Xiaogan
Xiaogan (Chinese: 孝感; pinyin: Xiàogǎn) is a prefecture-level city in east-central Hubei province, People's Republic of China, some 60 kilometres (37 mi) northwest of the provincial capital of Wuhan. According to the 2010 census, its population totaled 4,814,542, of whom 908,266 lived in the built-up (or metro) area of Xiaonan District.
Xiaogan
孝感市 Siaokan | |
|---|---|
 view west towards city's south central area | |
.png.webp) Location of Xiaogan City in Hubei and the PRC | |
 Xiaogan Location of the city centre in Hubei | |
| Coordinates (Xiaogan municipal government): 30°55′05″N 113°57′25″E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Hubei |
| Municipal seat | Xiaonnan District |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 8,922.72 km2 (3,445.08 sq mi) |
| • Urban (2017)[1] | 115.25 km2 (44.50 sq mi) |
| • Districts[1] | 1,018.3 km2 (393.2 sq mi) |
| Population (2010 census[2]) | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 4,814,542 |
| • Density | 540/km2 (1,400/sq mi) |
| • Urban (2017)[1] | 549,000 |
| • Urban density | 4,800/km2 (12,000/sq mi) |
| • Districts[1] | 1,001,000 |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 432100 |
| Area code(s) | 712 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-HB-09 |
| Website | www |
The city name Xiaogan, meaning Filial Piety Moves [the Heaven] (Chinese: 孝行感天), is from the story of Dong Yong (Chinese: 董永), who sold himself for his father's funeral, in The Twenty-four Filial Exemplars.[3]
The Sheshui River originates in Xiaogan's Dawu County. On the third day of the third month of the lunar calendar, many in Wuhan eat 'di cai zhu ji dan' (地菜煮鸡蛋) which is supposed to prevent illness in the coming year. This practice is related to a story involving Shennong in Xiaogan.[4]
Administrative divisions
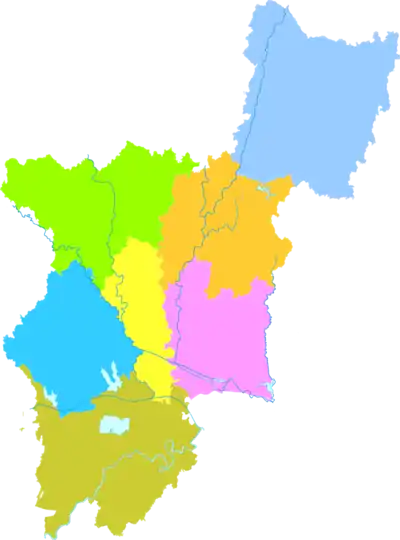
Since 2000, Xiaogan has been divided into 1 district, 3 cities and 3 counties:[5][6][7]
- Xiaonan District (孝南区)
- Yingcheng City (应城市)
- Anlu City (安陆市)
- Hanchuan City (汉川市)
- Xiaochang County (孝昌县)
- Dawu County (大悟县)
- Yunmeng County (云梦县)
| Map |
|---|
Geography
| Climate data for Xiaogan (1981–2010 normals) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 7.8 (46.0) |
10.4 (50.7) |
14.9 (58.8) |
21.7 (71.1) |
26.7 (80.1) |
29.7 (85.5) |
32.2 (90.0) |
32.0 (89.6) |
28.2 (82.8) |
22.7 (72.9) |
16.6 (61.9) |
10.4 (50.7) |
21.1 (70.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 3.4 (38.1) |
6.0 (42.8) |
10.3 (50.5) |
16.8 (62.2) |
22.0 (71.6) |
25.5 (77.9) |
28.3 (82.9) |
27.6 (81.7) |
23.2 (73.8) |
17.3 (63.1) |
11.1 (52.0) |
5.5 (41.9) |
16.4 (61.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 0.2 (32.4) |
2.5 (36.5) |
6.5 (43.7) |
12.7 (54.9) |
18.1 (64.6) |
22.2 (72.0) |
25.2 (77.4) |
24.3 (75.7) |
19.5 (67.1) |
13.4 (56.1) |
7.2 (45.0) |
1.8 (35.2) |
12.8 (55.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 38.6 (1.52) |
52.5 (2.07) |
78.1 (3.07) |
115.6 (4.55) |
154.6 (6.09) |
181.4 (7.14) |
194.5 (7.66) |
120.1 (4.73) |
65.9 (2.59) |
74.8 (2.94) |
52.8 (2.08) |
23.4 (0.92) |
1,152.3 (45.36) |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 77 | 77 | 78 | 78 | 78 | 82 | 83 | 82 | 79 | 79 | 77 | 75 | 79 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration[8] | |||||||||||||
Notable people from Xiaogan
References
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, ed. (2019). China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook 2017. Beijing: China Statistics Press. p. 66. Retrieved 11 January 2020.
- http://www.citypopulation.de/php/china-hubei-admin.php
- 孝行感天-孝感的由来. Huaxia.com (in Chinese). 17 September 2009. Retrieved 27 March 2018.
孝感既为董永故里,其遗址很多,集中分布于两地:今孝感市区和董永曾长期生活过的今孝南区毛陈镇。
- 三月三吃地菜煮鸡蛋能治头痛?专家:可防流感. 长江日报. 2018-04-19. Retrieved 2020-05-01 – via QQ News.
- "Historical Development". Xiaogan People's Government. 27 August 2014. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
In 2005, Xiaonan District under the administration of Xiaogan contained three counties, Dawu, Yunmeng and Xiaochang, and three cities, Hanchuan, Yingcheng and Anlu.
- 2016年统计用区划代码和城乡划分代码:孝感市 (in Chinese). National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. 2016. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
统计用区划代码 名称 420901000000 市辖区 420902000000 孝南区 420921000000 孝昌县 420922000000 大悟县 420923000000 云梦县 420981000000 应城市 420982000000 安陆市 420984000000 汉川市
- 孝感市历史沿革 (in Chinese). XZQH.org. 7 December 2011. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
2000年第五次全国人口普查,孝感市总人口4992537人。其中:孝南区883123人,孝昌县612166人,大悟县605786人,云梦县571591人,应城市650485人,安陆市611990人,汉川市1057396人。
- 中国气象数据网 - WeatherBk Data (in Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 2020-04-15.