Mount Elbrus
Mount Elbrus (Russian: Эльбру́с, tr. Elbrus, IPA: [ɪlʲˈbrus]; Karachay-Balkar: Минги тау, romanized: Mingi Taw) is the highest and most prominent peak in Russia and Europe. It is situated in the western part of the Caucasus; and is the highest peak of the Caucasus Mountains. The dormant volcano rises 5,642 m (18,510 ft) above sea level, and is the highest stratovolcano in Eurasia, and the tenth-most prominent peak in the world.[6] The mountain stands in Southern Russia, in the Russian republic of Kabardino-Balkaria.
| Mount Elbrus | |
|---|---|
 Mount Elbrus, from the North | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 5,642 m (18,510 ft) [1][2] |
| Prominence | 4,741 m (15,554 ft) Ranked 10th |
| Isolation | 2,473 km (1,537 mi) |
| Listing | Seven Summits Volcanic Seven Summits Country high point Ultra |
| Coordinates | 43°21′18″N 42°26′21″E |
| Naming | |
| Native name |
|
| Geography | |
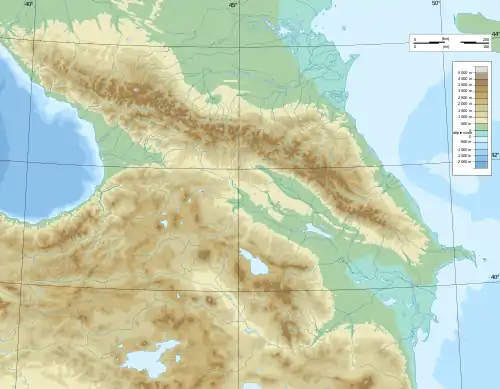 Mount Elbrus Location of Mount Elbrus within the Caucasus Mountains .jpg.webp) Mount Elbrus Location of Mount Elbrus within Russia  Mount Elbrus Location of Mount Elbrus within Europe .svg.png.webp) Mount Elbrus Location of Mount Elbrus on the Earth | |
| Country | |
| Federal subject | |
| Parent range | Caucasus Mountains |
| Topo map | Elbrus and Upper Baksan Valley by EWP[3][4] |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | Unknown |
| Mountain type | Stratovolcano (dormant) |
| Last eruption | 50 AD ± 50 years[5] |
| Climbing | |
| First ascent | (West summit) 1874, by Florence Crauford Grove, Frederick Gardner, Horace Walker and the guides Peter Knubel and Ahiya Sottaiev (Lower summit) 22 July 1829 by Khillar Khachirov |
| Easiest route | Basic snow/ice climb |
Elbrus has two summits, both of which are dormant volcanic domes. The taller, western summit is 5,642 metres (18,510 ft);[2] the eastern summit is 5,621 metres (18,442 ft). The eastern summit was first ascended on 10 July 1829 by Khillar Khachirov, and the western summit in 1874 by a British expedition led by F. Crauford Grove and including Frederick Gardner, Horace Walker, and the Swiss guide Peter Knubel.
Etymology
The name Elbrus /ˈɛlbrəs/ seems to have a connection with Alborz[7] (also called Elburz), which is also the name of a long mountain range in northern Iran, but the two should not be confused. The name is derived from Avestan Harā Bərəzaitī, a legendary mountain in Iranian mythology. Harā Bərəzaitī reflects Proto-Iranian *Harā Bṛzatī, which was reformed into Middle Persian as Harborz, and into Modern Persian as Alborz.[7] Bṛzatī is the feminine form of the adjective *bṛzant ("high"), the reconstructed ancestor of Modern Ossetian bærzond ("high", "peak"), Modern Persian barz ("high"), berāzande ("elegant"), and boland ("high", "tall"),[7] and Modern Kurdish barz ("high"). Harā may be interpreted as "watch" or "guard", from Indo-European *ser ("protect").[7] The name "Mingi Taw" used by Karachays and Balkars means "Eternal Mountain" in Turkic.[8]
Geography
Situation

Elbrus is situated in the northwest of the Caucasus, 100 kilometers from the Black Sea and 370 kilometers from the Caspian Sea, from where it is possible to see it in exceptionally clear weather.[9] It rises 5,642 meters above sea level, and is the highest point of the Caucasus Mountains. Located eleven kilometers north of the Greater Caucasus Watershed, marking the border with Georgia, it is shared between the respective territories of the Russian republics of Kabardino-Balkaria and Karachay-Cherkessia. It is the highest peak in both Russia and Europe, far ahead of Mont Blanc in the Alps, which rises 4,809 meters above sea level.
Elbrus is located 65 kilometers southwest of the city of Kislovodsk and 80 kilometers west-southwest of Nalchik. By road it is accessible from European route E50, known to Russians as either the M29 highway or the R217 highway. Nationalpark Elbrus, which is accessed by the A158 road out of Baksan, lies on its southeastern flank. Access permits are required south of Baksan because of border controls.
Topography
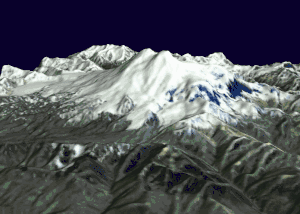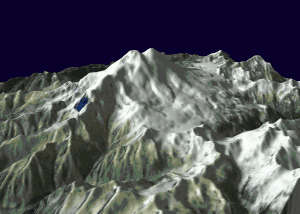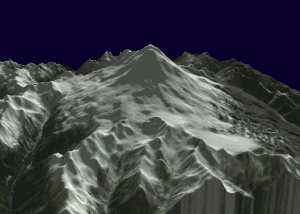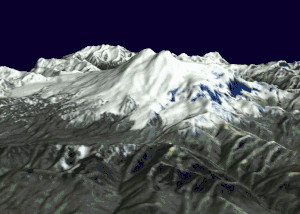
Elbrus is an almost symmetrical dormant volcano, in a vertical plane, with two main peaks, on either side of a pass located at 5,416 meters above sea level: the western summit is the highest point at 5,642 meters above sea level. while the eastern summit rises to 5,621 meters. The crater, 300 to 400 meters in diameter, located at the top of the eastern peak, was gradually filled with snow and ice. The snowfields of the volcano, covering an area of 138 km2, feed twenty-two (or twenty-three depending on the sources) main glaciers and seventy-seven secondary glaciers that give rise to the Baksan rivers: Kuban and Malka. Some of these glaciers, studied by scientists since the 1930s, can reach 400 meters in thickness but all are receding, having lost between 80 and 500 meters in length. The two main ones are called Bolshoi Azaou ("the great Azaou"), with an area of 23 km 2 and a length of 9.28 km, and Irik, with an area of 10.2 km2 and a length of 9, 31 km. This glacial activity has formed numerous small but deep lakes.
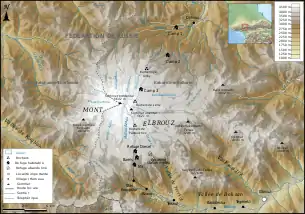

Geology
The Caucasus is formed by the northward collision of the Arabian Plate against the Eurasian Plate that causes numerous earthquakes in the region. The fault zone is complex and the largely lateral displacement at the level of Anatolia and Iran prevents the creation of a subduction phenomenon and explains the rarity of volcanoes in the mountain range. Elbrus is therefore one of the rare exceptions, made up of both metamorphic rocks (like schists or gneiss) and magmatic rocks (like granite, rhyolite or tuff).
Elbrus started to form there 10 million years ago. The ejecta from the volcano cover an area of 260 km2. Fragments of rhyolite and rhyodacite as well as tuff and ignimbrite formations have been found and have allowed by uranium-lead dating to situate the formation of the main caldera around −700,000 years, probably corresponding to the end of 'a major eruptive cycle. Geochronological dating has revealed subsequent synchronous eruptive cycles in different focimagmatic deposits of the Greater Caucasus, demonstrating the common geological origin of this volcanic activity. It happens that modest fumaroles still sometimes escape from the eastern flank of Elbrus, at the level of the ancient lava flow of 24 kilometers long oriented from the crater to the north-northeast, and hot springs originate on the slopes of the mountain.
Climate
As Elbrus is located in the Northern Hemisphere, the summer period, the least rigorous, takes place from June to mid-September with an average of 50% of sunny days favorable to the ascent of the summit. However, the winds, dominated by westerly air masses, can turn violent and temperatures drop very quickly. Above 4000 meters above sea level, even in summer, arctic blizzard conditions with near zero visibility can develop. It is not uncommon for the wind to exceed 100 km/h. In winter, the temperature can drop below −50° at the top, but in the valleys hot, dry downdrafts can cause heavy snowfall. At low altitudes, the average precipitation is 500 mm and can reach 1000 mm in some years, while above 2000 meters it can exceed 1500 mm.
Eruptive history
Mount Elbrus was formed more than 2.5 million years ago. The volcano is currently considered dormant. Elbrus was active in the Holocene, and according to the Global Volcanism Program, the last eruption took place about AD 50.[5] Evidence of recent volcanism includes several lava flows on the mountain, which look fresh, and roughly 260 square kilometres (100 sq mi) of volcanic debris. The longest flow extends 24 kilometres (15 mi) down the northeast summit, indicative of a large eruption. There are other signs of activity on the volcano, including solfataric activity and hot springs. The western summit has a well-preserved volcanic crater about 250 metres (820 ft) in diameter.[5]
History
The ancients knew the mountain as Strobilus, Latin for "pine cone", a direct loan from the ancient Greek strobilos, ('a twisted object') a long-established botanical term that describes the shape of the volcano's summit. In Greek mythology, the Titan Prometheus was chained to the mountain by Zeus as a punishment for stealing fire from the gods and giving it to mankind.
The lower of the two summits was first ascended on 22 July [O.S. 10 July] 1829 by Khillar Khachirov, a guide for an Imperial Russian army scientific expedition led by General Georgi Emmanuel, and the higher (by about 40 m; 130 ft) in 1874 by an English expedition led by F. Crauford Grove and including Frederick Gardner, Horace Walker, and the Swiss guide Peter Knubel from the Valais canton. During the early years of the Soviet Union, mountaineering became a popular sport of the populace, and there was tremendous traffic on the mountain. On 17 March 1936, a group of 33 inexperienced Komsomol members attempted the mountain, and ended up suffering four fatalities when they slipped on the ice and fell to their deaths.[10]
During the Battle of the Caucasus in World War II, the Wehrmacht occupied the area, surrounding the mountain from August 1942 to February 1943 with Gebirgsjäger from the 1st Mountain Division.[11] The Nazi Swastika was placed on the summit of Mount Elbrus on 21 August 1942.[12] A possibly apocryphal story tells of a Soviet pilot being given a medal for bombing the main mountaineering hut, Priyut 11 (Приют одиннадцати, "Refuge of the 11"), while it was occupied. He was later nominated for a medal for not hitting the hut, but instead the German fuel supply, leaving the hut standing for future generations. When news reached Adolf Hitler that a detachment of mountaineers was sent by the general officer commanding the German division to climb to the summit of Elbrus and plant the swastika flag at its top, he reportedly flew into a rage, called the achievement a "stunt" and threatened to court martial the general.[13][14]
The Soviet Union encouraged ascents of Elbrus, and in 1956 it was climbed en masse by 400 mountaineers to mark the 400th anniversary of the incorporation of Kabardino-Balkaria, the Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic where Elbrus was located.
Between 1959 and 1976, a cable car system was built in stages that can take visitors as high as 3,800 metres (12,500 ft). There are a wide variety of routes up the mountain, but the normal route, which is free of crevasses, continues more or less straight up the slope from the end of the cable car system. During the summer, it is not uncommon for 100 people attempt the summit via this route each day. Winter ascents are rare, and are usually undertaken only by very experienced climbers. Elbrus is notorious for its brutal winter weather, and summit attempts are few and far between. The climb is not technically difficult, but it is physically arduous because of the elevations and the frequent strong winds. The average annual death toll on Elbrus is 15–30, primarily due to "many unorganized and poorly equipped" attempts to reach the mountain's summit.[15]
Since 1986, Elbrus has been incorporated into Prielbrusye National Park, one of the Protected areas of Russia.
In 1997 a team led by the Russian mountaineer Alexander Abramov took a Land Rover Defender to the summit of the East Peak, entering the Guinness Book of Records.[16] The project took 45 days in total. They were able to drive the vehicle as high as the mountain huts at The Barrels (3,800 metres (12,500 ft)), but above this they used a pulley system to raise it most of the way. On the way down, a driver lost control of the vehicle and had to jump out. Although he survived the accident, the vehicle crashed onto the rocks and remains below the summit to this day.[17]
In 2016, the Russian climbers Artyom Kuimov and Sergey Baranov entered the Guinness Book of World Records by reaching the summit of Elbrus on ATVs.[18]
Due to the North Caucasus insurgency, travel to Mount Elbrus has become increasingly difficult. The United States Department of State has issued a travel advisory against climbing the mountain, as well as travel to the North Caucasian Federal District in general, due to the risk of terrorism and political instability.[19]
Ascents with horses
In August 1998 a group of climbers from the Karachai-Cherkess Republic were the first in history to climb Mount Elbrus with horses. The horses were Imbir, Daur and Khurzuk, of the Karachai breed, fitted with special horseshoes with removable steel spikes. The organiser of the climb was Klych-Gery Urusov. Six people reached the eastern summit: three Karachai horsemen (Dahir Kappushev, Mohammed Bidzhiev, Murat Dzhatdoev) and three mountaineers (Boris Begeulov, Umar Bairamukov, Leila Albogachieva (Ingush nationality)), with two of the three horses (Daur and Khurzuk).
A second equestrian climb was made in August 1999 by the same Karachai riders, with a Karachai horse (Igilik), reaching the higher western summit.[20]
A third equestrian ascent took place in 2019, by the Karachai horseman Aslan Khubiev with the Karachai horses Boz and Damly, helped by the Balkar guides Aslan Altuev and Askhat Guzoev.
A fourth equestrian ascent took place on 4 September 2020 (see photo below). Two Karachai horsemen, Ramazan Alchakov and Abrek Ediev, and their Russian friend Ivan Kulaga, together with the two Karachai horses Almaz and Dzhigit, reached the western summit.
A fifth equestrian ascent took place on 23 September 2020 by the Karachai horseman Taulan Achabaev and his cousin Rustam Achabaev, together with the stallion Bahr, reaching the higher western summit accompanied by the Balkar guide Aslan Altuev.
Infrastructure

Refuges
In 1929, eleven scientists erected a small hut at 4,160 metres and called it "Priyut 11" (Refuge of the 11). At the same site, a larger hut for 40 people was built in 1932.
A wilderness hut was built in 1933 in the saddle between the two summits but collapsed after only a few years. Its remains can still be seen.
In 1939, the Soviet Intourist travel agency built yet another structure a little above the "Priyut 11" site at 4,200 metres, covered in aluminium siding. It was meant to accommodate western tourists, who were encouraged to climb Mount Elbrus in commercial, guided tours to bring in foreign currency.
Not much later, this hut was converted into a mountain barracks, serving as a base, first for Soviet and later German troops in the Battle of the Caucasus of World War II.
On 16 August 1998, this hut completely burned down after a cooking stove fell over. After that, the new "Diesel hut" was built in the summer of 2001 a few metres below its ruins, so called because it is located at the site of the former Diesel generator station.
In addition, there is a collection of accommodations for six people each at the end of the short chairlift above the second cableway section. Painted red and white, these horizontal steel cylinders (called Barrels, Russian bochki), are used as a base and for acclimatization by many mountaineers on their way to the summit. Besides the "Barrels", there are several container accommodations between about 3,800 and 4,200 metres.
Observatory
The Terskol Observatory, an astronomical observatory with the IAU code B18, is located 2.5 km north-west of Terskol village at an altitude of 3,090 metres (10,140 ft).[21][22]

Activies
.jpg.webp)
Ski lifts
Three ski lifts take visitors up to an altitude of 3,847 meters.
Until the mid-2000s, the first section was provided by the Elbrouz-1 cable car, construction of which began in 1959. Starting from the Azaou road at 2,180 meters above sea level in the valley, it leads to the old viewpoint (Stari Krougozor) at an altitude of 2,970 meters; at the foot of the terminal tongue of the Mali glacier Azaou who has retreated since the construction of the facility. Its length is 1,740 meters, with a drop of 650 meters. The second section, built in 1976, leads to the Mir station at an altitude of 3,470 meters. Its length is 1,800 meters, with a drop of 500 meters. Finally, the last stretch is a chairlift single-seater which then makes it possible to avoid an hour's walk for hikers to the Garabachi huts, at an altitude of 3,847 meters. Built in the late 1970s, it is 1,000 meters long, with a drop of 250 meters.
In December 2006, the first section of the cable car is modernized to meet safety requirements, thanks to the construction of a new cable car in parallel with the existing one. Then inaugust 2009, a new cable car is built to reach the second section. In, December 27, 2015, the gondola to go up the third section is put into service, thus becoming the second highest gondola in Europe after that of Zermatt in Switzerland; which is 3,883 m high. Its capacity is 750 people per hour.
The ski resort makes the bulk of its turnover in April and May 6.
Mountaineering
There are many routes through the mountain. The normal route, devoid of crevasses, continues in an almost straight line on the slopes of the mountain from the end of the cable car to the summit. In summer, it is not uncommon to have around 100 people climbing the normal route every day. The course is not technically difficult but physically demanding, due to the steep slope and strong winds. Winter climbs are rare and undertaken mainly by seasoned climbers due to the extreme weather conditions.
The normal route, on the southern slope, is the easiest, the safest and the fastest, by using the ski lifts to the Garabachi 36 refuges offering 11 cylindrical cabins (the "barrels") of 6 beds each and a total of 80 berths, with water from the melting glacier in summer, and electric heating. At an hour and a half walk, at an altitude of 4,157 meters, is the Diesel refuge, offering 50 places and built in 2001 on the site of the former refuge of the 11 accidentally burned down onAug 16, 199828 , 36 , 40 . After an additional two hours of walking, the normal route passes close to the Pastoukhov rocks, which can be reached by a snowmobile. The rest of the ascent to the two main peaks can only be done on foot in about ten hours. The route is well signposted; but it can be risky to go more than fifty meters from it because of the few crevasses or in the event of under-equipment. A variant allows you to reach the Diesel refuge from the Ice camp, at an altitude of 3,680 meters.
Another route leads to the summit from Kioukiourtliou-Kolbachi (4,639 m) via the Dome of Koupol at 4,912 meters, on the western side of the mountain. This route, much longer, is accessible either from the first section of the cable car by crossing the moraines in a north-west direction via the Khoti Outaou pass then obliquely towards the summit, or from the Khourzouk valley. There is no refuge but the terrain is more suitable for camping.
Other routes by the east from the valley, the glacier and the Iryk pass (3,667 m), or by the north are possible but are more hazardous due to the absence or obsolescence of the installations.
During Soviet times, Mount Elbrus was home to climbing speed competitions and was training for national Himalayan expeditions (1982 and 1989). The best mountaineers tested their endurance during this prestigious event. In September 1987, Vladimir Balyberdine organizes the first official race between the refuge and the pass. In 1990, Anatoli Boukreev set a record by climbing from the refuge to the eastern summit in a time of 1 hour and 47 minutes. In 2005, with the growing enthusiasm for extreme sports and the increase in the number of mountaineers in Russia, this tradition was relaunched and a new race was organized between Bochki and the western summit. In 2006, the best mountaineers from the former Soviet republics participated in the competition: Denis Urubko from Kazakhstan, Sergei Seliverstov and Alexander Kerimov from Kyrgyzstan, and Sergei Sourmonin from Russia. For the first time, one of the routes offers a height difference of over 3,000 meters, starting at the Azaou glades at an altitude of 2,400 meters and arriving at the western summit. Denis Ouroubko sets a time of 3 hours 55 minutes and 58 seconds on this course. On the route starting from the Garabachi huts, Svetlana Sharipova is the best female with a time of 3 hours 21 minutes and 29 seconds.
It is possible to go around Mount Elbrus. The easiest route takes between eight and ten days of hiking, with the crossing of several glaciers and the crossing of many passes. It starts from the village of Baksan in the Kirtyk valley, then passes through the Kirtykaouch pass (3,242 m), descends to the Malka river where it is possible to discover the Sultan Falls from a height of forty meters near the sources. the Jilasu, then connects Khourzouk after the Bourountach pass (3,072 m), and finally crosses the Oullou-Kam river, the Khoti Outaou pass (3,456 m), the Azaou glacier to descend to Terskol and finally return to the point of departure.
In September 2012, an emergency shelter is installed on the "saddle" of Elbrus, between the eastern summit and the western summit, station EG 5300. It was then the highest mountain refuge in Europe. However, the shelter was destroyed by winds in December of the same year. In 2013, a new, more modest emergency shelter, capable of accommodating four to six people, was built 300 meters from the EG 5300 station , by the Russian Mountaineering Federation.
Elbrus Race
The first race on Elbrus took place in 1990, with Soviet and American climbers competing. The race was won by Anatoli Boukreev, with Kevin Cooney in second, followed by Patrick Healy. Route Priut 11 (4,050 m (13,287 ft)) – East (lower) was summited in 1 hour and 47 minutes.[23]
Regular competitions began to take place in 2005, with a choice of two routes: the "classic" climb from "Barrels" at 3,708 m (12,165 ft) to the western summit (5,642 m (18,510 ft)) and a long climb, from the Azau Meadow at 2,350 m (7,710 ft) to the same summit. In 2006, Denis Urubko won the long ascent in 3 hours, 55 minutes, 59 seconds.[23]
On 24 September 2010, under the Artur Hajzer program "Polish Winter Himalayism 2010–2015", the Polish Mountaineering Association sent a 13-person team for training purposes. Andrzej Bargiel set a new long course record of 3 hours, 23 minutes, 37 seconds.[24]
The record time for the full race, ascent and descent, of the long route is 4:20:45, set on 7 May 2017 by the Swiss-Ecuadorian mountain guide Karl Egloff. Egloff broke the previous record set in September 2014 by Vitaliy Shkel by more than 18 minutes. He reached the summit in 3:24:14, missing Bergiel's record ascent-only time by 37 seconds; the race organisation and the International Skyrunning Federation nevertheless consider Egloff's ascent a record as well.[25][26][27]
The fastest times by a woman on the long route were set by Diana Zelenova (4:30:12 for the ascent in 2017) and Oksana Stefanishina (6:25:23 for the full race in 2015).[27]
Environmental issues
Mount Elbrus is said to be home to the 'world's nastiest' outhouse which is close to being the highest toilet in Europe. The title was conferred by Outside magazine following a 1993 search and article.[28] The "outhouse" is surrounded by and covered in ice, perched on the end of a rock.[29]
See also
References
- The World Book Encyclopedia—Page 317 by World Book, Inc
- Mt. Elbrus : Image of the Day. Earthobservatory.nasa.gov. Retrieved on 15 May 2014.
- Mount Elbrus Map Sample. Ewpnet.com. Retrieved on 15 May 2014.
- Mount Elbrus and Upper Baksan Valley Map and Guide (Map) (2nd ed.). 1:50,000 with mountaineering information. EWP Map Guides. Cartography by EWP. EWP. 2007. ISBN 978-0-906227-95-4.
- "Elbrus: Summary". Global Volcanism Program. Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved 25 February 2010.
- "CIA World Factbook – Russia, Geography". US CIA. US Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 22 February 2016.
- "Alborz" in Encyclopædia Iranica
- Eric Alexander, (2010), The Summit: Faith Beyond Everest's Death Zone, p. 83
- Howard Tomb (27 August 1989). "Getting to the Top In the Caucasus". The New York Times. Retrieved 13 November 2020.
- Kudinov V.F. Трагедия на Эльбрусе. poxod.ru
- Landser took photos of them on the summit from August 1942 to February 1943 and the Abwehr and Caucasian Germans were active in that area, until November 1943.Mount Elbrus History. Ewpnet.com (10 January 1943). Retrieved on 15 May 2014.
- https://history.howstuffworks.com/world-war-ii/russian-army-repels-hitlers-forces2.htm
- Kershaw, Ian. Hitler: Nemesis 1936–1945.
- Speer, Albert (1995). Inside the Third Reich. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. p. 332. ISBN 9781842127353.
- SummitPost—Interview with Boris Tilov—the Chef of the rescue service of Elbrus region—Trip Reports. Summitpost.org. Retrieved on 15 May 2014.
- Land Rover Defender climbs Mount Elbrus Archived 6 January 2008 at the Wayback Machine, ExplorersWeb (18 January 2004)
- Horrell, Mark (9 August 2013). "Chapter 7: The wild side of Elbrus". Elbrus By Any Means. Smashwords. ISBN 9781301665822.
- "New World Record: Summiting Elbrus with a Quad". Archived from the original on 13 February 2017. Retrieved 15 February 2017.
- "Russia Travel Advisory". travel.state.gov. Retrieved 25 March 2019.
- "Traces of Elbrus - "Золотая площадь". Международный журнал. The Golden Plaza. International Magazine". goldenplazamagazine.ru. Retrieved 19 July 2020.
- "Terskol Observatory". wikimapia.org.
- "International Center for Astronomical, Medical and Ecological Research". terskol.com.
- Elbrus Records at russianclimb.com
- Polacy najszybsi na Elbrusie Archived 8 August 2013 at the Wayback Machine. polskihimalaizmzimowy.pl
- New records on SkyMarathon - Mt. Elbrus, 2350-5642 m! at the Redfox Elbrus Race website, May 7, 2017.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 30 December 2014. Retrieved 29 December 2014.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) elbrusrace.com
- Best performances at the International Skyrunning Federation website.
- Flinn, John (9 April 2006). "The pinnacle of success—and—disgust—for climbers". San Francisco Chronicle.
- Getting to the Top In the Caucasus, New York Times (27 August 1989)
Further reading
- Anthony Huxley, Standard Encyclopedia of the World's Mountains (New York: Putnam, 1962)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |
- Mount Elbrus on SummitPost
- "Elbrus, Mount." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2006. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 14 November 2006 <http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9032240>.
- Computer generated summit panoramas North South. There are a few discontinuities due to incomplete data.
- NASA Earth Observatory pages on Mount Elbrus: Mt. Elbrus (July 2003), Mt. Elbrus, Caucasus Range (November 2002)
- Mt. Elbrus Expedition Cybercast Archives
- Geographic Bureau. "Elbrus Region". Retrieved 5 January 2010.
- Horses on Elbrus, Kavkaz Karatchai Cinema Tebou TV (KKCTebouTV) video, 1999: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GTVzLGFYA1g