Shepherd's beaked whale
Shepherd's beaked whale (Tasmacetus shepherdi), also commonly called Tasman's beaked whale or simply the Tasman whale, is a cetacean of the family Ziphiidae. The whale has not been studied extensively. Only four confirmed at sea sightings have been made and 42 strandings recorded (as of 2006). It was first known to science in 1937, being named by W. R. B. Oliver after George Shepherd, curator of the Wanganui Museum, who collected the type specimen near Ohawe on the south Taranaki coast of New Zealand's North Island, in 1933.[2][3]
| Shepherd's beaked whale | |
|---|---|
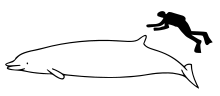 | |
| Size compared to an average human | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Infraorder: | Cetacea |
| Family: | Ziphiidae |
| Genus: | Tasmacetus Oliver, 1937 |
| Species: | T. shepherdi |
| Binomial name | |
| Tasmacetus shepherdi Oliver, 1937 | |
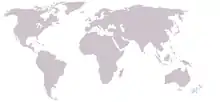 | |
| Shepherd's beaked whale range | |
Description
Adults can reach lengths of 6 metres (20 ft) to 7.1 metres (23 ft) and weigh about 2.32 to 3.48 tons. At birth they may be about 3 metres (9.8 ft) long. They are robust and large-bodied for beaked whales, having a bluff melon and a long, dolphin-like beak.[4] It is the only species of ziphiid with a full set of functional teeth (17 to 27 pairs in both the upper and lower jaws).[3] Adult males also have a pair of tusks at the tip of the lower jaw. They are dark brown dorsally and cream-colored ventrally, with a pale band extending up from the flipper and another pale area extending as a swathe on the posterior flank. The tall, falcate dorsal fin is set about two-thirds the way along the back.[4]
Population and distribution
No population estimates exist for Shepherd's beaked whale. As of 2006, there have been about 42 stranding records of the species from New Zealand (including the Chatham Islands, 24), Argentina (7), Tristan da Cunha (6), Australia (3), and the Juan Fernández Islands (2). There have been five unconfirmed sightings (mostly from New Zealand), as well as a "probable" sighting near Shag Rocks and four confirmed sightings—the first two confirmed sightings occurred in 1985, within a few minutes of each other, off the Tristan da Cunha group (first sighting at 37°18′S 12°32′W); the third in 2002 near Gough Island (40°19′S 9°53′W); and the fourth in 2004 south of Tasmania (48°50′S 150°06′E).[5] In January 2012, a group of up to a dozen of this species were photographed and filmed by the Australian Antarctic Division south of Portland, Victoria.[6] In 2016, at least two groups were observed on Taiaroa sea canyon off Otago Peninsula and this was the first confirmed sighting within New Zealand waters.[7]
Behaviour
Four of the confirmed sightings of this species involved three to six individuals (one group included a calf) in waters from 350 metres (1,150 ft) to 3,600 metres (11,800 ft) deep, while a 2012 sighting involved as many as ten to twelve individuals. The animals surfaced several times, giving a "small, bushy" blow (only visible from the aerial sightings), before arching to dive. Some were observed to come to the surface at a steep angle like many other ziphiids, raising their head and beaks out of the water.[5]
The species is seldom seen because of its deep, offshore distribution in waters where sighting conditions can be difficult (the "Roaring Forties" and "Furious Fifties").[5]
Research done on a stranded individual's stomach has indicated that Shepherd's beaked whales eat both fish and squid, as opposed to most beaked whales which only eat cephalopods.[8]
Conservation
There are no reports of this species being hunted or killed accidentally by humans. Shepherd's beaked whale is covered by the Memorandum of Understanding for the Conservation of Cetaceans and Their Habitats in the Pacific Islands Region (Pacific Cetaceans MOU).[9]
Taxonomy
Its nearest relative, the only other living member of the subfamily Ziphiinae, is Cuvier's beaked whale (Ziphius cavirostris).
See also
References
- Taylor, B.L.; Baird, R.; Barlow, J.; Dawson, S.M.; Ford, J.; Mead, J.G.; Notarbartolo di Sciara, G.; Wade, P. & Pitman, R.L. (2008). "Tasmacetus shepherdi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008: e.T21500A9291409. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T21500A9291409.en. Database entry includes a brief justification of why this species is of data deficient.
- Te Ara Encyclopedia - Beaked whales – George Shepherd
- Reeves, R.; Stewart, B.; Clapham, P. & Powell, J. (2003). Guide to Marine Mammals of the World. New York: A.A. Knopf. pp. 318–321. ISBN 0-375-41141-0.
- Shirihai, H. & Jarrett, B. (2006). Whales, Dolphins and Other Marine Mammals of the World. Princeton Field Guides. pp. 43–45. ISBN 0-691-12757-3. OCLC 73174536.
- Pitman R.L., van Helden A.L., Best P.B., Pym A. (2006). "Shepherd's beaked whale (Tasmacetus shepherdi): information on appearance and biology based on strandings and at-sea observations". Mar. Mammal Sci. 22 (3): 744–755. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2006.00066.x.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Whale trackers make rare sighting
- Gibb J.. 2016. Sighting of beaked whale a first. Otago Daily Times
- Best, P.B.; Smale, M.J.; Glass, J.; Herian, K.; Von Der Heyden, S. (2014). "Identification of stomach contents from a Shepherd's beaked whale Tasmacetus shepherdi stranded on Tristan da Cunha, South Atlantic". Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 94 (6): 1093–1097. doi:10.1017/s0025315412001658. hdl:2263/42919.
- Official webpage of the Memorandum of Understanding for the Conservation of Cetaceans and Their Habitats in the Pacific Islands Region