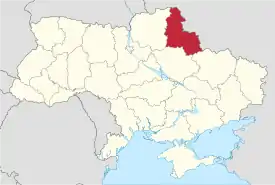
Sumy Oblast
Sumy Oblast (Ukrainian: Сумська область, translit. Sums’ka oblast; also referred to as Sumshchyna – Ukrainian: Сумщина) is an oblast (province) in the northeastern part of Ukraine. The administrative center of the oblast is the city of Sumy. Population: 1,068,247 (2020 est.)[4]
Sumy Oblast
Сумська область Sums’ka oblast | |
|---|---|
| Sumska oblast[1] | |
 Coat of arms | |
| Nickname(s): Сумщина (Sumshchyna) | |
 | |
| Country | |
| Administrative center | Sumy |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Vasyl Khoma[2] |
| • Oblast council | 64[3] seats |
| • Chairperson | Volodymyr Tokar |
| Area | |
| • Total | 23,834 km2 (9,202 sq mi) |
| Area rank | Ranked 16th |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 1,068,247 |
| • Rank | Ranked 19th |
| • Density | 45/km2 (120/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Postal code | |
| Area code | +380-54 |
| ISO 3166 code | UA-59 |
| Raions | 18 |
| Cities (total) | 15 |
| • Regional cities | 7 |
| Urban-type settlements | 20 |
| Villages | 1492 |
| FIPS 10-4 | UP21 |
| Website | sorada.gov.ua |
Other important cities within the oblast include Konotop, Okhtyrka, Romny, and Shostka.
Geography
The Sumy Oblast is situated in the northeastern part of Ukraine. It is situated on a border of two historical regions of Ukraine — Cossack Hetmanate (annexed by Russia in the 18th century as Little Russia, previously known as Severia) and Sloboda Ukraine. Elevation is 110–240m above sea level.[5] The area of the oblast (23,800 km2), comprises about 3.95% of the total area of the country.
The oblast borders Bryansk Oblast (Russia) on the northeast, Belgorod Oblast and Kursk Oblast (Russia) on the east, Poltava Oblast on the southwest, Kharkiv Oblast on the south, and the Chernihiv Oblast on the west.
Seven main rivers flow through the oblast, with the Desna River the largest.[5]
History
The region was created on the ukase of Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union on 10 January 1939 as part of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic. The newly created Sumy Oblast included 12 former raions of Kharkiv Oblast, 17 former raions of Chernihiv Oblast, and 2 former raions of Poltava Oblast.
During the World War II in 1941–43, it was occupied by the Nazi Germany under administration of the German Wehrmacht. After the German forces were driven out the Soviet Union regained control of the region under jurisdiction of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic.
In 1965 one of former Chernihiv Oblast raions (Talalaivka Raion) was returned to Chernihiv Oblast.
Points of interest
The following historic-cultural sited were nominated for the Seven Wonders of Ukraine.
- Monument to mamonth (Kulishivka)
- Kruhliy dvir (Round court)
- Sofroniiv monastery
Administrative divisions
It comprises 18 raions (districts), 15 cities, 7 city municipalities, 20 urban-type settlements, 384 village councils, and 1500 villages.
The following data incorporates the number of each type of administrative divisions of the Sumy Oblast:
- Administrative Center – 1 (Sumy)
- Raions – 18;
- City raions – 2;
- Settlements – 1526, including:
- Villages – 1491;
- Cities/Towns – 35, including:
- Urban-type settlement – 20;
- Cities – 15, including:
- Cities of oblast subordinance – 7;
- Cities of raion subordinance – 8;
- Selsovets – 384.
The local administration of the oblast is controlled by the Sumy Oblast council. The governor of the oblast (chairman of state regional administration) is appointed by the President of Ukraine.
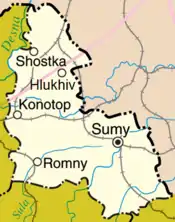
| Name | Ukrainian name | Area (km2) | Population census 2015[6] | Admin.center | Urban Population Only |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sumy | Суми (місто) | 145 | 270,870 | Sumy (city) | 267,944 |
| Hlukhiv | Глухів (місто) | 84 | 34,039 | Hlukhiv (city) | 33,828 |
| Konotop | Конотоп (місто) | 103 | 92,069 | Konotop (city) | 87,916 |
| Lebedyn | Лебедин (місто) | 10 | 26,274 | Lebedyn (city) | 25,637 |
| Okhtyrka | Охтирка (місто) | 30 | 48,850 | Okhtyrka (city) | 48,657 |
| Romny | Ромни (місто) | 65 | 41,224 | Romny (city) | 40,800 |
| Shostka | Шостка (місто) | 36 | 77,232 | Shostka (city) | 77,232 |
| Bilopilskyi Raion | Білопільський район | 1,500 | 50,713 | Bilopillia | 30,284 |
| Burynskyi Raion | Буринський район | 1,100 | 25,129 | Buryn | 8,836 |
| Hlukhivskyi Raion | Глухівський район | 1,700 | 23,223 | Hlukhiv (city) | N/A * |
| Konotopskyi Raion | Конотопський район | 1,700 | 29,145 | Konotop (city) | N/A * |
| Krasnopilskyi Raion | Краснопільський район | 1,350 | 28,670 | Krasnopillia | 10,339 |
| Krolevetskyi Raion | Кролевецький район | 1,300 | 38,496 | Krolevets | 23,339 |
| Lebedynskyi Raion | Лебединський район | 1,700 | 19,864 | Lebedyn (city) | N/A * |
| Lypovodolynskyi Raion | Липоводолинський район | 900 | 18,851 | Lypova Dolyna | 5,191 |
| Nedryhailivskyi Raion | Недригайлівський район | 1,025 | 24,614 | Nedryhailiv | 8,680 |
| Okhtyrskyi Raion | Охтирський район | 1,284 | 26,566 | Okhtyrka (city) | N/A* |
| Putyvlskyi Raion | Путивльський район | 1,100 | 27,913 | Putyvl | 15,888 |
| Romenskyi Raion | Роменський район | 1,900 | 33,297 | Romny (city) | N/A* |
| Seredyno-Buds'kyi Raion | Середино-Будський район | 1,100 | 16,503 | Seredyna-Buda | 9,040 |
| Sums'kyi Raion | Сумський район | 1,800 | 62,452 | Sumy (city) | N/A* |
| Trostianetskyi Raion | Тростянецький район | 1,065 | 35,246 | Trostianets | 20,772 |
| Shostkynskyi Raion | Шосткинський район | 1,211 | 20,684 | Shostka (city) | N/A* |
| Velyko-Pysarivskyi Raion | Великописарівський район | 830 | 19,210 | Velyka Pysarivka | 7,331 |
| Yampilskyi Raion | Ямпільський район | 944 | 23,917 | Yampil | 16,109 |
Note: Asterisks (*) Though the administrative center of the rayon is housed in the city/town that it is named after, cities do not answer to the rayon authorities only towns do; instead they are directly subordinated to the oblast government and therefore are not counted as part of rayon statistics.
Age structure
- 0-14 years: 12.7%
 (male 74,529/female 70,521)
(male 74,529/female 70,521) - 15-64 years: 70.8%
 (male 386,250/female 422,077)
(male 386,250/female 422,077) - 65 years and over: 16.5%
 (male 60,374/female 127,306) (2013 official)
(male 60,374/female 127,306) (2013 official)
Median age
- total: 42.0 years

- male: 38.6 years

- female: 45.4 years
 (2013 official)
(2013 official)
Environment
The Sumy Oblast contains 168 objects and territories of natural reserve. The oblast is rich in picturesque banks of numerous rivers, and sources of mineral waters. Major environmental problems are: soil erosion, pesticide pollution, air and water pollution. The city has a problem of garbage utilization. The only place for pesticide utilization in Ukraine is Shostka, Sumy region.
Economy
Industry
The main industrial activities of the oblast are: chemical mechanical engineering, pumping and energy mechanical engineering, agricultural machine-construction, instrument-making industry and radio electronics, technical equipment production for processing fields of agro-industrial complexes, mining and iron ore production industry, polygraph industry and medicine production, oil and gas processing, chemical production, film and photo material production (See: Svema), and chemical fertilizer production. In general, there are 273 large industry enterprises and 327 small industry enterprises.
Agriculture
In 1999, the gross grain yield was about 446,000 tons, sugar beets – 664,000 tons, sunflower seeds – 27,700 tons, potatoes – 343,600 tons. The region also produced 108,700 tons of meat, 517,800 tons of milk and 295,300,000 eggs. At the beginning of 1999, there were 781 registered farms in the oblast.
Notable people from Sumy Oblast
- Viktor Yushchenko – 3rd President of Ukraine (2005–2010); Khoruzhivka village
- Yevhen Adamtsevych – a Ukrainian bandurist, the author of Zaporizhian March
- Oleksi Berest – one of the soldiers who hoisted the Victory Banner in Berlin and a posthumous Hero of Ukraine.
- Dmitry Chechulin – architect; born Shostka 1901
- Andrei Chikatilo – murdered at least 52 people between 1978 and 1990
- Thomas de Hartmann, composer
- Oleh Husyev – Ukrainian internal footballer
- Ivan Nikitovich Kozhedub – WW2 ace and air marshal of the Soviet Union.
- Natalia Ivanovna Sedova – Wife of Leon Trotsky, born Romny 1882
- Stephen Timoshenko – the father of modern engineering mechanics (1878-1972)
Nomenclature
Most of Ukraine's oblasts are named after their capital cities, officially referred to as "oblast centers" (Ukrainian: обласний центр, translit. oblasnyi tsentr). The name of each oblast is a relative adjective, formed by adding a feminine suffix to the name of respective center city: Sumy is the center of the Sums’ka oblast (Sumy Oblast). Most oblasts are also sometimes referred to in a feminine noun form, following the convention of traditional regional place names, ending with the suffix "-shchyna", as is the case with the Sumy Oblast, Sumshchyna.
See also
References
- Syvak, Nina; Ponomarenko, Valerii; Khodzinska, Olha; Lakeichuk, Iryna (2011). Veklych, Lesia (ed.). "Toponymic Guidelines for Map and Other Editors for International Use" (PDF). United Nations Statistics Division. scientific consultant Iryna Rudenko; reviewed by Nataliia Kizilowa; translated by Olha Khodzinska. Kyiv: DerzhHeoKadastr and Kartographia. p. 20. ISBN 978-966-475-839-7. Retrieved 6 October 2020.
- (in Ukrainian) Zelensky appointed a new head of Sumy region, Ukrayinska Pravda (23 November 2020)
- (in Ukrainian) List of members of the Sumy Regional Council of the Sixth Convocation, Official website Sumy Parliament
- "Чисельність наявного населення України (Actual population of Ukraine)" (PDF) (in Ukrainian). State Statistics Service of Ukraine. Retrieved 30 September 2020.
- "ІNVESTMENT PASSPORT of Sumy oblast- STATE AGENCY FOR INVESTMENT AND NATIONAL PROJECTS OF UKRAINE" (PDF). 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 August 2014. Retrieved 12 August 2014.
- "Population Quantity". UkrStat (in Ukrainian). Retrieved 7 January 2016.
External links
- State Administration of Sumy Oblast – official site (in Ukrainian)
- Information Card of the Region – official site of the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine
- Independent regional Web-portal – news, features, entertainment & tourism info (in Ukrainian)
