Leukotriene-A4 hydrolase
Leukotriene A4 hydrolase, also known as LTA4H is a human gene.[1][2][3] The protein encoded by this gene is a bifunctional enzyme (EC 3.3.2.6) which converts leukotriene A4 to leukotriene B4 and acts as an aminopeptidase.[4]
| leukotriene-A4 hydrolase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 3.3.2.6 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 90119-07-6 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| leukotriene A4 hydrolase | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
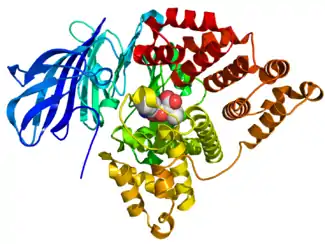 Crystallographic structure of LTA4H (rainbow colored N-terminus = blue, C-terminus = red) complexed with the protease inhibitor bestatin (space-filling model, carbon = white, oxygen = red, nitrogen = blue) based on the PDB: 1HS6 structure. | |||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | LTA4H | ||||||
| NCBI gene | 4048 | ||||||
| HGNC | 6710 | ||||||
| OMIM | 151570 | ||||||
| PDB | 1SQM | ||||||
| RefSeq | NM_000895 | ||||||
| UniProt | P09960 | ||||||
| Other data | |||||||
| EC number | 3.3.2.6 | ||||||
| Locus | Chr. 12 q22 | ||||||
| |||||||
Function
This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, specifically those acting on ether bonds (ether hydrolases). The systematic name of this enzyme class is (7E,9E,11Z,14Z)-(5S,6S)-5,6-epoxyicosa-7,9,11,14-tetraenoate hydrolase. Other names in common use include LTA4 hydrolase, LTA4H, and leukotriene A4 hydrolase. This enzyme participates in arachidonic acid metabolism.
Catalyzed reaction
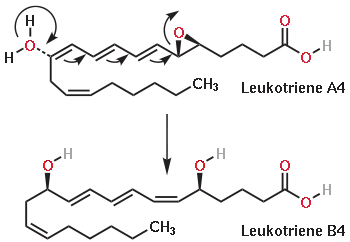
The chemical reaction catalyzed by LTA4H.
Structure
As of late 2007, 4 structures have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB accession codes 1GW6, 1H19, 1HS6, and 1SQM.
References
- Minami M, Ohno S, Kawasaki H, Rådmark O, Samuelsson B, Jörnvall H, Shimizu T, Seyama Y, Suzuki K (October 1987). "Molecular cloning of a cDNA coding for human leukotriene A4 hydrolase. Complete primary structure of an enzyme involved in eicosanoid synthesis". J. Biol. Chem. 262 (29): 13873–6. PMID 3654641.
- FFunk CD, Rådmark O, Fu JY, Matsumoto T, Jörnvall H, Shimizu T, Samuelsson B (October 1987). "Molecular cloning and amino acid sequence of leukotriene A4 hydrolase". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84 (19): 6677–81. Bibcode:1987PNAS...84.6677F. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.19.6677. PMC 299146. PMID 2821541.
- Mancini JA, Evans JF (July 1995). "Cloning and characterization of the human leukotriene A4 hydrolase gene". Eur. J. Biochem. 231 (1): 65–71. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20671.x. PMID 7628486.
- Rudberg PC, Tholander F, Andberg M, Thunnissen MM, Haeggström JZ (June 2004). "Leukotriene A4 hydrolase: identification of a common carboxylate recognition site for the epoxide hydrolase and aminopeptidase substrates". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (26): 27376–82. doi:10.1074/jbc.M401031200. PMID 15078870.
Further reading
- Evans JF, Dupuis P, Ford-Hutchinson AW (1985). "Purification and characterisation of leukotriene A4 hydrolase from rat neutrophils". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 840 (1): 43–50. doi:10.1016/0304-4165(85)90160-6. PMID 3995081.
- Shimizu T, Seyama Y, Suzuki K (1987). "Molecular cloning of a cDNA coding for human leukotriene A4 hydrolase. Complete primary structure of an enzyme involved in eicosanoid synthesis". J. Biol. Chem. 262 (29): 13873–6. PMID 3654641.
- Haeggstrom J, Meijer J, Radmark O (1986). "Leukotriene A4. Enzymatic conversion into 5,6-dihydroxy-7,9,11,14-eicosatetraenoic acid by mouse liver cytosolic epoxide hydrolase". J. Biol. Chem. 261 (14): 6332–7. PMID 3009453.
- Newman JW, Morisseau C, Hammock BD (2005). "Epoxide hydrolases: their roles and interactions with lipid metabolism". Prog. Lipid Res. 44 (1): 1–51. doi:10.1016/j.plipres.2004.10.001. PMID 15748653.
- Fretland AJ, Omiecinski CJ (2000). "Epoxide hydrolases: biochemistry and molecular biology" (PDF). Chem. Biol. Interact. 129 (1–2): 41–59. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.462.3157. doi:10.1016/S0009-2797(00)00197-6. PMID 11154734.
- Orning L, Gierse JK, Fitzpatrick FA (1994). "The bifunctional enzyme leukotriene-A4 hydrolase is an arginine aminopeptidase of high efficiency and specificity". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (15): 11269–73. PMID 8157657.
- Ohishi N, Izumi T, Minami M, Kitamura S, Seyama Y, Ohkawa S, Terao S, Yotsumoto H, Takaku F, Shimizu T (1987). "Leukotriene A4 hydrolase in the human lung. Inactivation of the enzyme with leukotriene A4 isomers". J. Biol. Chem. 262 (21): 10200–5. PMID 3038871.
External links
- leukotriene A4 hydrolase at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.