Soccsksargen
Soccsksargen (officially styled in uppercase[2]) (pronounced [sokˈsardʒɛn]), formerly known as Central Mindanao, is an administrative region of the Philippines, located in south-central Mindanao. It is numerically designated as Region XII. The name is an acronym that stands for the region's four provinces and one highly urbanized city (South Cotabato, Cotabato, Sultan Kudarat, Sarangani and General Santos). The regional center is in Koronadal located in the province of South Cotabato, and the center of commerce and industry is General Santos, which is the most populous city in the region.
Soccsksargen
Region XII Central Mindanao (formerly) | |
|---|---|
     Left to right, top to bottom: Sarangani Bay; shoreline of Lebak, Sultan Kudarat; Asik-Asik Falls in Alamada, North Cotabato; Lake Sebu; and General Santos City the Commerce and Industrial Center of Region 12 | |
 Location in the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 6°30′N 124°51′E | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Island group | Mindanao |
| Regional center | Koronadal |
| Area | |
| • Total | 22,513.30 km2 (8,692.43 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 4,245,838 |
| • Density | 190/km2 (490/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ISO 3166 code | PH-12 |
| Provinces | |
| Cities | |
| Municipalities | 45 |
| Barangays | 1,195 |
| Cong. districts | 6 |
| Languages | |
Geography
The region is bounded on the north by Northern Mindanao, on the east by the Davao Region, and on the southwest by the Celebes Sea. The region also shares a maritime border with Gorontalo and North Sulawesi provinces of Indonesia. The province of Maguindanao is situated between Cotabato City, North Cotabato province, and Sultan Kudarat.
The region has extensive coastlines, valleys and mountain ranges. Known for its river system, the region is the drainage basin of Mindanao, particularly at the Cotabato Basin, a large depression surrounded by mountain ranges on three sides.[3][4] Within the basin runs the Rio Grande de Mindanao, the longest river in Mindanao and the second longest in the Philippines. The river empties into the Illana Bay of the larger Moro Gulf at the west of Cotabato City.
At the south of the basin lie the Tiruray Highlands, a moderately high mountain range blocking the basin from the southern coastline.[3] Southeast of the mountains lie the Sarangani Bay.
Administrative divisions
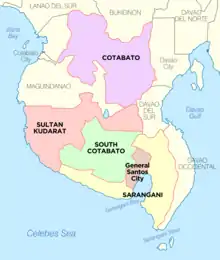
Soccsksargen comprises 4 provinces, 1 highly urbanized city, 3 component cities, 45 municipalities and 1,195 barangays.
| Province or City | Capital | Population (2015) [1] | Area[5][6] | Density | Cities | Muni. | Barangay | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km2 | sq mi | /km2 | /sq mi | ||||||||
| Kidapawan | 30.4% | 1,379,747 | 9,008.90 | 3,478.36 | 150 | 390 | 1 | 17 | 543 | ||
| Sarangani | Alabel | 12.0% | 544,261 | 3,601.25 | 1,390.45 | 150 | 390 | 0 | 7 | 141 | |
| Koronadal | 20.1% | 915,289 | 3,935.95 | 1,519.68 | 230 | 600 | 1 | 10 | 199 | ||
| Isulan | 17.9% | 812,095 | 5,298.34 | 2,045.70 | 150 | 390 | 1 | 11 | 249 | ||
| General Santos | † | — | 13.1% | 594,446 | 492.86 | 190.29 | 1,200 | 3,100 | — | — | 26 |
| Total | 4,545,276 | 22,513.30 | 8,692.43 | 200 | 520 | 5 | 45 | 1,195 | |||
| |||||||||||
Component cities
Highly-urbanized city
- General Santos — a highly urbanized city, it serves as the center of the Metropolitan and Regional Center for trade and industry of Soccsksargen.
- † Regional center
| Rank | City | Area
in sq.km |
Population
as of 2015 |
Tax collection
as of 2012[7] |
IRA
as of 2015 |
Income class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | General Santos | 492.86 | 594,446 | P1.175 billion | Php 1,086.25 million | 1st |
| 2. | † Koronadal | 277.00 | 174,942 | P917 million
(including South Cotabato) |
Php 504.77 million | 3rd |
| 3. | Kidapawan | 358.47 | 140,195 | P554 million
(including Cotabato Province) |
Php 509.68 million | 3rd |
| 4. | Tacurong | 153.40 | 98,316 | P555 million
(including Sultan Kudarat Province) |
Php 350.57 million | 4th |
History
The oldest civilization in the region is located in Maitum, Sarangani, where the Maitum Anthropomorphic Pottery were found. The jars have been declared as National Cultural Treasures, and are subject to the high protections ensured by Philippine and international laws.
Central Mindanao
The region used to be named Central Mindanao. Prior to the creation of the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM) it comprised the following provinces:
With the creation of ARMM, Lanao del Sur and Maguindanao (excluding Cotabato City) were removed from the region, leaving Lanao del Norte, Cotabato and Sultan Kudarat, and Iligan, Marawi and Cotabato City as constituent provinces and cities.[8] Lanao del Norte and Iligan were later transferred to Northern Mindanao, while Marawi became part of the ARMM.
SOCCSKSARGEN
On September 2001, Executive Order No. 36 was signed by President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo transferring South Cotabato, Sarangani, General Santos (also known as the SocSarGen District), from Southern Mindanao to Region XII, and renaming the region, from Central Mindanao, to SOCCSKSARGEN.[2][9]
Koronadal as new regional center
By virtue of Executive Order No. 304 signed by then President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo, Koronadal was named as the regional political and socio-economic center of Soccsksargen on March 30, 2004. Regional departments, bureaus and offices were ordered to move from Cotabato City, the former regional center of the region.
Special Cotabato barangays and Cotabato City exit
Traditionally resisting efforts for inclusion to the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao despite serving as the government center of the ARMM, the January 21, 2019 Bangsamoro Autonomous Region creation plebiscite resulted in the surprise ratification of the Bangsamoro Organic Law in Cotabato City. This means the city may now formally serve as the capital of the region and the offices of the current ARMM will be retained for use by the Bangsamoro Regional Government and now formally no longer constitutes part of the Soccsksargen Region.
In addition to Cotobato City, 63 barangays in Cotabato province opted to join Bangsamoro, thus exiting the region as well.
Demographics
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Data includes Cotabato City, which is now part of Bangsamoro. Source: Philippine Statistics Authority [1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Economy

The region contributes to the national GDP with 2.6% with 5% growth compared to 2016. 18.3% of Mindanao Gross Regional Domestic Product (GRDP).[17]
Musical heritage

The culture of native Maguindanaon and other native groups, both Muslim and non-Muslim, revolves around kulintang music, a specific type of gong music, found in the Soccsksargen.
Government
- Cotabato – Gov. Emmylou "Lala" J. Talino-Mendoza (Liberal)
- South Cotabato – Gov. Reynaldo S. Tamayo Jr. (Partido Federal ng Pilipinas (PFP)
- Sultan Kudarat – Gov. Datu Suharto "Teng" T. Mangudadatu (Liberal)
- Sarangani – Gov. Steve C. Solon (UNA)
- General Santos (HUC) – Mayor Ronnel “Nel” Rivera
References
- Census of Population (2015). "Region XII (Soccsksargen)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved June 20, 2016.
- "Executive Order No. 36; Providing for the Reorganization of the Administrative Regions in Mindanao and for Other Purposes". Official Gazette of the Republic of the Philippines. Malacañang, Manila, Philippines. September 19, 2001. Retrieved March 29, 2016.
SECTION 4. Region XII is hereby reorganized to be known as SOCCSKSARGEN and shall be composed of the following provinces and cities: a. Provinces i. North Cotabato ii. Sarangani iii. South Cotabato iv. Sultan Kudarat b. Cities i. Cotabato City ii. General Santos City iii. Kidapawan City iv. Koronadal City v. Tacurong City
- Wernstedt, Frederick L.; Spencer, Joseph Earl (1978). The Philippine Island World: A Physical, Cultural, and Regional Geography. Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 32-37. ISBN 9780520035133. Retrieved January 27, 2016.
- Hinz, Erhard (1985). Human Helminthiases in the Philippines the Epidemiological and Geomedical Situation. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. pp. 129–131. ISBN 9783642708411. Retrieved January 27, 2016.
- "List of Provinces". PSGC Interactive. Makati City, Philippines: National Statistical Coordination Board. Retrieved March 20, 2013.
- "List of Cities". PSGC Interactive. Makati City, Philippines: National Statistical Coordination Board. Retrieved March 20, 2013.
- Zonio, Aquiles Z. "Central Mindanao PH's top tax revenue generator next to Metro Manila". business.inquirer.net. Retrieved May 18, 2017.
- "2000 Census of Population and Housing; Central Mindanao: Literacy Rate at 87 Percent". Philippine Statistics Authority. December 9, 2002. Retrieved March 29, 2016.
As of May 1, 2000, the total population of Central Mindanao which covers the provinces of Lanao del Norte, North Cotabato, and Sultan Kudarat; and the cities of Iligan, Marawi and Cotabato, was 2,598,210 persons.
- "Southern Mindanao Is Now All Davao Region". RDC XI Bulletin (Oct-Dec 2001, Volume 7). National Statistical Coordination Board. January 29, 2002. Archived from the original on January 2, 2016. Retrieved March 29, 2016.
Southern Mindanao or Region XI is now known as Davao Region and comprises four provinces (Compostela Valley, Davao del Norte, Davao del Sur and Davao Oriental) and five cities (Davao, Digos, Panabo, Tagum and the Island Garden City of Samal. Said provinces and cities are situated along the Davao Gulf area. South Cotabato, Sarangani, General Santos City (SOCSARGEN) and Koronadal City, which were part of the old Region XI) have been transferred to Region XII.
- "Poverty incidence (PI):". Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved December 28, 2020.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/NSCB_LocalPovertyPhilippines_0.pdf; publication date: 29 November 2005; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/2009%20Poverty%20Statistics.pdf; publication date: 8 February 2011; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/Table%202.%20%20Annual%20Per%20Capita%20Poverty%20Threshold%2C%20Poverty%20Incidence%20and%20Magnitude%20of%20Poor%20Population%2C%20by%20Region%20and%20Province%20%20-%202006%2C%202009%2C%202012%20and%202015.xlsx; publication date: 27 August 2016; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/Table%202.%20%20Annual%20Per%20Capita%20Poverty%20Threshold%2C%20Poverty%20Incidence%20and%20Magnitude%20of%20Poor%20Population%2C%20by%20Region%20and%20Province%20%20-%202006%2C%202009%2C%202012%20and%202015.xlsx; publication date: 27 August 2016; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/Table%202.%20%20Annual%20Per%20Capita%20Poverty%20Threshold%2C%20Poverty%20Incidence%20and%20Magnitude%20of%20Poor%20Population%2C%20by%20Region%20and%20Province%20%20-%202006%2C%202009%2C%202012%20and%202015.xlsx; publication date: 27 August 2016; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/Table%202.%20%20Updated%20Annual%20Per%20Capita%20Poverty%20Threshold%2C%20Poverty%20Incidence%20and%20Magnitude%20of%20Poor%20Population%20with%20Measures%20of%20Precision%2C%20by%20Region%20and%20Province_2015%20and%202018.xlsx; publication date: 4 June 2020; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- NEDA launches regional dev't plan in SOCCSKSARGEN.
External links
 Media related to Soccsksargen at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Soccsksargen at Wikimedia Commons Soccsksargen travel guide from Wikivoyage
Soccsksargen travel guide from Wikivoyage