National Capital Parks
The National Capital Parks is an official unit of the National Park System of the United States. It encompasses a variety of federally owned properties in and around the District of Columbia including memorials, monuments, parks, interiors of traffic circles and squares, triangles formed by irregular intersections, and other open spaces.
History
Selection of the Site and Design of the City
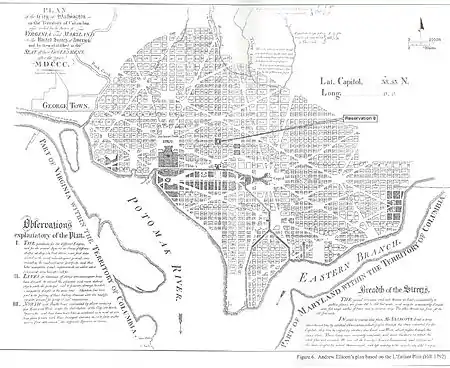
In 1790, Congress, through the Residence Act, authorized President George Washington to procure an area along the Potomac River to locate a new capital for the nation.[1] In 1791, President Washington appointed Pierre Charles L'Enfant to design what would become the City of Washington under the supervision of three Commissioners appointed to oversee the development of what would become the District of Columbia.[2] L’Enfant’s plan was ultimately modified by Andrew Ellicott when he ended in a dispute with the commissioners and Washington ultimately dismissed him.[3] The design created many of the spaces which would ultimately become the National Capital Parks.
Acquisition of Park Lands
The original lands of the National Capital Parks were acquired pursuant to Congress' authorization with the Residence Act of 1790.[1] Under this authority, between 1790 and 1867, The Mall, Monument Grounds, Capitol Grounds, President's Park, Lafayette Park, Franklin Park, Garfield Park and a total of 301 separate reservations in the original City of Washington were acquired as public properties.[4] Much of this land remains Federal property today and is part of the National Capital Parks.[5][6]
During the American Civil War, 1861–1865, the Union Army built a ring of fortifications to protect the city. These fortifications resulted in additional property becoming federally owned. In 1924, Congress created the National Capital Park Commission to acquire land in the District for the purpose of creating and preserving the sites of the Civil War fortifications and interconnecting parkways.[7]
In 1926, Congress passed legislation to create a system of parks out of the Civil War fortifications, which allowed acquisition of additional property to provide an interconnecting roadway as a parkway ring around the city.[8] This is known today as the Fort Circle Parks. Although the roadway was never built, the property remains today in Federal hands.
In 1933, title and control of parklands in the District was transferred to the National Park Service, creating a new unit of the National Park System called the ‘’’National Capital Parks’’’. No legislation explicitly created the National Capital Parks. Rather, it was created as a result of an Executive Order which, among other things, abolished several federal agencies including the Arlington Memorial Bridge Commission, Public Buildings Commission, Public Buildings and Public Parks of the National Capital, National Memorial Commission, and Rock Creek and Potomac Parkway Commission and consolidated their functions into the Office of National Parks, Buildings, and Reservations of the Department of the Interior.[9] In 1935, the name was changed back to National Park Service.[10]
In 1975, Baltimore–Washington Parkway was incorporated into the unit.[11]
Administration
Today, National Capital Parks remains a formal Congressionally authorized unit of the National Park System, but administration of the parklands is divided among several administrative units of the National Park Service:
- National Capital Parks-East – administers National Park properties in the District to the East of the Capitol Building, including several properties in Maryland
- National Mall and Memorial Parks – formerly called National Capital Parks-Central, this unit administers all properties in and around the Mall.
- White House and President's Park – administers The White House, a visitor center, Lafayette Square, and The Ellipse.
- Rock Creek Park – administers properties in the north and the northwest of the District
- George Washington Memorial Parkway – In addition to properties in Virginia, this unit administers properties in the District: Clara Barton Parkway; Theodore Roosevelt Island; Arlington Memorial Bridge; and the Columbia Island parks, including Lady Bird Johnson Park, Lyndon Baines Johnson Memorial Grove, Navy – Merchant Marine Memorial, and the Columbia Island Marina
- Chesapeake and Ohio Canal National Historical Park – administers the entire C&O Canal NHP, including the portion inside the District.
References
- "Residence Act". Library of Congress. Retrieved 4 August 2014.
- Leach, Sara Amy; Barthold, Elizabeth (1994-07-20). "L'Enfant Plan of the City of Washington, District of Columbia". National Register of Historic Places Registration Form. United States Department of the Interior: National Park Service. Retrieved 2012-01-08.
- Bowling, Kenneth R., Creating the federal city, 1774–1800 : Potomac fever. American Institute of Architects Press, Washington, D.C., 1988
- "A History of the National Capital Parks". National Park Service.
- "Reservation List: The Parks of the National Park System, Washington, DC" (PDF). www.nps.gov. National Park Service; Land Resources Program Center; National Capital Region. Retrieved 1 May 2016.
- Act of July 16, 1790, 1 Stat., 130
- Act of June 6, 1924, Chapter 270, 43 Stat 463
- Act of April 30, 1926, Chapters 197,198, 44 Stat. 374
- "Executive Order 6166--Organization of executive agencies". www.archives.gov. National Archives. Retrieved 2 December 2017.
- "A Brief History of the National Park Service". www.nps.gov. National Park Service. Retrieved 2 December 2017.
- "Important Anniversaries and Dates of Designation for National Park Service Units" (PDF). www.nps.gov. National Park Service. Retrieved 2 December 2017.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to National parks in Washington, D.C.. |
- Official website

- National Park Foundation.org: official National Capital Parks website
- NPS.gov: National Capital Parks-East
- NPS.gov: National Mall and Memorial Parks
- NPS.gov: President’s Park (White House)
- NPS.gov: Rock Creek Park
- NPS.gov: George Washington Memorial Parkway
- NPS.gov: Chesapeake and Ohio Canal National Historical Park
- Works by National Capital Parks at Open Library

- The National Parks: Index 2012-2016
- National Park Service Index Addendum (2016-2017)