Lindlar catalyst
A Lindlar catalyst is a heterogeneous catalyst that consists of palladium deposited on calcium carbonate or barium sulfate which is then poisoned with various forms of lead or sulfur. It is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes to alkenes (i.e. without further reduction into alkanes) and is named after its inventor Herbert Lindlar.
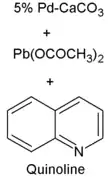
Synthesis
Lindlar catalyst is commercially available but may also be prepared by the reduction of palladium chloride in a slurry of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) followed by the addition of lead acetate.[1][2] A variety of other "catalyst poisons" have been used, including lead oxide and quinoline. The palladium content of the supported catalyst is usually 5% by weight.
Catalytic properties
The catalyst is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes to alkenes (i.e. without further reduction into alkanes). The lead serves to deactivate the palladium sites, further deactivation of the catalyst with quinoline or 3,6-dithia-1,8-octanediol enhances its selectivity, preventing formation of alkanes. Thus if a compound contains a double bond as well as a triple bond, only the triple bond is reduced. An example being the reduction of phenylacetylene to styrene.

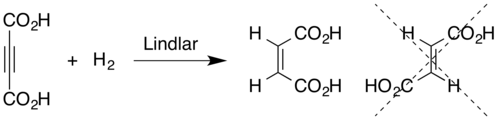
Alkyne hydrogenation is stereospecific, occurring via syn addition to give the cis-alkene.[3] For example the hydrogenation of acetylenedicarboxylic acid using Lindlar catalyst gives maleic acid rather than fumaric acid.
An example of commercial use is the organic synthesis of vitamin A which involves an alkyne reduction with the Lindlar catalyst. These catalysts are also used in the synthesis of dihydrovitamin K1.[4]
See also
- Rosenmund reduction, a reduction using palladium on barium sulfate, poisoned with sulfur compounds.
- Urushibara Iron, an iron based catalyst used to hydrogenate alkynes to alkenes.
References
- Lindlar, H.; Dubuis, R. (1966). "Palladium Catalyst for Partial Reduction of Acetylenes". Organic Syntheses. 46: 89. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.046.0089.
- Lindlar, H. (1 February 1952). "Ein neuer Katalysator fur selektive Hydrierungen". Helvetica Chimica Acta. 35 (2): 446–450. doi:10.1002/hlca.19520350205.
- Overman, L. E.; Brown, M. J.; McCann, S. F. (1993). "(Z)-4-(Trimethylsilyl)-3-Buten-1-ol". Organic Syntheses. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.068.0182.; Collective Volume, 8, p. 609
- Fritz Weber, August Rüttimann "Vitamin K" Ullmann's Encyclopedia Of Industrial Chemistry, 2012, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.o27_o08
