Mughal emperors
The Mughal emperors (or Moghul) built and ruled the Mughal Empire on the Indian subcontinent, mainly corresponding to the modern countries of India, Pakistan, Afghanistan and Bangladesh. The Mughals began to rule parts of India from 1526, and by 1700 ruled most of the sub-continent. After that they declined rapidly, but nominally ruled territories until the 1850s. The Mughals were a branch of the Timurid dynasty of Turco-Mongol origin from Central Asia. Their founder Babur, a Timurid prince from the Fergana Valley (in modern Uzbekistan), was a direct descendant of Timur (generally known in western nations as Tamerlane) and also affiliated with Genghis Khan through Timur's marriage to a Genghisid princess.
| Shahanshāh of Hindustan | |
|---|---|
| شہنشاہ ہندوستان | |
Imperial | |
| Details | |
| Style | His Imperial Majesty |
| First monarch | Babur |
| Last monarch | Bahadur Shah Zafar |
| Formation | 20 April 1526 |
| Abolition | 21 September 1857 |
| Residence | |
| Appointer | Hereditary |
Many of the later Mughal emperors had significant Indian Rajput and Persian ancestry through marriage alliances as emperors were born to Rajput and Persian princesses.[1][2] Akbar, for instance, was half-Persian (his mother was of Persian origin), Jahangir was half-Rajput and quarter-Persian, and Shah Jahan was three-quarters Rajput.[3]
During the reign of Aurangzeb, the empire, as the world's largest economy, worth over 25% of global GDP, controlled nearly all of the Indian subcontinent, extending from Chittagong in the east to Kabul and Baluchistan in the west, Kashmir in the north to the Kaveri River basin in the south.[4]
Its population at the time has been estimated as between 110 and 150 million (a quarter of the world's population), over a territory of more than 4 million square kilometres (1.2 million square miles).[5] Mughal power rapidly dwindled during the 18th century and the last emperor, Bahadur Shah II, was deposed in 1857, with the establishment of the British Raj.[6]
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was founded by Babur, a Timurid prince and ruler from Central Asia. Babur was a direct descendant of the Timurid Emperor Tamerlane on his father's side, and the Mongol ruler Genghis Khan on his mother's side.[7] Ousted from his ancestral domains in Turkistan by Sheybani Khan, the 14-year-old Prince Babur turned to India to satisfy his ambitions. He established himself in Kabul and then pushed steadily southward into India from Afghanistan through the Khyber Pass.[7] Babur's forces occupied much of northern India after his victory at Panipat in 1526.[7] The preoccupation with wars and military campaigns, however, did not allow the new emperor to consolidate the gains he had made in India.[8] The instability of the empire became evident under his son, Humayun, who was driven into exile in Persia by rebels.[7] Humayun's exile in Persia established diplomatic ties between the Safavid and Mughal Courts, and led to increasing West Asian cultural influence in the Mughal court. The restoration of Mughal rule began after Humayun's triumphant return from Persia in 1555, but he died from an accident shortly afterwards.[7] Humayun's son, Akbar, succeeded to the throne under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped consolidate the Mughal Empire in India.[9]
Through warfare and diplomacy, Akbar was able to extend the empire in all directions, and controlled almost the entire Indian subcontinent north of the Godavari river.[10] He created a new ruling elite loyal to him, implemented a modern administration, and encouraged cultural developments. He increased trade with European trading companies.[7] The Indian historian Abraham Eraly wrote that foreigners were often impressed by the fabulous wealth of the Mughal court, but the glittering court hid darker realities, namely that about a quarter of the empire's gross national product was owned by 655 families while the bulk of India's 120 million people lived in appalling poverty.[11] After suffering what appears to have been an epileptic seizure in 1578 while hunting tigers, which he regarded as a religious experience, Akbar grew disenchanted with Islam, and came to embrace a syncretistic mixture of Hinduism and Islam.[12] Akbar allowed freedom of religion at his court, and attempted to resolve socio-political and cultural differences in his empire by establishing a new religion, Din-i-Ilahi, with strong characteristics of a ruler cult.[7] He left his son an internally stable state, which was in the midst of its golden age, but before long signs of political weakness would emerge.[7]
Akbar's son, Jahangir, "was addicted to opium, neglected the affairs of the state, and came under the influence of rival court cliques.[7] During the reign of Jahangir's son, Shah Jahan, the splendour of the Mughal court reached its peak, as exemplified by the Taj Mahal. The cost of maintaining the court, however, began to exceed the revenue coming in.[7]

Shah Jahan's eldest son, the liberal Dara Shikoh, became regent in 1658, as a result of his father's illness. Dara championed a syncretistic Hindu-Muslim religion and culture. With the support of the Islamic orthodoxy, however, a younger son of Shah Jahan, Aurangzeb, seized the throne. Aurangzeb defeated Dara in 1659 and had him executed.[7] Although Shah Jahan fully recovered from his illness, there was a succession war for the throne between Dara and Aurangzeb. Finally, Aurangzeb succeeded the throne and kept Shah Jahan under house arrest.
During Aurangzeb's reign, the empire gained political strength once more, and it became the world's largest economy, over a quarter of the world GDP, but his establishment of Sharia caused huge controversies. Aurangzeb expanded the empire to include a huge part of South Asia. At its peak the kingdom stretched to 3.2 million square kilometres, including parts of what are now India, Pakistan, Afghanistan and Bangladesh.[13] but after his death in 1707, "many parts of the empire were in open revolt".[7] Aurangzeb's attempts to reconquer his family's ancestral lands in Central Asia were not successful while his successful conquest of the Deccan region proved to be a Pyrrhic victory that cost the empire heavily in both blood and treasure.[14] A further problem for Aurangzeb was the army had always been based upon the land-owning aristocracy of northern India who provided the cavalry for the campaigns, and the empire had nothing equivalent to the Janissary corps of the Ottoman Empire.[14] The long and costly conquest of the Deccan had badly dented the "aura of success" that surrounded Aurangzeb, and from the late 17th century onwards, the aristocracy become increasing unwilling to provide forces for the empire's wars as the prospect of being rewarded with land as a result of a successful war was seen as less and less likely.[14] Furthermore, the fact that at the conclusion of the conquest of the Deccan, Aurangzeb had very selectively rewarded some of the noble families with confiscated land in the Deccan had left those aristocrats who received no confiscated land as reward and for whom the conquest of the Deccan had cost dearly, feeling strongly disgruntled and unwilling to participate in further campaigns.[14] Aurangzeb's son, Shah Alam, repealed the religious policies of his father, and attempted to reform the administration. "However, after his death in 1712, the Mughal dynasty sank into chaos and violent feuds. In the year 1719 alone, four emperors successively ascended the throne".[7]
During the reign of Muhammad Shah, the empire began to break up, and vast tracts of central India passed from Mughal to Maratha hands. Mughal warfare had always been based upon heavy artillery for sieges, heavy cavalry for offensive operations and light cavalry for skirmishing and raids.[14] To control a region, the Mughals had always sought to occupy a strategic fortress in some region, which would serve as a nodal point from which the Mughal army would emerge to take on any enemy that challenged the empire.[14] This system was not only expensive, but also made the army somewhat inflexible as the assumption was always the enemy would retreat into a fortress to be besieged or would engage in a set-piece decisive battle of annihilation on open ground.[14] The Hindu Marathas were expert horsemen who refused to engage in set-piece battles, but rather engaged in campaigns of guerrilla warfare, a war of raids, ambushes and attacks upon the Mughal supply lines.[14] The Marathas were unable to take the Mughal fortresses via storm or formal siege as they lacked the artillery, but by constantly intercepting supply columns, they were able to starve Mughal fortresses into submission.[14] Successive Mughal commanders refused to adjust their tactics and develop an appropriate counter-insurgency strategy, which led to the Mughals losing more and more ground to the Maratha.[14] The Indian campaign of Nader Shah of Persia culminated with the Sack of Delhi and shattered the remnants of Mughal power and prestige, as well as drastically accelerating its decline. Many of the empire's elites now sought to control their own affairs, and broke away to form independent kingdoms. The Mughal Emperor, however, continued to be the highest manifestation of sovereignty. Not only the Muslim gentry, but the Maratha, Hindu, and Sikh leaders took part in ceremonial acknowledgements of the emperor as the sovereign of India.[15]
In the next decades, the Afghans, Sikhs, and Marathas battled against each other and the Mughals, only to prove the fragmented state of the empire. The Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II made futile attempts to reverse the Mughal decline, and ultimately had to seek the protection of outside powers. In 1784, the Marathas under Mahadji Scindia won acknowledgement as the protectors of the emperor in Delhi, a state of affairs that continued until after the Second Anglo-Maratha War. Thereafter, the British East India Company became the protectors of the Mughal dynasty in Delhi.[15] After a crushed rebellion which he nominally led in 1857–58, the last Mughal, Bahadur Shah Zafar, was deposed by the British, who then assumed formal control of a large part of the former empire,[7] marking the start of the British Raj.
List of Mughal Emperors
| Portrait | Titular Name | Birth Name | Birth | Reign | Death | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Bābur بابر |
Zahir-ud-din Muhammad ظہیر الدین محمد |
14 February 1483 Andijan, Uzbekistan | 20 April 1526 – 26 December 1530 | 26 December 1530 (aged 47) Agra, India | Founded the Empire |
 |
Humayun ہمایوں |
Nasir-ud-din Muhammad Humayun نصیر الدین محمد ہمایوں |
6 March 1508 Kabul, Afghanistan | 26 December 1530 – 17 May 1540
22 February 1555 – 27 January 1556 |
27 January 1556 (aged 47) Delhi, India | Humayun was overthrown in 1540 by Sher Shah Suri of the Suri dynasty but returned to the throne in 1555 after the death of Islam Shah Suri (Sher Shah Suri's son and successor). |
 |
Akbar-i-Azam اکبر اعظم |
Jalal-ud-din Muhammad جلال الدین محمد اکبر |
15 October 1542 Umerkot, Pakistan | 11 February 1556 – 27 October 1605 | 27 October 1605 (aged 63) Agra, India | His mother was Persian Hamida Banu Begum.[16] |
 |
Jahangir جہانگیر |
Nur-ud-din Muhammad Salim نور الدین محمد سلیم |
31 August 1569 Agra, India | 3 November 1605 – 28 October 1627 | 28 October 1627 (aged 58) Jammu and Kashmir, India | His mother was Rajput princess Mariam-uz-Zamani.[17] |
 |
Shah-Jahan شاہ جہان |
Shahab-ud-din Muhammad Khurram شہاب الدین محمد خرم |
5 January 1592 Lahore, Pakistan | 19 January 1628 – 31 July 1658 | 22 January 1666 (aged 74) Agra, India | His mother was Rajput princess Jagat Gosaini.[18] Built Taj Mahal. |
 |
Alamgir I عالمگیر |
Muhy-ud-din Muhammad Aurangzeb محی الدین محمداورنگزیب |
4 November 1618 Gujarat, India | 31 July 1658 – 3 March 1707 | 3 March 1707 (aged 88) Ahmednagar, India | His mother was Persian Mumtaz Mahal. He was married to Safavid Dynasty Princess Dilras Banu Begum. He established Islamic law throughout India. After his death, His younger Son Azam Shah became the King (for 3 months) .[19] |
 |
Bahadur Shah بہادر شاہ |
Qutb-ud-Din Muhammad Mu'azzam Shah Alam قطب الدین محمد معزام |
14 October 1643 Burhanpur, India | 19 June 1707 – 27 February 1712 | 27 February 1712 (aged 68) Lahore, Pakistan | He made settlements with the Marathas, tranquilised the Rajputs, and became friendly with the Sikhs in the Punjab. |
 |
Jahandar Shah جہاندار شاہ |
Mu'izz-ud-Din Jahandar Shah Bahadur معز الدین جہاندار شاہ بہادر |
9 May 1661 Deccan, India | 27 February 1712 – 11 February 1713 | 12 February 1713 (aged 51) Delhi, India | Highly influenced by his Grand Vizier Zulfikar Khan. |
 |
Farrukhsiyar فرخ سیر |
Farrukhsiyar فرخ سیر |
20 August 1685 Aurangabad, India | 11 January 1713 – 28 February 1719 | 19 April 1719 (aged 33) Delhi, India | Granted a firman to the East India Company in 1717 granting them duty-free trading rights for Bengal, strengthening their posts on the east coast. The firman or decree helped British East India company to import goods into Bengal without paying customs duty to the government. |
 |
Rafi ud-Darajat رفیع الدرجات |
Rafi ud-Darajat رفیع الدرجات |
1 December 1699 | 28 February – 6 June 1719 | 6 June 1719 (aged 19) Agra, India | Rise of Syed Brothers as power brokers. |
 |
Shah Jahan II شاہ جہان دوم |
Rafi ud-Daulah شاہ جہاں دوم |
June 1696 | 6 June 1719 – 17 September 1719 | 18 September 1719 (aged 23) Agra, India | ---- |
 |
Muhammad Shah محمد شاہ |
Roshan Akhtar Bahadur روشن اختر بہادر |
7 August 1702 [[Ghazni|Ghazni, Afghanistan | 27 September 1719 – 26 April 1748 | 26 April 1748 (aged 45) Delhi, India | Got rid of the Syed Brothers. Fought a long war with the Marathas, losing Deccan and Malwa in the process. Suffered the invasion of Nader Shah of Persia in 1739. He was the last emperor to possess effective control over the empire. |
 |
Ahmad Shah Bahadur احمد شاہ بہادر |
Ahmad Shah Bahadur احمد شاہ بہادر |
23 December 1725 Delhi, India | 29 April 1748 – 2 June 1754 | 1 January 1775 (aged 49) Delhi, India | Mughal forces defeated by the Marathas at the Battle of Sikandarabad. |
 |
Alamgir II عالمگیر دوم |
Aziz-ud-din عزیز اُلدین |
6 June 1699 Burhanpur, India | 3 June 1754 – 29 November 1759 | 29 November 1759 (aged 60) Kotla Fateh Shah, India | Domination of Vizier Imad-ul-Mulk. |
| Shah Jahan III شاہ جہان سوم |
Muhi-ul-millat محی اُلملت |
1711 | 10 December 1759 – 10 October 1760 | 1772 (aged 60–61) | Consolidation of power by the Nawab of Bengal-Bihar-Odisha. | |
 |
Shah Alam II شاہ عالم دوم |
Ali Gauhar علی گوہر |
25 June 1728 Delhi, India | 10 October 1760 – 19 November 1806 | 19 November 1806 (aged 78) Delhi, India | Defeat in the Battle of Buxar. |
| Muhammad Shah Bahadur Jahan IV شاہ جہان محمد شاه بهادر |
Bidar Bakht بیدار بخت |
1749 Delhi, India | 31 July 1788 – 11 October 1788 | 1790 (aged 40–41) Delhi, India | Enthroned as a puppet Emperor by the Rohilla Ghulam Qadir, following the temporary overthrow of Shah Alam II.[20] | |
 |
Akbar Shah II اکبر شاہ دوم |
Mirza Akbar میرزا اکبر |
22 April 1760 Mukundpur, India | 19 November 1806 – 28 September 1837 | 28 September 1837 (aged 77) Delhi, India | Titular figurehead under British protection. |
 |
Bahadur Shah II بہادر شاہ دوم |
Abu Zafar Sirajuddin Muhammad Bahadur Shah Zafar ابو ظفر سراج اُلدین محمد بہادر شاہ ظفر |
24 October 1775 Delhi, India | 28 September 1837 – 21 September 1857 | 7 November 1862 (aged 87) Yangon, Myanmar | Last Mughal Emperor. Deposed by the British and was exiled to Burma after the Indian Rebellion of 1857. |
Note: The Mughal Emperors practised polygamy. Besides their wives, they also had a number of concubines in their harem, who produced children. This makes it difficult to identify all the offspring of each emperor.[21]
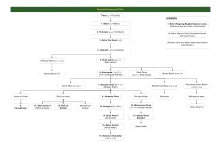
Family tree
See also
References
Citations
- Jeroen Duindam (2015), Dynasties: A Global History of Power, 1300–1800, page 105, Cambridge University Press
- Mohammada, Malika (1 January 2007). The Foundations of the Composite Culture in India. Akkar Books. p. 300. ISBN 978-8-189-83318-3.
- Dirk Collier (2016). The Great Mughals and their India. Hay House. p. 15. ISBN 9789384544980.
- Chandra, Satish. Medieval India: From Sultanate To The Mughals. p. 202.
- Richards, John F. (1 January 2016). Johnson, Gordon; Bayly, C. A. (eds.). The Mughal Empire. The New Cambridge history of India: 1.5. I. The Mughals and their Contemporaries. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 1, 190. doi:10.2277/0521251192. ISBN 978-0521251198.
- Spear 1990, pp. 147–148
- Berndl, Klaus (2005). National Geographic Visual History of the World. National Geographic Society. pp. 318–320. ISBN 978-0-7922-3695-5.
- Keay, 293–296
- Keay, 309–311
- Keay, 311–319
- Eraly, Abraham The Mughal Throne The Sage of India's Great Emperors, London: Phonenix, 2004 page 520.
- Eraly, Abraham The Mughal Throne The Sage of India's Great Emperors, London: Phonenix, 2004 page 191.
- "The great Aurangzeb is everybody's least favourite Mughal – Audrey Truschke | Aeon Essays". Aeon. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- D'souza, Rohan "Crisis before the Fall: Some Speculations on the Decline of the Ottomans, Safavids and Mughals" pages 3–30 from Social Scientist, Volume 30, Issue # 9/10, September–October 2002 page 21.
- Bose, Sugata; Jalal, Ayesha (2004). Modern South Asia: History, Culture, Political Economy (2nd ed.). Routledge. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-203-71253-5.
- Begum, Gulbadan (1902). The History of Humayun (Humayun-Nama). Royal Asiatic Society. pp. 237–9.
- Marc Jason Gilbert (2017). South Asia in World History. Oxford University Press. p. 79. ISBN 9780199760343.
- Emperor of Hindustan Jahangir (2010). The Tuzuk-i-Jahangiri; Or, Memoirs of Jahangir Translated by Alexander Rogers Edited by Henry Beveridge. General Books LLC. p. 18. ISBN 978-1-152-49040-6.
- Mohammada, Malika (1 January 2007). The Foundations of the Composite Culture in India. Aakar Books. p. 300. ISBN 978-8-189-83318-3.
- The Honorary Secretaries, Proceedings of the Asiatic Society of Bengal: 1871, (1871) p.97
- Dalrymple, William (2006). The Last Mughal. London: Bloomsbury Publishing Plc. p. 44. ISBN 978-1-4088-0092-8.
Sources
- Keay, John, India, a History, 2000, HarperCollins, ISBN 0002557177
 This article incorporates public domain material from the Library of Congress Country Studies website http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/. – India Pakistan
This article incorporates public domain material from the Library of Congress Country Studies website http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/. – India Pakistan
Further reading
- Majumdar, Ramesh Chandra; Pusalker, A. D.; Majumdar, A. K., eds. (1973). The History and Culture of the Indian People. VII: The Mughal Empire. Bombay: Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan.
