer; G. D. Prestwich (1993). "Enzymatic cyclization of squalene and oxidosqualene to sterols and triterpenes". Chemical Reviews. 93 (6): 2189–2206. doi:10.1021/cr00022a009.
- A. Eschenmoser, L. Ruzicka, O. Jeger, D. Arigoni (1955). "Zur Kenntnis der Triterpene. 190. Mitteilung. Eine stereochemische Interpretation der biogenetischen Isoprenregel bei den Triterpenen". Helvetica Chimica Acta. 38 (7): 1890–1904. doi:10.1002/hlca.19550380728.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.