Outline of Colorado prehistory
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the prehistoric people of Colorado, which covers the period of when Native Americans lived in Colorado prior to contact with the Domínguez–Escalante expedition in 1776. People's lifestyles included nomadic hunter-gatherering, semi-permanent village dwelling, and residing in pueblos.

Apache 
Navajo 
Cheyenne
Periods and peoples
Paleo-Indian
Paleo-Indian period – the first people who entered, and subsequently inhabited, the Americas during the final glacial episodes of the late Pleistocene period. Evidence suggests big-game hunters crossed the Bering Strait from Asia into North America over a land and ice bridge (Beringia), that existed between 45,000 BCE – 12,000 BCE,[1] following herds of large herbivores far into Alaska.[2]
- Pre-Clovis – Paleo-Indian hunting, before the use of Clovis points.[3]:53–54 Lamb Spring in Littleton, with mammoth bones dated 14,140 to 12,140 years ago and hunting by use of stone tools other than Clovis points, is an example. Other examples include Dutton and Selby in the far eastern edge of Colorado.[3]:54–57
- Clovis culture – the oldest Paleo-Indian division, marked by the use of Clovis points, the first fluted projectile points used in North America. Dent, Dutton the Drake Clovis Cache site are examples of Clovis sites in Colorado. The Dent Site was the first site to provide evidence that men and mammoth co-existed and that man hunted mammoth.[3]:58–67
- Folsom tradition – as megafauna, like the mammoth, became extinct man adapted by hunting smaller animals with the smaller Folsom projectile point. Examples are the Lindenmeier Site, dated 10,600 to 10,720 B.P.[3]:70 and the Jones-Miller Bison Kill Sites.
- Plano cultures
- Cody complex – a Plano culture that used unfluted projectile points and other tools like the Folsom and Clovis cultures from about 9,000 to 7,000 B.C.[3]:82–83 Olsen-Chubbuck Bison Kill Site, Jurgens Site and Lamb Spring are Cody complex sites.
- Goshen complex / Plainview complex – at the Phillips-Williams Fork Reservoir Site.
- Hell Gap complex – Plano culture from 10,060 to 9,600 before present (estimated 8,050 to 7,590 B.C.), distinguished by the long stemmed, convex, and unfluted Hell Gap points. Jones-Miller Bison Kill Site is the only Hell Gap location in Colorado.[3]:79
- Other Paleo-Indian sites – Canyons of the Ancients National Monument, Picture Canyon, Phillips-Williams Fork Reservoir Site and Roxborough State Park Archaeological District.
Archaic period
Archaic period – people hunted small game, such as deer, antelope, and rabbits, and gathered wild plants. They moved seasonally to hunting and gathering sites. Late in the Archaic period, about 200-500 A.D., maize was introduced into the diet and pottery-making became an occupation for storing and caring food.[4]
- Apex complex – a Middle Archaic period was dated from about 3000 to 500 BC and first appeared in the Magic Mountain Site near Apex Creek.[5]:33–34
- Archaic–Early Basketmaker Era – cultural period from 7000 - 1500 BC of ancestors to the Ancient Pueblo People, who used baskets to gather and store wild seeds, grasses, nuts and fruit. They moved seasonally to gather food and hunt, using spears with small projectile points, atlatl and darts and lived in simple dwellings.[6][7][8][9]
- Mount Albion complex – early Archaic culture (4050 to 3050 BC), distinguished by the Mount Albion corner-notched projectile.[5]:28–29 Examples are: LoDaisKa Site, Magic Mountain Site, and Franktown Cave.
- Oshara Tradition – was an Archaic culture dated from 5,440 B.C. to A.D. 460 that is believed to be a predecessor to the Basketmaker culture of the Ancient Pueblo People. Six phases spanned a period from early Archaic period to the introduction of cultivation and pottery.[10]
Post-Archaic period
- Post-Archaic, hunter and gathers
- Apishapa culture – prehistoric culture from A.D. 1000-1400, named for an archaeological site in the Lower Apishapa canyon in Colorado.[11]:24 At least 68 Apishapa sites have been identified on the Chaquaqua Plateau in southeastern Colorado.[5]:89 Some sites where Apishapa archaeological evidence has been found include Franktown Cave, Picture Canyon and Trinchera Cave Archeological District.
- Dismal River culture – first seen in the Dismal River area of Nebraska. Dated between 1650-1750 A.D., it is different than other precontact Central Plains and Woodland traditions of the western Plains.[3]:234[11]:212, 213, 768[12] Some Colorado sites include Cedar Point Village and Franktown Cave
- Panhandle culture – of the southern High Plains dated about AD 1200-1400 and primarily located in the panhandle and west central Oklahoma and the northern half of the Texas Panhandle. Distinguishing characteristics of the Panhandle culture are: great similarity to the Central Plains complexes; some evidence of trading or influence of Southwestern Ancestral Pueblo peoples; and single or multi-roomed stone structures.[5]:87 For Colorado sites, see Trinchera Cave Archeological District as well as the Apishapa culture and Sopris Phase articles.
- Plains Woodland or Ceramic Period – The Woodland period, or Early Ceramic period, began in the Plains about AD 0 with the defining distinction of the creation of cordwrapped pottery, development of settlement areas, and use of smaller projectile points for hunting smaller game and/or bow and arrow technology.[5]:41 Sites include Colorado Millennial Site, Franktown Cave, LoDaisKa Site, Magic Mountain Site, Picture Canyon, and Roxborough State Park Archaeological District
- Sopris Phase – dated about AD 1000-1250 was first found in southeastern Colorado, near the present town of Trinidad. Although the culture appeared to have been greatly influenced by pueblo people, such as the Taos Pueblo and trade in the Upper Rio Grande, the Sopris culture was generally a hunter-gatherer tradition.[5]:94–95 See Trinchera Cave Archeological District
- Another Post-Archaic site is the Chimney Rock National Monument.
- Post-Archaic, Puebloan people
- Ancestral Pueblo peoples – ancient to protohistoric Native American culture centered on the present-day Four Corners area of the United States, comprising southern Utah, northern Arizona, northwest New Mexico, and southern Colorado.
- Basketmaker culture – American southwestern culture of the Ancient Pueblo People, dated about 1500 BC to AD 500, named for the large number of baskets found at archaeological sites. This group was preceded by the Archaic–Early Basketmaker Era, Durango Rock Shelters Archeology Site and followed by the Pueblo I Era. Basketmaker sites include Canyons of the Ancients National Monument, Hovenweep National Monument and Ute Mountain Ute Tribe site 5MT10525.
- Pueblo culture – began AD 500 with the Pueblo I Era when people lived in pueblo structures and realized an evolution in architecture, artistic expression, and water conservation. Pueblo eras continued through to the contemporary Pueblo V Era. There are many Pueblo sites in southwestern Colorado, most notably: Canyon of the Ancients, Hovenweep National Monument, Mesa Verde National Park, Ute Mountain Ute Tribe portion of the Mesa Verde Region.
- Tipi ring period – a late Post-Archaic period when tipi rings were found, signifying habitation of nomadic hunters. This period continued into the protohistoric and historic periods. Evidence of the Apishapa culture disappeared after AD 1400, followed by sites with tipi rings. See Picture Canyon, which has evidence of both Apishapa and Tipi ring periods.
- Ancestral Pueblo peoples – ancient to protohistoric Native American culture centered on the present-day Four Corners area of the United States, comprising southern Utah, northern Arizona, northwest New Mexico, and southern Colorado.
Culture in prehistoric Colorado
- Paleolithic lifestyle – a hunter-gatherer distinguished by their nomadic lifestyle and use of stone tools.
- Pueblo culture – village life typified by the development of communities centered upon agriculture, pottery and trade.
- See also the cultures under the Paleo-Indian, Archaic and Post-Archaic period sections above.
Art
- Rock art – human-made carvings or paintings markings made on natural stone, including petroglyphs and pictographs. See Cañon Pintado, Colorado Millennial Site, Dinosaur National Monument, Hawkins Preserve, Hovenweep National Monument, Mantle's Cave, Mesa Verde National Park, Picture Canyon, Piñon Canyon Maneuver Site, Ute Mountain Ute Tribe
- Solar calendar – a calendar whose dates indicate the position of the earth on its revolution around the sun, including passage of the seasons by the summer and winter equinox. See Hovenweep National Monument and Picture Canyon.
Clothing and personal adornment
- Blankets – turkey feathers, yucca fibers and rabbit fur were woven into blankets. Hides were likely also used as blankets for warmth.[13][14]
- Clothing – little evidence of clothing, aside from a few loin-cloths found at archaeological sites.
- Cradleboards – made from yucca, twigs and rabbit fur.[15]
- Hairstyles – based upon burial remains, men of the Basketmaker culture sometimes wore fancy hairstyles and it's hypothesized that women generally wore their hair cut short.[14]
- Jewelry – both men and women of the Basketmaker culture wore necklaces, bracelets and pendants made of shell, stone, bone and dried berries. Shells, such as abalone, conus and olivella from the coast of the Pacific ocean, would have been obtained through trade.[14]
- Robes – turkey feathers were woven into robes.[13]
- Sandals – made of woven yucca fibers or strips of leaves.[14]
Diet
- Cultivation – maize, squash, beans were cultivated by Ancient Pueblo People and some hunter-gatherers. Cultivation required at least some seasonal residency at the cultivation site for planting and harvesting.
- Paleolithic diet – diet of hunter-gatherers, reliant upon seasonal attainment of wild plants and animals.
Dwellings
- Adobe dwellings – building material made from sand, clay, water, and some kind of fibrous or organic material (sticks, straw, and/or manure).
- Crude lean-tos – shelters made of poles covered with brush and/or hides and having a roof with a single slope.
- Rock shelters – cave-like opening in a bluff or cliff, which may have construction of walls for protection from the elements.
- Pit-houses – dwellings built partially below ground, covered with poles, brush, earth and/or hides.
- Tipis – cone-shaped shelters made of wooden poles covered with animal skins.
- Wikiup – downed branches upturned with small ends forming a tight knit top and large branch ends forming the circular base. Often covered with more, smaller branches and/grasses, allowing for one opening. Similar in shape to a tipi but not portable, nor more than seasonal in use.
Medicine
- Prehistoric medicine – practice of use of natural resources, such as plants and earth, to treat disease and injury.
Tools
Precontanct peoples made a number of tools from stone, such as knives and other tools to pound, scrape, and cut.[15]
- Food gathering, storing, cultivation, preparation and cooking
- Baskets – container which is traditionally constructed from stiff fibers, which was used to gather, store and, when pitch-lined, cook food.
- Digging sticks – used to plant seeds.[15]
- Manos – a stone used as the upper millstone for grinding foods (as Indian corn) by hand in a metate.
- Metate – stone tool used for processing grain and seeds.
- Pottery – ceramic ware made from clay and fired for durability.
- Storage pits – underground pits, generally stone-lined for protection of surplus food against the elements and rodents.
- Hunting
- Atlatl – spear-thrower used to hunt game.
- Bow and arrow – projectile weapon used to hunt game, a significant improvement over the atlatl.
- Nets and snares – to trap small game.[15]
- Projectile points – a stone object crafted to a projectile, such as a spear, dart, arrow, or knife.
- Spears – pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head.
- Other
- Bone awls – simple tool used for sewing or to puncture holes, such as to create clothing from animal skins.
- Fire – Native American use of fire
- Rope – woven from yucca.[15]
- Scraper – unifacial tools that were used either for hideworking or woodworking.
- Yucca – a source of food, material for clothing and sandals, soap and more.
Origins of contemporary tribes
The Ute arrived in Colorado by the 17th century and occupied much of the present state of Colorado. They were followed by the Comanches from the south in the 18th century, and then the Arapaho and Cheyenne from the plains who then dominated the plains of Colorado. The Cheyenne, Arapaho, and Comanche were the largest groups of indigenous people in Colorado at the time of contact with settlers.[16] The following are the language groups and ancestors to contemporary Native American tribes:
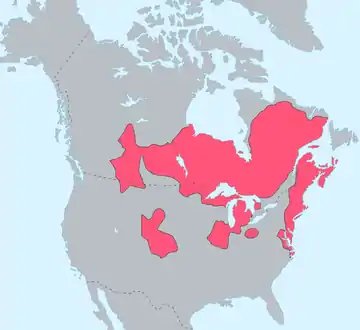
- Algonquians – were located prehistorically in Canada and the United States from the Rocky Mountains to the eastern seaboard. The Plains Algonquians, a geographic subdivision of the Algonquians, included the Arapaho, Cheyenne and Blackfoot people.
- Arapaho – lived on the eastern plains of Colorado, Wyoming and across the Great Plains. They were close allies of the Cheyenne people with whom they shared territory in eastern Colorado and southeastern Wyoming. They wintered in the foothills of the Rocky Mountains, hunted buffalo on the plains during the spring and fall and in mid-summer hunted game in the parks of Colorado.
- Cheyenne – lived on the plains east of the Rocky Mountains with the Arapaho.[16]
- Southern Athabaskans – consists of the Apachean and Navajo Nations, migrated from the present-day state of Alaska and northwestern Canada to the Great Plains of the United States, including Colorado, before settling in Southwestern United States.
- Apache
- Dismal River culture – the Apache presence in Colorado began with Dismal River cultures.
- Carlana (also Carlanes) – lived in southeastern Colorado on Raton Mesa and in 1726, they had joined with the Cuartelejo and Paloma, and by the 1730s, they were living with the Jicarilla.
- Jicarilla Apache – by A.D. 1525, the Jicarilla Apache who lived in northern New Mexico and southern Colorado and ranged throughout the plains of Texas, Oklahoma and Kansas.[17][18] See Cedar Point Village, Picture Canyon, Trinchera Cave Archeological District
- Apache
- Caddoan – of the Great Plains of the central United States, from North Dakota south to Oklahoma.
- Pawnee – ranged through the Great Plains and were first documented by Francisco Vásquez de Coronado when he met a Pawnee chief from Nebraska in 1541. Regarding Colorado, they hunted bison on plains of eastern Colorado.[16]
- Tanoan languages – a major family of Pueblo languages (Jemez, Tewa, Tiwa) and the Kiowa, ancestral to the pueblo people
- Kiowa – lived or ranged in the southwestern plains adjacent to the Arkansas River in southeastern Colorado.
- Uto-Aztecan languages
- Central Numic – the homeland of the Numic branch has been placed near Death Valley, California.
- Colorado River Numic language – like the Central Numic, the homeland of the Colorado River Numic branch has been placed near Death Valley, California.
- Ute – migrated from Utah and the Great Basin before the 17th century, occupied most of Colorado and were prehistoric hunters of western Colorado. They are the only native people with reservations in Colorado,[16] the Southern Ute Indian Reservation and the Ute Mountain Ute Tribe Reservation.
Archaeologists
- Cynthia Irwin-Williams – notable sites are LoDaisKa Site, Magic Mountain Site, and her work on Oshara Tradition and Picosa culture
- Paul Sidney Martin – excavated many ancient pueblo sites, including Lowry Pueblo
- Waldo Rudolph Wedel – a notable site is Lamb Spring, and also see his work on the Dismal River culture
- Joe Ben Wheat – the hallmark excavation site of his career is Joe Ben Wheat Site Complex, also see Jurgens Site, Olsen-Chubbuck Bison Kill Site
Gallery
- Language groups pre-contact locations
 Algonquian:
Algonquian:
Arapaho, Cheyenne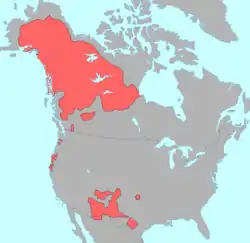 Athabaskan:
Athabaskan:
Apache, Navajo Caddoan:
Caddoan:
Pawnee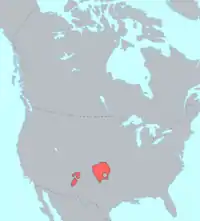 Kiowa-Tanoan:
Kiowa-Tanoan:
Kiowa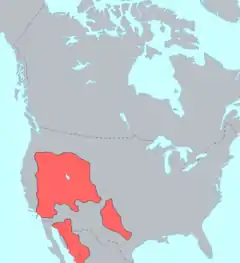 Uto-Aztecan:
Uto-Aztecan:
Comanche, Shoshone, Ute
- Historic map, representing prehistoric tribal regions
 1845 map. The Arkansas River was a boundary, with the Comanche and Kiowa to the south and the Arapaho and Cheyenne to the north of the river. The Ute were pressured to the western part of present-day Colorado
1845 map. The Arkansas River was a boundary, with the Comanche and Kiowa to the south and the Arapaho and Cheyenne to the north of the river. The Ute were pressured to the western part of present-day Colorado
See also
References
- "Atlas of the Human Journey-The Genographic Project." National Geographic Society. 1996-2008.
- Viegas, Jennifer. "First Americans Endured 20,000-Year Layover." Discovery News.
- Cassells, E. Steve. (1997). The Archeology of Colorado, Revised Edition. Boulder, Colorado: Johnson Books. ISBN 1-55566-193-9.
- Kipfer, Barbara Ann. (2000). Encyclopedic Dictionary of Archaeology. New York:Plenum Publisher. p. 341. ISBN 0-306-46158-7.
- Gunnerson, James H. (1987). Archaeology of the High Plains. Denver: United States Forest Service.
- Archaic: 5500 to 500 B.C.- Overview. Crow Canyon Archaeological Center. 2011. Retrieved 10-18-2011.
- Time-Life Book Editors. (1993) [1992] The First Americans. Alexandria, Virginia: Time-Life Books. pp. 29, 30. ISBN 0-8094-9400-0.
- Archaic-Early Basketmaker Period. Chaco Culture National Historical Park, National Park Service. Retrieved 10-15-2011.
- Archaic: 5500 to 500 B.C. - Housing Crow Canyon Archaeological Center. Peoples of the Mesa Verde Region. 2011. Retrieved 10-17-2011.
- Stiger, Mark. (2008). Hunter-Gather Archaeology of the Colorado High Country. Boulder: The University Press of Colorado. pp. 28-29. ISBN 0-87081-612-8.
- Gibbon, Guy E.; Ames, Kenneth M. (1998) Archaeology of Prehistoric Native America: An Encyclopedia. ISBN 0-8153-0725-X.
- The Dismal River Culture. Archived 2016-03-15 at the Wayback Machine. Nebraska Studies. Retrieved November 26, 2011.
- Wenger, Gilbert R. (1991) [1980]. The Story of Mesa Verde National Park. Mesa Verde Museum Association, Mesa Verde National Park, Colorado. pp. 33-37. ISBN 0-937062-15-4.
- Man of the San Juan Valley: The Basketmakers. Aztec Ruins National Monument, National Park Service. Retrieved 10-16-2011.
- Ancestral Puebloan Chronology (teaching aid). Mesa Verde National Park, National Park Service. Retrieved 10-16-2011.
- Indians of Colorado. The William E. Hewitt Institute for History and Social Science Education. University of Northern Colorado. Retrieved December 7, 2011.
- "Spanish Relations with the Apache Nations east of the Rio Grande", Jeffrey D. Carlisle, B.S., M.A., University of North Texas, May 2001, pages 4-5.
- Velarde Tiller, Veronica E. (2011) Culture and Customs of the Apache Indians. Santa Barbara, CA: Greenwood of ABC-CLIO. p. 28. ISBN 978-0-313-36452-5.