Lathosterol oxidase
In enzymology, a lathosterol oxidase (EC 1.14.21.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
| Lathosterol oxidase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 1.14.21.6 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 37255-37-1 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
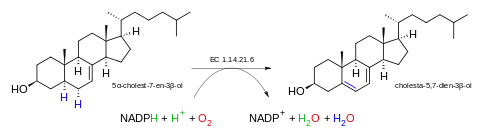
The 5 substrates of this enzyme are 5α-cholest-7-en-3β-ol, NADH, NADPH, H+, and O2, whereas its 4 products are cholesta-5,7-dien-3β-ol (provitamin D3), NAD+, NADP+, and H2O.
Classification
This enzyme is one of C-5 sterol desaturases, belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on paired donors, with O2 as oxidant and incorporation or reduction of oxygen. The oxygen incorporated need not be derived from O2 with NADH or NADPH as one donor, and the other dehydrogenated.
Nomenclature
The systematic name of this enzyme class is 5α-cholest-7-en-3β-ol,NAD(P)H:oxygen 5-oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include Δ7-sterol Δ5-dehydrogenase, Δ7-sterol 5-desaturase, Δ7-sterol-C5(6)-desaturase, and 5-DES.
Biological role
This enzyme participates in biosynthesis of steroids. It has 2 cofactors: FAD, and FMN.
References
- Dempsey ME, Seaton JD, Schroepfer GJ, Trockman RW (1964). "The Intermediary Role of Δ5,7-cholestadien-3-β-ol in Cholesterol Biosynthesis". J. Biol. Chem. 239: 1381–7. PMID 14189869.
- Nishino H, Nakaya J, Nishi S, Kurosawa T, Ishibashi T (1997). "Temperature-induced differential kinetic properties between an initial burst and the following steady state in membrane-bound enzymes: studies on lathosterol 5-desaturase". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 339 (2): 298–304. doi:10.1006/abbi.1996.9871. PMID 9056262.
- Taton M, Rahier A (1996). "Plant sterol biosynthesis: identification and characterization of higher plant Δ7-sterol C5(6)-desaturase". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 325 (2): 279–88. doi:10.1006/abbi.1996.0035. PMID 8561508.
- Taton M, Husselstein T, Benveniste P, Rahier A (2000). "Role of highly conserved residues in the reaction catalyzed by recombinant Δ7-sterol-C5(6)-desaturase studied by site-directed mutagenesis". Biochemistry. 39 (4): 701–11. doi:10.1021/bi991467t. PMID 10651635.