Tuttlingen
Tuttlingen (Alemannic: Duttlinga) is a town in Baden-Württemberg, capital of the district Tuttlingen. Nendingen, Möhringen and Eßlingen are three former municipalities that belong to Tuttlingen. The district (Kreis) includes several surrounding towns including Trossingen, Spaichingen, and Mühlheim an der Donau. Tuttlingen is located in Swabia east of the Black Forest region in the Swabian Jura.
Tuttlingen | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Tuttlingen within Tuttlingen district 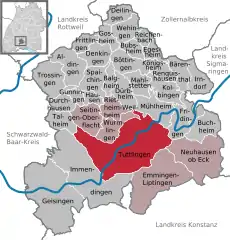 | |
 Tuttlingen  Tuttlingen | |
| Coordinates: 47°59′06″N 08°49′24″E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Baden-Württemberg |
| Admin. region | Freiburg |
| District | Tuttlingen |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Michael Beck (CDU) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 90.48 km2 (34.93 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 645 m (2,116 ft) |
| Population (2019-12-31)[1] | |
| • Total | 36,102 |
| • Density | 400/km2 (1,000/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 78501–78532 |
| Dialling codes | 07461 |
| Vehicle registration | TUT |
| Website | www.tuttlingen.de |
Geography
The town lies in the valley of the Upper Danube on both sides of the stream, the source of which is located 30 km nearby in Donaueschingen. The early river flowed around the Honberg mountain, where ruins of a fortress built in the Middle Ages remain.
History
The name indicates Tuttlingen likely was a Celtic settlement long before the Romans erected a border castellum at the limes. Spurious archeological findings in 1874 support the theory, but due to its probable location under the foundations of houses in the city center expansive excavations will not be done. During the Middle Ages Tuttlingen was first mentioned in 797, and belonged to the monastery of Reichenau shortly thereafter. The town received its town privileges before 1338 and belonged to Württemberg since 1376/77. Since that time the town was ruled by the "Twelve", consisting of the Mayor, the Sheriff (Schultheiss), and 10 other members of the judiciary/court. Eberhard im Bart upgraded the citadel of Honberg around 1460 to a first-class border fortress. During the Thirty Year War Tuttlingen as the southern outpost of Württemberg, was constantly embattled. A key event was the "Battle of Tuttlingen" on 24 November 1643 in which the entire French army was defeated by the United Imperial-Bavarian troupes under Melchior Graf von Hatzfeldt, Franz von Mercy and Johann von Werth.
Tuttlingen was an administrative seat ("Obervogteiamt") early on, and in 1755 it became an administrative seat of Württemberg, which has morphed over time.
On November 1, 1803, a fire destroyed all of Tuttlingen within the city walls in a matter of hours, and only a small section of the original town remained. Starting in 1804 the city was rebuilt by master architect Carl Leonard von Uber according to classicist plans with right-angle streets and rectangular housing settlements.
Since 1822 the city has elected its council and mayor. In 1869 Tuttlingen was connected to the railway system, which was important for its industrial development. The original station was replaced in 1933.

During the NS regime Tuttlingen had prison camps and forced labor camps, whose inmates worked for the local industry. A total of 3,645 victims of the so-called „Euthanasia-campaign T4" were cremated in the cemetery of the city, including murdered inmates of regional concentration camps. In 1947 an obelisk was erected and plaques installed in their memory. In February and March 1945 Tuttlingen experienced 5 air raids, 4 of which were aimed at the station. On April 21, 1945 Tuttlingen was occupied by parts of the French first army and became part of the "French Zone of Occupation". Railroad bridges were detonated and until 1952 the prison camp „Mühlau“ was the "Dépôt de transit N°2", a Transit and Exit encampment of the French Zone of Occupation for hundreds of thousands of German prisoners of war. In its location are the Immanuel-Kant-High School and the Otto-Hahn-High School today.
In 1945 Tuttlingen became part of Württemberg-Hohenzollern, and in 1952 part of the newly founded state Baden-Württemberg and the subsection of Südwürttemberg-Hohenzollern within it.
As its population had already grown beyond 20,000 in 1949, Tuttlingen was declared to be "Große Kreisstadt" as soon as the Baden-Württemberg council regulations were implemented on April 1, 1956. With the district reform of 1973 the district of Tuttlingen received its present-day extension, which increased its population by a third and its area 3 times. At the same time, Tuttlingen came under the administrative government of Freiburg.
Number of inhabitants
|
|
Sources: Census results or Statistical office
Mayors and Lord mayors of Tuttlingen
- 1829–1866: Jakob Schnekenburger, Stadtschultheiß
- 1866–1876: Julius Schad, Stadtschultheiß
- 1877–1903: Christian Storz, Stadtschultheiß
- 1903–1908: Julius Keck, Lord mayor
- 1908–1938: Paul Scherer, Lord mayor
- 1938–1945: Max Haug, mayor
- 1945: Gustav Zimmermann, temporary mayor
- 1945–1946: Franz Heinkele, temporary mayor
- 1946: Fritz Fleck (SPD), temporary mayor
- 1946–1951: Otto Fink (CDU), mayor
- 1951–1980: Walter Balz (SPD), till 1952 mayor, then Lord mayor
- 1980–2004: Heinz-Jürgen Koloczek (CDU), Lord mayor
- since 2004: Michael Beck (CDU), Lord mayor
Economy

Tuttlingen has 1,900 businesses ranging from one-man to multinational companies.
It is the home of more than 600 surgical equipment companies. Fifty percent of the world's surgical equipment is manufactured in Tuttlingen. Tuttlingen's Medical technology firms are closely linked with the medical technology cluster in the Pakistani district Sialkot.
Up until recently Tuttlingen was also a center for shoe manufacturing, as historically many tanneries were located at the Danube.
List of important companies:
- Aesculap(or try this one instead https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aesculap-Werke ), the oldest and most renowned company of surgical equipment manufacturing in Tuttlingen, belongs to B. Braun Melsungen since 1998, largest employer, company buildings dominate the cityscape near the railroad station. The roundabout where federal Highway 14 and 311 cross is named "Aesculap-Platz".
- Chiron-Werke
- Hettich Instruments (Centrifuges)
- Instrumed International Inc.(Medical technology)
- Karl Storz GmbH (ENT equipment, endoscopy) [2]
- KLS Martin, founded as "Gebrueder Martin" in 1923 (Vertrieb Medizintechnik) [3]
- Berchtold GmbH & Co. KG (Medical technology) (a part of Stryker Corporation since 2014)
- Schwäbische Hüttenwerke, Ludwigstal (Brake pads)
- Rieker (Shoe manufacture)
- City Works Tuttlingen (Energy- and Water supply)
- Smith & Nephew (Medical technology), Produktionsstätte in Tuttlingen
- Volksbank Donau-Neckar (Bank)
- BINDER GmbH (Environmental simulation chambers, incubators)
Cultural Events

Each summer the festival "Honberg Sommer" attracts visitors to concerts with international bands, cabaret artists, and beer gardens. Tuttlingen's pedestrian precinct offers a market twice a week, a fountain, shops, and art displays.
The German poet Goethe wrote that the town and surrounding area has a strange and beautiful landscape, hilly with fields and patches of forest. He is said to have left his watch in the town.
International relations
Tuttlingen is twinned with:[4]
 Battaglia Terme, Italy
Battaglia Terme, Italy Bex, Switzerland
Bex, Switzerland Bischofszell, Switzerland
Bischofszell, Switzerland Draguignan, France
Draguignan, France Waidhofen an der Ybbs, Austria
Waidhofen an der Ybbs, Austria
Sons and daughters of the town
- Hermann Dold (1892–1953), entrepreneur and politician (CDU), parliamentary deputy
- Johann Georg Gödelmann (1559–1611), legal professor and diplomat, also interested in witches
- Edmund Heckler (1906-1960), engineer & weapons manufacturer,
- Jürgen Lässig (born 1943), racing driver
- Wolfgang Volz (born 1948), photographer, mainly known for his collaboration with the artist couple Christo and Jeanne-Claude
- Laura Weihenmaier (born 1991), volleyball player
Notes
- "Bevölkerung nach Nationalität und Geschlecht am 31. Dezember 2019". Statistisches Landesamt Baden-Württemberg (in German). September 2020.
- Endoskope, KARL STORZ. "Welcome to the world of endoscopy - KARL STORZ Endoskope". www.karlstorz.com. Retrieved 23 April 2018.
- "History". KLS Martin. Retrieved 23 April 2018.
- "Städtepartnerschaften". tuttlingen.de (in German). Tuttlingen. Retrieved 2019-11-23.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tuttlingen. |
 Works related to Tuttlingen at Wikisource
Works related to Tuttlingen at Wikisource- Official website
 (in German)
(in German) - Notes from Tuttlingen – a description of the surgical instruments industry in the town
