Mitsubishi Q2M
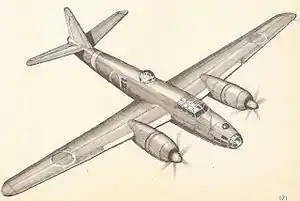
The Mitsubishi Q2M "Taiyō" design was derived from the Mitsubishi Ki-67-I Hiryū ("Peggy") heavy/torpedo bomber of the Japanese Army (and "Yasukuni" Navy's torpedo bomber version). It was ordered for design and construction in the last stages of war.
| Q2M | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Anti-Submarine Patrol aircraft |
| National origin | Japan |
| Manufacturer | Mitsubishi |
| Developed from | Mitsubishi Ki-67 |
Development
Powerful engines of 1,380 kW (1,850 hp) would have been used to drive five-blade propellers. Such an aircraft would have been managed by five or six crew. Due to technical troubles and a long development of the theoretical design, this aircraft did not advance from paper plans in last days of conflict.
Specification (Q2M)
General characteristics
- Crew: 6
- Length: 18.75 m (61 ft 6 in)
- Wingspan: 25 m (82 ft 0 in)
- Height: 4.75 m (15 ft 7 in)
- Empty weight: 8,850 kg (19,511 lb)
- Gross weight: 13,600 kg (29,983 lb)
- Powerplant: 2 × Mitsubishi Kasei 25 Otsu 14-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engines, 1,030 kW (1,380 hp) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 490 km/h (300 mph, 260 kn)
- Range: 2,415 km (1,501 mi, 1,304 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 3,704 m (12,152 ft)
Armament
- Guns: 3 × 13 mm (0.51 in) MG 131 machine gun
- Bombs: 4 × 250 kg (550 lb)
Avionics
- Type 3 Model 1 Magnetic Anomaly Detector (KMX)
- Type 3 Ku-6 Model 4 Radar
- ESM Antenna equipment
References
Notes
Sources
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.