2008 Tyrolean state election
The 2008 Tyrolean state election was held on 8 June 2008 to elect the members of the Landtag of Tyrol.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
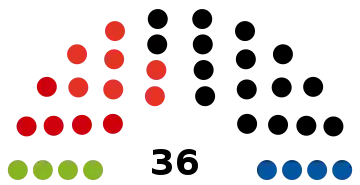
All 36 seats in the Landtag of Tyrol 19 seats needed for a majority | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 342,713 (65.8%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
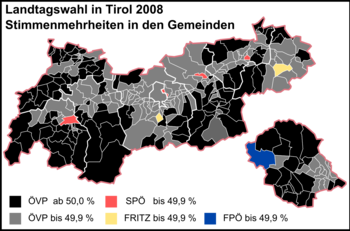 Results by municipality. The lighter shade indicates a plurality; the darker shade indicates a majority. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The election saw major losses of almost ten percentage points for both the governing Austrian People's Party (ÖVP) and the opposition Social Democratic Party of Austria (SPÖ), with each suffering its worst ever result up to this point. The ÖVP lost its absolute majority for only the second time in history, while the SPÖ fell to third place for the first time. The major winner of the election was the Fritz Dinkhauser List, which debuted at a strong 18.4%, immediately becoming the second largest party. The Freedom Party of Austria (FPÖ) made gains, while The Greens fell by almost five points compared to their best-ever result from 2003.[1]
Despite its losses, the ÖVP under Governor Herwig van Staa remained by far the largest party. After leading post-election coalition negotiations, in which the ÖVP secured a coalition with the SPÖ, van Staa resigned and was replaced by Günther Platter on 23 June.[2]
Background
In the 2003 election, the ÖVP under new Governor Herwig van Staa regained its absolute majority, which it had lost in 1999. The SPÖ made gains, while the FPÖ lost more than half its voteshare. The Greens were the biggest winner, doubling their result to almost 16% and placing third. Despite its majority, the ÖVP chose to form a coalition with the SPÖ.
In 2008, Fritz Dinkhauser founded his own party in Tyrol, named the Fritz Dinkhauser List. Dinkhauser was chairman of the ÖAAB, the ÖVP-affiliated trade union association, and known for his criticism of his own party, including the ÖVP government of Herwig van Staa. With his new party, he promoted affordable housing, support for families, and improved education.
Electoral system
The 36 seats of the Landtag of Tyrol are elected via open list proportional representation in a two-step process. The seats are distributed between nine multi-member constituencies, corresponding to the districts of Tyrol. For parties to receive any representation in the Landtag, they must either win at least one seat in a constituency directly, or clear a 5 percent state-wide electoral threshold. Seats are distributed in constituencies according to the Hare quota, with any remaining seats allocated using the D'Hondt method at the state level, to ensure overall proportionality between a party's vote share and its share of seats.
Contesting parties
The table below lists parties represented in the previous Landtag.
| Name | Ideology | Leader | 2003 result | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes (%) | Seats | |||||
| ÖVP | Austrian People's Party Österreichische Volkspartei |
Christian democracy | Herwig van Staa | 49.9% | 20 / 36 | |
| SPÖ | Social Democratic Party of Austria Sozialdemokratische Partei Österreichs |
Social democracy | Hannes Gschwentner | 25.9% | 9 / 36 | |
| GRÜNE | The Greens – The Green Alternative Die Grünen – Die Grüne Alternative |
Green politics | Georg Willi | 15.6% | 5 / 36 | |
| FPÖ | Freedom Party of Austria Freiheitliche Partei Österreichs |
Right-wing populism Euroscepticism |
Gerald Hauser | 8.0% | 2 / 36 | |
In addition to the parties already represented in the Landtag, three parties collected enough signatures to be placed on the ballot.
- Fritz Dinkhauser List (FRITZ)
- The Christians (DC)
- Communist Party of Austria (KPÖ)
Results
 | ||||||
| Party | Votes | % | +/− | Seats | +/− | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austrian People's Party (ÖVP) | 136,401 | 40.50 | –9.39 | 16 | –4 | |
| Fritz Dinkhauser List (FRITZ) | 61,795 | 18.35 | New | 7 | New | |
| Social Democratic Party of Austria (SPÖ) | 52,066 | 15.46 | –10.39 | 5 | –4 | |
| Freedom Party of Austria (FPÖ) | 41,788 | 12.41 | +4.44 | 4 | +2 | |
| The Greens – The Green Alternative (GRÜNE) | 36,136 | 10.73 | –4.86 | 4 | –1 | |
| The Christians (DC) | 4,699 | 1.40 | New | 0 | New | |
| Communist Party of Austria (KPÖ) | 3,896 | 1.16 | +0.46 | 0 | ±0 | |
| Invalid/blank votes | 5,932 | – | – | – | – | |
| Total | 342,713 | 100 | – | 36 | 0 | |
| Registered voters/turnout | 520,527 | 65.84 | +4.93 | – | – | |
| Source: Tyrolean Government | ||||||
Results by constituency
| Constituency | ÖVP | FRITZ | SPÖ | FPÖ | Grüne | Others | Total seats |
Turnout | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | S | % | S | % | S | % | S | % | S | % | |||
| Innsbruck City | 28.5 | 1 | 20.2 | 1 | 14.6 | 13.3 | 20.4 | 1 | 2.9 | 3 | 58.5 | ||
| Imst | 48.3 | 1 | 14.4 | 16.4 | 10.8 | 7.5 | 2.7 | 1 | 67.7 | ||||
| Innsbruck-Land | 36.0 | 3 | 21.6 | 1 | 15.1 | 1 | 12.4 | 1 | 12.2 | 1 | 2.7 | 7 | 68.7 |
| Kitzbühel | 42.7 | 1 | 19.0 | 16.4 | 12.4 | 7.5 | 2.1 | 1 | 64.8 | ||||
| Kufstein | 39.9 | 2 | 17.0 | 17.3 | 15.1 | 8.8 | 2.0 | 2 | 66.8 | ||||
| Landeck | 50.9 | 1 | 12.7 | 18.3 | 9.3 | 5.9 | 2.9 | 1 | 68.9 | ||||
| Lienz | 48.8 | 1 | 13.1 | 12.6 | 14.4 | 8.8 | 0.9 | 1 | 67.7 | ||||
| Reutte | 55.8 | 1 | 17.0 | 10.0 | 7.5 | 6.7 | 3.0 | 1 | 67.6 | ||||
| Schwaz | 41.6 | 1 | 20.5 | 16.4 | 11.4 | 7.7 | 2.3 | 1 | 65.4 | ||||
| Remaining seats | 4 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 18 | |||||||
| Total | 40.5 | 16 | 18.4 | 7 | 15.5 | 5 | 12.4 | 4 | 10.7 | 4 | 2.6 | 36 | 65.8 |
| Source: Tyrolean Government | |||||||||||||
Aftermath
During the election campaign, Governor van Staa had stated he would resign if the ÖVP fell below 40% of votes. The party narrowly exceeded this threshold, and van Staa was re-affirmed as ÖVP leader by the party after the election. However, his presence was a stumbling block in coalition negotiations, as both the Fritz list and Greens desired his resignation.[3][4] The ÖVP thus sought to form government with the SPÖ instead;[5] a coalition agreement was finalised on 23 June. However, van Staa announced on the same day that he would indeed resign.[2] His successor was Günther Platter, who became the new Governor.
The SPÖ's disastrous result, following losses in the recent Graz local election, compounded pressure on federal Chancellor Alfred Gusenbauer. He was replaced as federal SPÖ chairman a week after the election, and ultimately resigned as Chancellor in December.
References
- "State results - 2008 Landtag election". Tyrolean Government.
- "Tyrol: Governor Van Staa resigns". Die Presse. 23 June 2008.
- "Coalition negotiations this week: Tyrolean ÖVP explores with the SPÖ and the Greens". News.at. 16 June 2008.
- "ÖVP-Greens possible, ÖVP-SPÖ likely". ORF. 13 June 2008.
- "Tyrol: ÖVP and SPÖ start coalition negotiations". Die Presse. 18 June 2008.
.jpg.webp)
