Tropical cyclones in 2000
During 2000, tropical cyclones formed in seven different areas called basins.
| Tropical cyclones in 2000 | |
|---|---|
| Year boundaries | |
| First system | Babiola |
| Formed | January 3, 2000 |
| Last system | Ando |
| Dissipated | December 3, 2001 |
| Strongest system | |
| Name | Hudah |
| Lowest pressure | 905 mbar/hPa; 26.72 inHg |
| Longest lasting system | |
| Name | Leon–Eline |
| Duration | 28 days |
| Year statistics | |
| Total systems | None |
| Named systems | None |
| Total fatalities | Unknown |
| Total damage | Unknown |

Global atmospheric and hydrological conditions
A La Niña was present for the year, with overall global conditions conducive to increased activity in the North Atlantic basin,[1] though the La Niña began to weaken towards the latter part of 2000.[2]
Summary
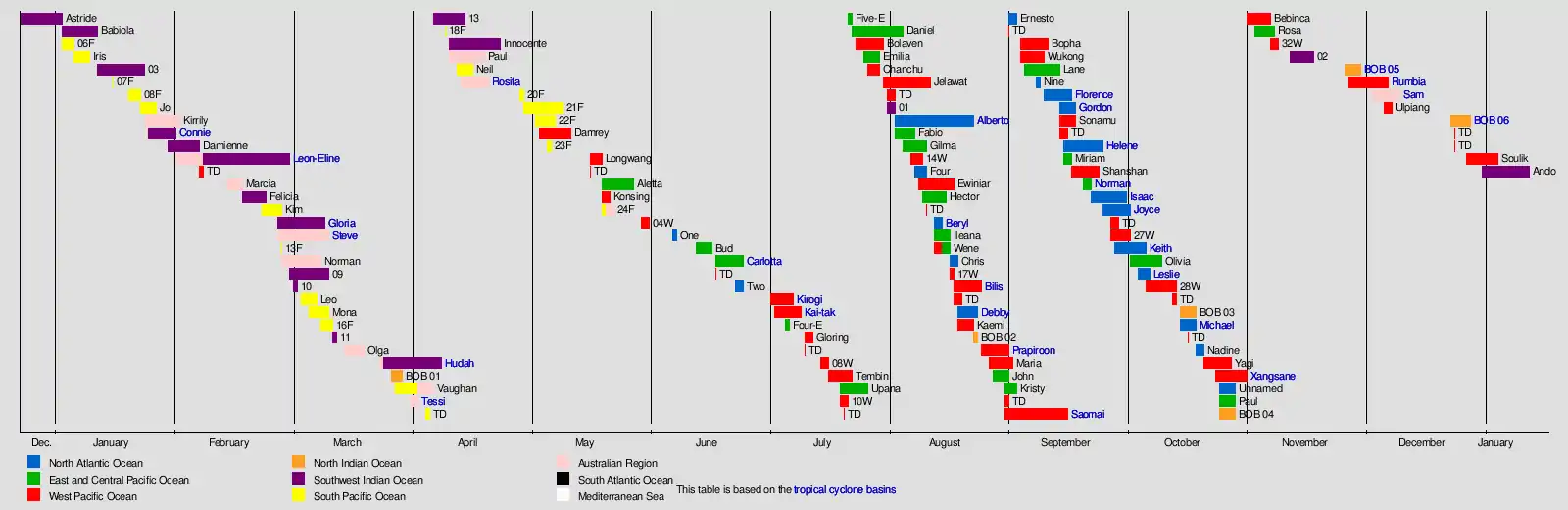
Systems
January
10 storms formed in the month of January, of which 6 were named by their respective agencies. Babiola was the first storm of the season, intensifying into one of the 4 storms that attained hurricane-force winds. Iris was an unusually small tropical cyclone, weakening while passing through Vanuatu. Connie was the strongest storm of the month, becoming an intense tropical cyclone and causing 3 fatalities.
| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Babiola | January 3–12 | 155 (100) | 950 | Île Amsterdam | None | None | |
| 06F | January 3–6 | 45 (30) | 1004 | None | None | None | |
| Iris | January 6–10 | 150 (90) | 964 | Vanuatu, Fiji | None | None | |
| 03 | January 12–26 | Not specified | Unknown | Madagascar | Unknown | Unknown | |
| 07F | January 16–16 | Not specified | Not specified | None | None | None | |
| 08F | January 20–26 | 75 (45) | 996 | None | None | None | |
| Jo | January 23–27 | 120 (75) | 972 | None | None | None | |
| Kirrily | January 24–February 2 | 140 (85) | 975 | None | None | None | |
| Connie | January 25–February 1 | 185 (115) | 930 | Mauritius, Réunion, Southern Africa | Unknown | 3 | [3][4] |
| Damienne | January 30–February 7 | 65 (40) | 994 | None | None | None | |
February
February saw the formation of 10 systems, of which 7 were named. Leon–Eline, the first storm of the month, was the longest-lasting Indian Ocean tropical cyclone, causing significant damages in Madagascar and much of Southern Africa. Leon–Eline was tied for strongest storm of the month with Cyclone Norman. Gloria made landfall on Madagascar weeks after Leon–Eline made landfall, contributing to the early 2000 Madagascar floods. Steve traversed the northern and western coasts of Australia, making 4 landfalls in the process.
| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leon–Eline | February 1–29 | 185 (115) | 930 | Mauritius, Réunion, Rodrigues, Madagascar, Mozambique, South Africa, Swaziland, Malawi, Botswana, Namibia | >$309 million | 114-722 | [nb 1] |
| TD | February 7–8 | Not specified | 1004 | Mariana Islands | None | None | |
| Marcia | February 14–18 | 65 (40) | 995 | None | None | None | |
| Felicia | February 18–24 | 110 (70) | 975 | None | None | None | |
| Kim | February 23–29 | 165 (105) | 935 | French Polynesia | Minimal | None | |
| Gloria | February 27–March 10 | 95 (60) | 985 | St. Brandon, Tromelin Island, Madagascar, Mozambique | Unknown | 66 | [nb 2] |
| Steve | February 27–March 11 | 110 (70) | 975 | North Queensland, Northern Territory, Western Australia | $100 million | None | [5] |
| 13F | February 28–29 | 65 (40) | 994 | None | None | None | |
| Norman | February 29–March 9 | 185 (115) | 930 | Western Australia | None | None | |
| 09 | February 29–March 11 | Not specified | Unknown | None | None | None | |
March
| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | March 1–3 | Not specified | Unknown | None | None | None | |
| Leo | March 4–8 | 95 (60) | 985 | French Polynesia | Minimal | None | |
| Mona | March 6–11 | 140 (85) | 960 | French Polynesia | Minimal | None | |
| 16F | March 9–12 | Not specified | Not specified | None | None | None | |
| 11 | March 10 | Not specified | Unknown | None | None | None | |
| Olga | March 15–20 | 95 (60) | 985 | None | None | None | |
| Hudah | March 24–April 9 | 220 (140) | 905 | St. Brandon, Tromelin Island, Rodrigues, Madagascar, Mozambique | Unknown | 114 | [6][7] |
| BOB 01 | March 27–30 | 85 (50) | 998 | Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India | Minimal | None | |
| Vaughan | March 28–April 7 | 110 (70) | 985 | Queensland | None | None | |
April
| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tessi | April 1–3 | 130 (80) | 980 | Queensland | $50 million | None | |
| TD | April 5–6 | Not specified | Not specified | None | None | None | |
| 13 | April 7–15 | 95 (60) | 992 | Mozambique | None | None | |
| 18F | April 10 | Not specified | Not specified | None | None | None | |
| Innocente | April 12–24 | 70 (45) | 993 | Mauritius | None | None | |
| Paul | April 11–20 | 220 (140) | 915 | Cocos Islands | None | None | |
| Neil | April 12–17 | 75 (45) | 992 | Fiji | None | None | |
| Rosita | April 14–21 | 205 (125) | 930 | Western Australia | None | None | |
| 20F | April 29–30 | 75 (45) | 996 | Queensland | Minimal | None | |
| 21F | April 30–May 1 | 75 (45) | 1000 | Queensland | Minimal | None | |
May
| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22F | May 3–8 | 75 (45) | 1001 | None | None | None | |
| Damrey (Asiang) | May 4–12 | 165 (105) | 930 | Caroline Islands | None | None | |
| 23F | May 6 | Not specified | Not specified | None | None | None | |
| Longwang (Biring) | May 17–20 | 85 (50) | 990 | Philippines, Ryukyu Islands | None | None | |
| TD | May 17–18 | Not specified | 1000 | None | None | None | |
| Aletta | May 22–28 | 165 (105) | 970 | Southwestern Mexico | None | None | |
| 03W (Konsing) | May 20–22 | 55 (35) | 1002 | Philippines, Taiwan | None | None | |
| 24F | May 20–23 | 75 (45) | 1002 | None | None | None | |
| 04W | May 30–June 1 | 55 (35) | 1002 | Vietnam | None | None | |
June
June tied with November for least active month of 2000. 5 storms developed, of which 2 developed gale-force winds and were named by their respective agencies. Tropical Storm Bud was the first named storm, affecting Western Mexico. Hurricane Carlotta was the strongest storm of the month, becoming a high-end Category 4 hurricane. Carlotta caused the deaths of 18 people after sinking the M/V Linkuva.
| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| One | June 7–8 | 45 (30) | 1008 | Mexico, Texas | None | None | |
| Bud | June 13–17 | 85 (50) | 994 | Revillagigedo Islands, Baja California Peninsula | Minimal | None | |
| Carlotta | June 18–25 | 250 (155) | 932 | Mexico | Minimal | 18 | [8] |
| TD | June 18 | 55 (35) | 1002 | South China | None | None | |
| Two | June 23–25 | 55 (35) | 1008 | None | None | None | |
July
| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kirogi (Ditang) | July 2–8 | 155 (100) | 940 | Japan | $140 million | 5 | [9][10] |
| Kai-tak (Edeng) | July 3–10 | 140 (85) | 960 | Philippines, Taiwan, East China, Korea | Unknown | 188 | [11] |
| Four-E | July 6–7 | 45 (30) | 1007 | None | None | None | |
| 07W (Gloring) | July 11–13 | 55 (35) | 1000 | Philippines | None | None | |
| TD | July 11 | Not specified | 1000 | South China | None | None | |
| 08W | July 15–17 | 45 (30) | 996 | South China | None | None | |
| Tembin | July 17–23 | 75 (45) | 992 | None | None | None | |
| Upana | July 20–24 | 75 (45) | 1006 | None | None | None | |
| 10W | July 20–22 | 45 (30) | 1000 | Philippines | None | None | |
| TD | July 21 | Not specified | 1004 | South China, Vietnam | None | None | |
| Five-E | July 22–23 | 55 (35) | 1005 | None | None | None | |
| Daniel | July 23–August 5 | 205 (125) | 954 | Hawaiian Islands, Aleutian Islands | None | None | |
| Bolaven (Huaning) | July 24–31 | 95 (60) | 980 | Philippines, Ryukyu Islands, Japan, Korea, Russian Far East | $21.6 million | None | |
| Emilia | July 26–30 | 100 (65) | 994 | Clarion Island, Revillagigedo Islands | None | None | |
| Chanchu | July 27–30 | 65 (40) | 996 | None | None | None | |
| Jelawat | July 31–August 12 | 155 (100) | 940 | Ryukyu Islands, East China | None | None | |
August
| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TD | August 1–3 | Not specified | 1004 | Ryukyu Islands, Japan, Korea | None | None | |
| 01 | August 1–3 | Not specified | Unknown | None | None | None | |
| Alberto | August 3–23 | 205 (125) | 950 | West Africa, Bermuda, Iceland, Greenland, Jan Mayen | None | None | |
| Fabio | August 3–8 | 85 (50) | 1000 | None | None | None | |
| Gilma | August 5–11 | 130 (80) | 984 | None | None | None | |
| 14W | August 7–10 | 55 (35) | 1008 | None | None | None | |
| Four | August 8–11 | 55 (35) | 1009 | None | None | None | |
| Ewiniar | August 9–18 | 120 (75) | 975 | Mariana Islands | None | None | |
| Hector | August 10–16 | 130 (80) | 983 | None | None | None | |
| Ileana | August 13–17 | 110 (70) | 991 | Baja California Peninsula, Mexico | None | None | |
September
| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
October
| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Olivia | October 2–10 | 100 (65) | 994 | Southwestern United States | None | None | |
| Leslie | October 4–7 | 75 (45) | 1006 | Cuba, Florida, Bermuda, Newfoundland | $950 million | 3 | [12][13] |
| 28W | October 6–13 | 55 (35) | 998 | Vietnam, South China | None | None | |
| TD | October 13–14 | Not specified | 1008 | None | None | None | |
| BOB 03 | October 15–19 | 65 (40) | 996 | Western India, Gujarat | Moderate | None | |
| Michael | October 15–19 | 155 (100) | 965 | Bermuda, Maine, Atlantic Canada | Unknown | None | |
| TD | October 17–18 | Not specified | 1008 | None | None | None | |
| Nadine | October 19–22 | 95 (60) | 999 | None | None | None | |
| Yagi (Paring) | October 21–28 | 130 (80) | 965 | Ryukyu Islands, Taiwan | None | None | |
| Xangsane (Reming) | October 24–November 1 | 140 (85) | 960 | Caroline Islands, Philippines, Taiwan, Japan | Unknown | 182 | [11][14] |
| Unnamed | October 25–29 | 100 (65) | 976 | New England, Atlantic Canada | Unknown | None | |
| Paul | October 25–29 | 75 (45) | 1003 | Hawaii | $70 million | None | |
| BOB 04 | October 25–29 | 65 (40) | 998 | Bangladesh, Odisha | $13 million | 77 | [15][16] |
November
The month of November saw 5 systems form, tying with June for the least active month. 3 systems attained gale-force winds, though only 2 were given names by their respective agencies. Rosa was the first storm of the month, forming on November 3 and peaking as a tropical storm. 2 more systems formed before BOB 05, also known as the 2000 South India cyclone, formed in the Bay of Bengal. The cyclone peaked as an extremely severe cyclonic storm, making it the strongest storm of the month before weakening at landfall. The last storm of the month, Rumbia, affected the Philippines and Vietnam, causing 48 fatalities.
| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rosa | November 3–8 | 100 (65) | 993 | Southwestern Mexico, Central America | $21 thousand | None | |
| 32W | November 7–9 | 55 (35) | 1004 | Ryukyu Islands | None | None | |
| 02 | November 12–18 | Unknown | Unknown | None | None | None | |
| BOB 05 | November 26–30 | 190 (115) | 958 | South India, Somalia | $15 million | 12 | [17] |
| Rumbia (Toyang) | November 27–December 7 | 75 (45) | 990 | Philippines, Vietnam | $1 million | 48 | [18] |
December
The month of December saw 7 systems form, with 4 of the storms being named by their respective agencies. The month began with Cyclone Sam, which intensified into a Category 5 severe tropical cyclone on the Australian scale, making landfall on Western Australia at peak intensity. Ulpiang was a short-lived storm that caused flooding and deaths in the Philippines. BOB 06, also known as the 2000 Sri Lanka cyclone was the strongest storm to hit Sri Lanka since 1978, being attributed to 9 deaths. 2 tropical depressions formed in the West Pacific before Soulik formed and rapidly intensified into a moderately strong typhoon. The year finished with Cyclone Ando, peaking offshore as an intense tropical cyclone.
| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sam | December 3–10 | 205 (125) | 935 | Western Australia | Minor | None | |
| Ulpiang | December 6–8 | 55 (35) | 1004 | Philippines | None | 3 | [19] |
| BOB 06 | December 23–28 | 165 (105) | 970 | Sri Lanka, India | Minimal | 9 | [20] |
| TD | December 24 | Not specified | 1008 | None | None | None | |
| TD | December 24 | Not specified | 1006 | None | None | None | |
| Soulik (Welpring) | December 29–January 4 | 150 (90) | 955 | None | None | None | |
| Ando | December 31–January 9 | 195 (120) | 925 | Seychelles, Agaléga, Tromelin, Mauritius, Réunion | None | 2 | [21][22] |
Global effects
| Season name | Areas affected | Systems formed | Named storms | Damage (USD) | Deaths |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 Atlantic hurricane season | |||||
| 2000 Pacific hurricane season | |||||
| 2000 Pacific typhoon season | |||||
| 2000 North Indian Ocean cyclone season | |||||
| 1999–2000 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season | |||||
| 2000–01 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season | |||||
| 1999–2000 Australian region cyclone season | |||||
| 2000–01 Australian region cyclone season | |||||
| 1999–2000 South Pacific cyclone season | |||||
| 2000–01 South Pacific cyclone season | |||||
| Worldwide | (See above) |
Notes
- In Madagascar, Eline killed at least 64 people, although subsequent Tropical Storm Gloria affected the same region just two weeks later. The death toll for both storms is 205, with 66 confirmed fatalities related to Gloria, resulting in 139 deaths potentially related to Eline. There were only 17 confirmed fatalities in Mozambique, although the death toll from the cyclone and preceding floods was around 700, with 150 deaths before Eline's arrival. Therefore, there are up to 550 deaths related to the storm in that country. Elsewhere, Eline killed 12 people in Zimbabwe and 21 in South Africa.
- Gloria killed at least 66 people, although the exact toll was initially unknown due to disrupted communications.
References
- NOAA: 2000 Atlantic hurricane outlook. Climate Prediction Center (Report). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. May 10, 2000. Retrieved January 26, 2008.
- "Climate Prediction Center - Expert Assessments: Atlantic Hurricane Outlook". www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov. Retrieved 2021-02-07.
- "Island Cyclone Kills Two". AP News Archive. Associated Press. January 30, 2000.
- "La Réunion échappe au cyclone Connie". Liberation Societe (in French). January 31, 2000.
- Bureau of Meteorology. "BoM-Impact from Steve". Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 16 June 2006.
- Centre des Cyclones Tropicaux de La Réunion. Saison Cyclonique - Sud-Ouest de l'océan Indien (PDF). La Saison Cyclonique A Madagascar (Report) (in French and English). La Réunion: Météo-France. Retrieved May 25, 2013.
- "Cyclone Hudah bringing heavy rain to flood-hit Mozambique". ReliefWeb. Agence France-Presse. April 7, 2000. Retrieved September 29, 2014.
- Lawrence; et al. (2007). "2000 Eastern Pacific Hurricane Summary". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2007-07-15.
- Associated Press (July 9, 2000). "Typhoon Kirogi ravages Japanese cities, killing 3". The Milwaukee Journal Sentinel. Retrieved August 9, 2009.
- Marcos Calo Medina (July 9, 2000). "Typhoon Hits Taiwan". Associated Press. Archived from the original on October 26, 2012. Retrieved August 9, 2009.
- 2000 Annual Tropical Cyclone Report (PDF) (Report). p. 181. Retrieved February 7, 2021.
- James L. Franklin; Daniel P. Brown (2000-11-05). Tropical Storm Leslie Tropical Cyclone Report (Subtropical Depression One) (PDF) (Report). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2010-11-13.
- Susan Candiotti (2000-10-04). "Miami bails out after floods take city by storm". CNN. Archived from the original on 2007-02-04. Retrieved 2010-11-24.
- "Fate of SQ006". Channel News Asia. Archived from the original on 5 November 2008. Retrieved 31 October 2008.
- "25 dead, hundreds missing in Bangladesh cyclone". ReliefWeb. Deutsche Presse Agentur. 2000-10-29. Retrieved 2015-05-22.
- "Death toll rises in Bangladesh storms". BBC. 2000-10-29. Retrieved 2015-05-22.
- Report on Cyclonic Disturbances Over North Indian Ocean During 2000 (PDF) (Report). India Meteorological Department. February 2001. Retrieved 2015-05-22.
- Dartmouth Flood Observatory (February 14, 2001). "2000 Global Register of Extreme Flood Events". Dartmouth College. Retrieved 20 January 2014.
- "Monthly Global Tropical Cyclone Summary December 2000". australiasevereweather.com. Retrieved 2021-02-03.
- Vijitha Silva (2001). "Cyclone wreaks havoc across northern Sri Lanka". World Socialist Web Site. Archived from the original on 15 December 2006. Retrieved January 4, 2007.
- "Monthly Global Tropical Cyclone Summary January 2001". Retrieved 2014-07-07.
- Cyclone Season 2000–2001. RSMC La Reunion (Report). Meteo-France. Retrieved 2014-07-07.
External links
| Tropical cyclone year articles (2000–2009) |
|---|
| 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009 |
Regional Specialized Meteorological Centers
- US National Hurricane Center – North Atlantic, Eastern Pacific
- Central Pacific Hurricane Center – Central Pacific
- Japan Meteorological Agency – NW Pacific
- India Meteorological Department – Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea
- Météo-France – La Reunion – South Indian Ocean from 30°E to 90°E
- Fiji Meteorological Service – South Pacific west of 160°E, north of 25° S
Tropical Cyclone Warning Centers
- Meteorology, Climatology, and Geophysical Agency of Indonesia – South Indian Ocean from 90°E to 141°E, generally north of 10°S
- Australian Bureau of Meteorology (TCWC's Perth, Darwin & Brisbane) – South Indian Ocean & South Pacific Ocean from 90°E to 160°E, generally south of 10°S
- Papua New Guinea National Weather Service – South Pacific Ocean from 141°E to 160°E, generally north of 10°S
- Meteorological Service of New Zealand Limited – South Pacific west of 160°E, south of 25°S
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Weather Service.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Weather Service.