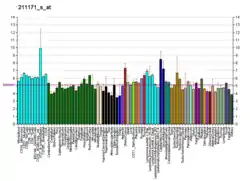
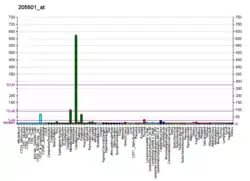
PDE10A
cAMP and cAMP-inhibited cGMP 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 10A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDE10A gene.[5][6]
Various cellular responses are regulated by the second messengers cAMP and cGMP. Phosphodiesterases, such as PDE10A, eliminate cAMP- and cGMP-mediated intracellular signaling by hydrolyzing the cyclic nucleotide to the corresponding nucleoside 5-prime monophosphate.[6][7]
Inhibitors
_in_tube_model.png.webp)
3d model of compound #96 (Malamas, 2011)[8]
- Compound 96: IC50 = 700 pM, high selectivity against all other members of the PDE family[8]
- Papaverine[9]
- PF-2545920[10]
- TAK-063: IC50 = 300 pM[11]
- AMG 579[12]
Research
Preliminary evidence indicates a possible link between PDE10A expression and obesity in mice and humans.[13]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000112541 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000023868 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Fujishige K, Kotera J, Michibata H, Yuasa K, Takebayashi S, Okumura K, Omori K (Jul 1999). "Cloning and characterization of a novel human phosphodiesterase that hydrolyzes both cAMP and cGMP (PDE10A)". J Biol Chem. 274 (26): 18438–45. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.26.18438. PMID 10373451.
- "Entrez Gene: PDE10A phosphodiesterase 10A".
- Fujishige K, Kotera J, Yuasa K, Omori K (October 2000). "The human phosphodiesterase PDE10A gene genomic organization and evolutionary relatedness with other PDEs containing GAF domains". Eur. J. Biochem. 267 (19): 5943–51. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01661.x. PMID 10998054.
- Malamas, MS; et al. (2011). "Highly potent, selective, and orally active phosphodiesterase 10A inhibitors". J. Med. Chem. 54 (21): 7621–38. doi:10.1021/jm2009138. PMID 21988093.
- Siuciak JA, Chapin DS, Harms JF, et al. (August 2006). "Inhibition of the striatum-enriched phosphodiesterase PDE10A: a novel approach to the treatment of psychosis". Neuropharmacology. 51 (2): 386–96. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2006.04.013. PMID 16780899. S2CID 13447370.
- Verhoest PR, Chapin DS, Corman M, et al. (August 2009). "Discovery of a novel class of phosphodiesterase 10A inhibitors and identification of clinical candidate 2-[4-(1-methyl-4-pyridin-4-yl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-phenoxymethyl]-quinoline (PF-2545920) for the treatment of schizophrenia". J. Med. Chem. 52 (16): 5188–96. doi:10.1021/jm900521k. PMID 19630403.
- Kunitomo J, Yoshikawa M, Fushimi M, et al. (2014). "Discovery of 1-[2-Fluoro-4-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]-5-methoxy-3-(1-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)pyridazin-4(1H)-one (TAK-063), a Highly Potent, Selective, and Orally Active Phosphodiesterase 10A (PDE10A) Inhibitor". J. Med. Chem. 57 (22): 9627–43. doi:10.1021/jm5013648. PMID 25384088.
- Hu; et al. (2014). "Discovery of Clinical Candidate 1-(4-(3-(4-(1Hbenzo[d]imidazole-2-carbonyl)phenoxy)pyrazin-2-yl)piperidin-1-yl)ethanone (AMG 579), a Potent, Selective, and Efficacious Inhibitor of Phosphodiesterase 10A (PDE10A)"". J Med Chem. 57 (15): 6632–41. doi:10.1021/jm500713j. PMID 25062128.
- Hankir, Mohammed K; et al. (2016). "A novel thermoregulatory role for PDE10A in mouse and human adipocytes". EMBO Molecular Medicine. 8 (7): 796–812. doi:10.15252/emmm.201506085. PMC 4931292. PMID 27247380.
Further reading
- Loughney K, Snyder PB, Uher L, et al. (1999). "Isolation and characterization of PDE10A, a novel human 3', 5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase". Gene. 234 (1): 109–17. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00171-7. PMID 10393245.
- Kotera J, Fujishige K, Yuasa K, Omori K (1999). "Characterization and phosphorylation of PDE10A2, a novel alternative splice variant of human phosphodiesterase that hydrolyzes cAMP and cGMP". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 261 (3): 551–7. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.1013. PMID 10441464.
- Zauli G, Milani D, Mirandola P, et al. (2001). "HIV-1 Tat protein down-regulates CREB transcription factor expression in PC12 neuronal cells through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/cyclic nucleoside phosphodiesterase pathway". FASEB J. 15 (2): 483–91. doi:10.1096/fj.00-0354com. PMID 11156964. S2CID 26315564.
- Frame M, Wan KF, Tate R, et al. (2001). "The gamma subunit of the rod photoreceptor cGMP phosphodiesterase can modulate the proteolysis of two cGMP binding cGMP-specific phosphodiesterases (PDE6 and PDE5) by caspase-3". Cell. Signal. 13 (10): 735–41. doi:10.1016/S0898-6568(01)00193-0. PMID 11602184.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Mungall AJ, Palmer SA, Sims SK, et al. (2003). "The DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 6". Nature. 425 (6960): 805–11. Bibcode:2003Natur.425..805M. doi:10.1038/nature02055. PMID 14574404.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Gross-Langenhoff M, Hofbauer K, Weber J, et al. (2006). "cAMP is a ligand for the tandem GAF domain of human phosphodiesterase 10 and cGMP for the tandem GAF domain of phosphodiesterase 11". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (5): 2841–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.M511468200. PMID 16330539.
- Chappie TA, Helal CJ, Hou X (2012). "Current Landscape of Phosphodiesterase 10A (PDE10A) Inhibition". J. Med. Chem. 55 (17): 7299–7331. doi:10.1021/jm3004976. PMID 22834877.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.