2009 South African general election
South Africa held national and provincial elections to elect a new National Assembly as well as the provincial legislature in each province on 22 April 2009.[1]
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 400 seats to the National Assembly of South Africa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 77.30% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
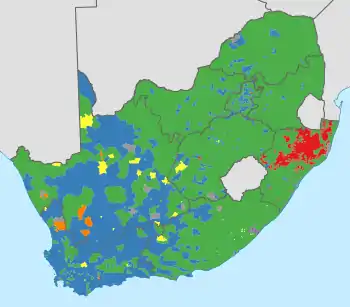 Voting districts won by each party. Green: African National Congress; Blue: Democratic Alliance; Yellow: Congress of the People; Red: Inkatha Freedom Party; Orange: Independent Democrats; Purple: United Democratic Movement; Brown: other parties; Grey: tied between two or more parties. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of South Africa |
|
|

The National Assembly consists of 400 members elected by proportional representation with a closed list approach. Two hundred members are elected from national party lists; the other 200 are elected from provincial party lists in each of the nine provinces. The President of South Africa is chosen by the National Assembly after each election; in 2009, the presidential election was on 6 May. The premiers of each province are chosen by the winning majority in each provincial legislature.
This was the fourth general election held since the end of the apartheid era.
The North Gauteng High Court ruled on 9 February 2009 that South African citizens living abroad should be allowed to vote in elections.[2] The judgment was confirmed by the Constitutional Court on 12 March 2009, when it decided that overseas voters who were already registered would be allowed to vote.[3] Also, registered voters who found themselves outside their registered voting districts on election day were permitted to vote for the national ballot at any voting station in South Africa.
Background and campaign
African National Congress – ruling party
The African National Congress was the ruling party in parliament going into the 2009 elections, having won 69.69% of the vote at the 2004 elections. During its term in office a number of internal changes occurred, the primary one being the election of Jacob Zuma to the party presidency ahead of Thabo Mbeki at the 52nd National Conference of the African National Congress held on 18 December 2007.[4] Zuma's victory in the election was partly due to the wide degree of support for him from the ANC Youth League, the South African Communist Party and the Congress of South African Trade Unions.
Subsequent to this, in 2008 Zuma's ongoing corruption trial in relation to a multi-billion Rand arms deal was dismissed by the courts, which insinuated that Mbeki had unduly influenced the investigation into Zuma. In light of the court's findings, the ANC's National Executive Committee asked Mbeki to resign as president of the country, which he duly did on 20 September 2008.
Mbeki was replaced by Kgalema Motlanthe, who had been elected as ANC deputy president at the 2007 conference. Motlanthe was not the presidential candidate of the ANC for the 2009 general election, but rather the current President of the ANC, Jacob Zuma.[5] The ANC's electoral list was led by Zuma, followed by Motlanthe, Deputy President of South Africa Baleka Mbete, finance minister Trevor Manuel and Winnie Mandela, former wife of Nelson Mandela.[6]
The recall of Mbeki, amongst other issues, created severe tensions and splits within the party, and eventually led to the formation of the Congress of the People, a new political party formed by former ANC members. Nevertheless, most pre-poll predictions gave the ANC between sixty and seventy per cent of the popular vote; even the lowest prediction, giving the ANC 47 per cent, still rendered it comfortably South Africa's most favoured political party.[7]
Democratic Alliance – official opposition
The Democratic Alliance, South Africa's main opposition party, had undergone a leadership change, with Cape Town mayor and former anti-apartheid activist Helen Zille having succeeded long-serving Tony Leon in May 2007.
With a disproportionate focus on the Western Cape province, which it had identified as winnable, the DA launched its election campaign with the slogan "Vote to Win". It released its manifesto on 14 February.[8]
The party was expected to perform strongly in the Western Cape, with analysts suggesting it would take control of the province from the ruling ANC.[9] The ANC's support in the province was on the wane, while the DA had performed well in by-elections in the province leading up to the poll.[10]
The party projected that it would govern in the Western Cape province – a task made easier by the ANC-COPE split – though it expected to need to form a governing coalition in order to do so.[11] The party anticipated that it would take control of several other major cities and towns in the 2011 local elections, and, with what it termed a "realignment of SA politics", predicted it would take its "winning streak" into the 2014 elections, when it plans to challenge for the mantle of ruling party.[12]
The DA's relationship with ANC breakaway party Cope started strongly. Cope leader Mosiuoa Lekota showed a willingness to co-operate with Zille in the future.[13][14] Subsequently, Zille criticised COPE's internal structures and suggested many of the party's new members were merely Mbeki loyalists hoping to resurrect defunct political careers.[15]
In the closing stages of the DA's campaign, it launched its "Stop Zuma" drive, which came under considerable criticism in the press—political analysts dubbing the tactic an example of "negative" politics. Zille later retorted, however, that what was really negative was the idea of handing over the right to change the Constitution unilaterally to Jacob Zuma and his "closed, crony network", as they would abuse that right both to enrich themselves and to protect themselves from prosecution. She later claimed the decline in the ANC's support base and the concomitant increase in that of her own party was a result of the DA 'Stop Zuma' campaign.
Election boycott
A number of communities, organisations, social movements and well-known personalities threatened not to vote in the 2009 elections.[16] The most well-known personality was Archbishop Desmond Tutu who at first said he would not vote but then changed his mind.[17] South Africa's Poor People's Alliance, the Anti-Privatisation Forum, NOPE, and the independent farmworkers' union Sikhula Sonke resolved to boycott the election under the banner No Land! No House! No Vote!.[18]
Results

African National Congress
Democratic Alliance
Congress of the People
Inkatha Freedom Party
Independent Democrats
United Democratic Movement
The ANC, which has been in power since 1994, obtained 65.90% of valid votes cast on the national ballot, making it just shy of being able to change the constitution. The DA retained its position as the official opposition and also won the election in the Western Cape province with an outright majority.
Some 23-million people were registered for the 2009 general elections, which was about 2.5 million more than in 2004. There was a 77.3% turnout of registered voters, 1.34% of whom spoiled their ballots rendering them invalid.[19] About 12-million people eligible to vote either did not register to vote (about 7-million), or did register but did not vote (5.4 million).[20] In this election, there was a slight decrease in voter abstention though there was at least one high-profile election and registration boycotts campaign, the No Land! No House! No Vote! Campaign.
The Independent Electoral Commission made results available on their website as they were received from voting districts, filtered by national, provincial, municipality, and voting district.[21]
National Assembly results
| Party | Leader | Votes | % | +/− | Seats | +/− from last election[lower-alpha 1] |
+/− from before this election[lower-alpha 2] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANC | Jacob Zuma | 11,650,748 | 65.90 | −3.80 | 264 | −15 | −33 | |
| Democratic Alliance | Helen Zille | 2,945,829 | 16.66 | +4.29 | 67 | +17 | +20 | |
| Congress of the People[lower-alpha 3] | Mosiuoa Lekota | 1,311,027 | 7.42 | +7.42 | 30 | +30 | +30 | |
| IFP | Mangosuthu Buthelezi | 804,260 | 4.55 | −2.42 | 18 | −10 | −5 | |
| Independent Democrats | Patricia de Lille | 162,915 | 0.92 | −0.81 | 4 | −3 | 0 | |
| UDM | Bantu Holomisa | 149,680 | 0.85 | −1.43 | 4 | −5 | −2 | |
| Freedom Front Plus | Pieter Mulder | 146,796 | 0.83 | −0.06 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |
| ACDP | Kenneth Meshoe | 142,658 | 0.81 | −0.80 | 3 | −4 | −1 | |
| United Christian Democratic Party | Lucas Mangope | 66,086 | 0.37 | −0.38 | 2 | −1 | −1 | |
| Pan Africanist Congress | Letlapa Mphahlele | 48,530 | 0.27 | −0.45 | 1 | −2 | 0 | |
| Minority Front | Amichand Rajbansi | 43,474 | 0.25 | −0.11 | 1 | −1 | −1 | |
| Azanian People's Organisation | Jacob Dikobo | 38,245 | 0.22 | −0.03 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| African People's Convention[lower-alpha 4] | Themba Godi | 35,867 | 0.20 | +0.20 | 1 | +1 | −1 | |
| Movement Democratic Party[lower-alpha 3] | 29,747 | 0.17 | +0.17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Al Jama-ah[lower-alpha 3] | 25,947 | 0.15 | +0.15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Christian Democratic Alliance[lower-alpha 5] | Theunis Botha | 11,638 | 0.07 | −0.13 | 0 | 0 | −1 | |
| National Democratic Convention[lower-alpha 6] | 10,830 | 0.06 | +0.06 | 0 | 0 | −4 | ||
| New Vision Party[lower-alpha 3] | 9,296 | 0.05 | +0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| United Independent Front[lower-alpha 6] | Nomakhaya Mdaka | 8,872 | 0.05 | +0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Great Kongress of South Africa[lower-alpha 3] | 8,271 | 0.05 | +0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| South African Democratic Congress[lower-alpha 3] | Ziba Jiyane | 6,035 | 0.03 | +0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Keep It Straight and Simple Party | 5,440 | 0.03 | −0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Pan Africanist Movement[lower-alpha 3] | 5,426 | 0.03 | +0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Alliance of Free Democrats[lower-alpha 6] | 5,178 | 0.03 | +0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Women Forward[lower-alpha 3] | 5,087 | 0.03 | +0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| National Party South Africa[lower-alpha 3] | 3,378 | 0.02 | +0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| A Party[lower-alpha 3] | 2,847 | 0.02 | +0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Total | 17,680,729 | 100.00 | 400 | |||||
| Spoilt votes | 239,237 | |||||||
Provincial legislature results
The following table summarises the results of the elections to the provincial legislatures. The majority party in each province is indicated in bold.
| Party | EC | FS | G | KZN | L | M | NW | NC | WC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANC | 44 | 22 | 47 | 51 | 43 | 27 | 25 | 19 | 14 | |
| Democratic Alliance | 6 | 3 | 16 | 7 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 22 | |
| Congress of the People | 9 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 3 | |
| IFP | 1 | 18 | ||||||||
| Independent Democrats | 1 | 2 | 2 | |||||||
| ACDP | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| UDM | 3 | |||||||||
| Freedom Front Plus | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| Minority Front | 2 | |||||||||
| United Christian Democratic Party | 2 | |||||||||
| African Independent Congress | 1 | |||||||||
| Total | 63 | 30 | 73 | 80 | 49 | 30 | 33 | 30 | 42 | |
Eastern Cape
| Party | Votes | % | +/− | Seats | +/− from last election[lower-alpha 1] |
+/− from before this election[lower-alpha 2] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANC | 1,552,676 | 68.82 | −10.45 | 44 | −7 | −9 | |
| Congress of the People[lower-alpha 3] | 308,439 | 13.67 | +13.67 | 9 | +9 | +9 | |
| Democratic Alliance | 225,310 | 9.99 | +2.65 | 6 | +1 | +1 | |
| UDM | 93,196 | 4.13 | −5.10 | 3 | −3 | −1 | |
| African Independent Congress[lower-alpha 3] | 17,306 | 0.77 | +0.77 | 1 | +1 | +1 | |
| Pan Africanist Congress | 12,108 | 0.54 | −0.46 | 0 | −1 | 0 | |
| ACDP | 11,974 | 0.53 | −0.25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Independent Democrats | 10,466 | 0.46 | −0.31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Azanian People's Organisation | 4,598 | 0.20 | +0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| African People's Convention[lower-alpha 4] | 4,517 | 0.20 | +0.20 | 0 | 0 | −1 | |
| Freedom Front Plus | 4,428 | 0.20 | −0.06 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| IFP | 2,270 | 0.10 | −0.10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| National Democratic Convention[lower-alpha 6] | 2,027 | 0.09 | +0.09 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pan Africanist Movement[lower-alpha 3] | 1,921 | 0.09 | +0.09 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| United Christian Democratic Party | 1,908 | 0.08 | −0.04 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Christian Democratic Alliance[lower-alpha 3] | 1,663 | 0.07 | +0.07 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| New Vision Party[lower-alpha 3] | 1,281 | 0.06 | +0.06 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 2,256,088 | 100.00 | 63 | ||||
| Spoilt votes | 32,299 | ||||||
Free State
| Party | Votes | % | +/− | Seats | +/− [lower-alpha 7] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANC | 734,688 | 71.10 | −10.68 | 22 | −3 | ||
| Congress of the People[lower-alpha 3] | 120,018 | 11.61 | +11.61 | 4 | +4 | ||
| Democratic Alliance | 119,844 | 11.60 | +3.12 | 3 | 0 | ||
| Freedom Front Plus | 20,780 | 2.01 | −0.45 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Dikwankwetla Party | 11,257 | 1.09 | +0.12 | 0 | 0 | ||
| ACDP | 7,556 | 0.73 | −0.57 | 0 | −1 | ||
| UDM | 3,722 | 0.36 | −0.52 | 0 | 0 | ||
| United Christian Democratic Party | 3,459 | 0.33 | −0.44 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Pan Africanist Congress | 3,449 | 0.33 | −0.85 | 0 | 0 | ||
| African People's Convention[lower-alpha 4] | 3,200 | 0.31 | +0.31 | 0 | 0 | ||
| IFP | 2,232 | 0.22 | −0.14 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Independent Democrats | 1,654 | 0.16 | −0.36 | 0 | 0 | ||
| National Democratic Convention[lower-alpha 6] | 1,065 | 0.10 | +0.10 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Peace and Justice Congress[lower-alpha 3] | 398 | 0.04 | +0.04 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Total | 1,033,322 | 100.00 | 30 | ||||
| Spoilt votes | 15,744 | ||||||
Gauteng
| Party | Votes | % | +/− | Seats | +/− from last election[lower-alpha 1] |
+/− from before this election[lower-alpha 2] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANC | 2,662,013 | 64.04 | −4.36 | 47 | −4 | −4 | |
| Democratic Alliance | 908,616 | 21.86 | +1.08 | 16 | +1 | +3 | |
| Congress of the People[lower-alpha 3] | 323,327 | 7.78 | +7.78 | 6 | +6 | +6 | |
| Freedom Front Plus | 67,660 | 1.63 | +0.29 | 1 | 0 | −1 | |
| IFP | 61,856 | 1.49 | −1.02 | 1 | −1 | −1 | |
| ACDP | 36,099 | 0.87 | −0.77 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Independent Democrats | 25,243 | 0.61 | −0.92 | 1 | 0 | −1 | |
| UDM | 16,480 | 0.40 | −0.59 | 0 | −1 | 0 | |
| Pan Africanist Congress | 12,880 | 0.31 | −0.54 | 0 | −1 | 0 | |
| United Christian Democratic Party | 10,091 | 0.24 | −0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Azanian People's Organisation | 8,927 | 0.21 | −0.04 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Movement Democratic Party[lower-alpha 3] | 5,731 | 0.14 | +0.14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| African People's Convention[lower-alpha 4] | 5,123 | 0.12 | +0.12 | 0 | 0 | −1 | |
| Christian Democratic Alliance[lower-alpha 8] | 2,901 | 0.07 | −0.16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| African Christian Alliance[lower-alpha 3] | 2,541 | 0.06 | +0.06 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Women Forward[lower-alpha 3] | 1,974 | 0.05 | +0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Great Kongress of South Africa[lower-alpha 3] | 1,909 | 0.05 | +0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| National Democratic Convention[lower-alpha 6] | 1,497 | 0.04 | +0.04 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Alliance of Free Democrats[lower-alpha 6] | 1,101 | 0.03 | +0.03 | 0 | 0 | −1 | |
| New Vision Party[lower-alpha 3] | 1,079 | 0.03 | +0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 4,157,048 | 100.00 | 73 | ||||
| Spoilt votes | 42,815 | ||||||
KwaZulu-Natal
| Party | Votes | % | +/− | Seats | +/− from last election[lower-alpha 1] |
+/− from before this election[lower-alpha 2] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANC | 2,192,516 | 62.95 | +15.97 | 51 | +13 | +10 | |
| IFP | 780,027 | 22.40 | −14.42 | 18 | −12 | −9 | |
| Democratic Alliance | 318,559 | 9.15 | +0.80 | 7 | 0 | +2 | |
| Minority Front | 71,507 | 2.05 | −0.56 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| Congress of the People[lower-alpha 3] | 44,890 | 1.29 | +1.29 | 1 | +1 | +1 | |
| ACDP | 23,537 | 0.68 | −1.11 | 1 | −1 | 0 | |
| UDM | 7,953 | 0.23 | −0.52 | 0 | −1 | −1 | |
| Al Jama-ah[lower-alpha 3] | 7,612 | 0.22 | +0.22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| National Democratic Convention[lower-alpha 6] | 6,881 | 0.20 | +0.20 | 0 | 0 | −3 | |
| Independent Democrats | 6,853 | 0.20 | −0.30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Freedom Front Plus | 5,760 | 0.17 | −0.12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| African People's Convention[lower-alpha 4] | 5,087 | 0.15 | +0.15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| South African Democratic Congress[lower-alpha 3] | 3,883 | 0.11 | +0.11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pan Africanist Congress | 2,578 | 0.07 | −0.11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Women Forward[lower-alpha 3] | 1,816 | 0.05 | +0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| United Christian Democratic Party | 1,798 | 0.05 | −0.09 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Great Kongress of South Africa[lower-alpha 3] | 1,730 | 0.05 | +0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 3,482,987 | 100.00 | 80 | ||||
| Spoilt votes | 43,713 | ||||||
Limpopo
| Party | Votes | % | +/− | Seats | +/− from last election[lower-alpha 1] |
+/− from before this election[lower-alpha 2] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANC | 1,265,631 | 84.88 | −4.30 | 43 | −2 | −3 | |
| Congress of the People[lower-alpha 3] | 112,325 | 7.53 | +7.53 | 4 | +4 | +4 | |
| Democratic Alliance | 51,856 | 3.48 | −0.11 | 2 | 0 | +1 | |
| ACDP | 10,246 | 0.69 | −0.58 | 0 | −1 | −1 | |
| Freedom Front Plus | 9,035 | 0.61 | +0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pan Africanist Congress | 7,934 | 0.53 | −0.41 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| New Vision Party[lower-alpha 3] | 6,497 | 0.44 | +0.44 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Azanian People's Organisation | 5,640 | 0.38 | −0.13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| UDM | 5,193 | 0.35 | −1.37 | 0 | −1 | 0 | |
| African People's Convention[lower-alpha 4] | 4,455 | 0.30 | +0.30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Ximoko Party | 3,452 | 0.23 | −0.36 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| United Independent Front[lower-alpha 6] | 1,769 | 0.12 | +0.12 | 0 | 0 | −1 | |
| Black Consciousness Party[lower-alpha 3] | 1,432 | 0.10 | +0.10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Independent Democrats | 1,333 | 0.09 | −0.08 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| United Christian Democratic Party | 1,320 | 0.09 | −0.13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Alliance of Free Democrats[lower-alpha 6] | 1,041 | 0.07 | +0.07 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Women Forward[lower-alpha 3] | 977 | 0.07 | +0.07 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| IFP[lower-alpha 3] | 936 | 0.06 | +0.06 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 1,491,072 | 100.00 | 49 | ||||
| Spoilt votes | 22,549 | ||||||
Mpumalanga
| Party | Votes | % | +/− | Seats | +/− from last election[lower-alpha 1] |
+/− from before this election[lower-alpha 2] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANC | 1,110,190 | 85.55 | −0.76 | 27 | 0 | 0 | |
| Democratic Alliance | 97,204 | 7.49 | +0.55 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| Congress of the People[lower-alpha 3] | 37,789 | 2.91 | +2.91 | 1 | +1 | +1 | |
| Freedom Front Plus | 11,590 | 0.89 | −0.34 | 0 | −1 | 0 | |
| ACDP | 6,565 | 0.51 | −0.58 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| IFP | 6,540 | 0.50 | −0.45 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Sindawonye Progressive Party | 6,423 | 0.49 | −0.04 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| African People's Convention[lower-alpha 4] | 4,834 | 0.37 | +0.37 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pan Africanist Congress | 4,097 | 0.32 | −0.37 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| UDM | 3,366 | 0.26 | −0.74 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Azanian People's Organisation | 2,928 | 0.23 | +0.04 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Christian Party[lower-alpha 6] | 2,435 | 0.19 | +0.19 | 0 | 0 | −1 | |
| Independent Democrats | 1,527 | 0.12 | −0.19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| National Democratic Convention[lower-alpha 6] | 1,374 | 0.11 | +0.11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| United Christian Democratic Party | 913 | 0.07 | −0.10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 1,297,775 | 100.00 | 30 | ||||
| Spoilt votes | 19,119 | ||||||
North West
| Party | Votes | % | +/− | Seats | +/− [lower-alpha 7] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANC | 783,794 | 72.89 | −7.82 | 25 | −2 | ||
| Congress of the People[lower-alpha 3] | 89,573 | 8.33 | +8.33 | 3 | +3 | ||
| Democratic Alliance | 88,728 | 8.25 | +3.25 | 3 | +1 | ||
| United Christian Democratic Party | 56,678 | 5.27 | −3.22 | 2 | −1 | ||
| Freedom Front Plus | 19,463 | 1.81 | +0.49 | 0 | −1 | ||
| ACDP | 7,366 | 0.69 | −0.48 | 0 | 0 | ||
| UDM | 5,467 | 0.51 | −0.46 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Independent Democrats | 4,984 | 0.46 | +0.02 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Movement Democratic Party[lower-alpha 3] | 4,432 | 0.41 | +0.41 | 0 | 0 | ||
| African People's Convention[lower-alpha 4] | 3,116 | 0.29 | +0.29 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Pan Africanist Congress | 2,831 | 0.26 | −0.58 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Azanian People's Organisation | 2,712 | 0.25 | −0.03 | 0 | 0 | ||
| South African Political Party[lower-alpha 3] | 1,832 | 0.17 | +0.17 | 0 | 0 | ||
| African Christian Alliance[lower-alpha 3] | 1,750 | 0.16 | +0.16 | 0 | 0 | ||
| IFP | 1,619 | 0.15 | −0.10 | 0 | 0 | ||
| National Democratic Convention[lower-alpha 6] | 978 | 0.09 | +0.09 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Total | 1,075,323 | 100.00 | 33 | ||||
| Spoilt votes | 21,007 | ||||||
Northern Cape
| Party | Votes | % | +/− | Seats | +/− from last election[lower-alpha 1] |
+/− from before this election[lower-alpha 2] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANC | 245,699 | 60.75 | −8.08 | 19 | −2 | −6 | |
| Congress of the People[lower-alpha 3] | 67,416 | 16.67 | +16.67 | 5 | +5 | +5 | |
| Democratic Alliance | 50,817 | 12.57 | +1.49 | 4 | +1 | +2 | |
| Independent Democrats | 19,995 | 4.94 | −2.11 | 2 | 0 | +1 | |
| Freedom Front Plus | 5,034 | 1.24 | −0.31 | 0 | −1 | −1 | |
| United Christian Democratic Party | 4,889 | 1.21 | +0.88 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| ACDP | 4,041 | 1.00 | −0.88 | 0 | −1 | −1 | |
| Azanian People's Organisation | 2,439 | 0.60 | +0.09 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| African People's Convention[lower-alpha 4] | 1,364 | 0.34 | +0.34 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pan Africanist Congress | 882 | 0.22 | −0.22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| IFP | 757 | 0.19 | −0.05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| UDM | 604 | 0.15 | −0.30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Christian Democratic Alliance[lower-alpha 3] | 481 | 0.12 | +0.12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 404,418 | 100.00 | 30 | ||||
| Spoilt votes | 6,190 | ||||||
Western Cape
| Party | Votes | % | +/− | Seats | +/− from last election[lower-alpha 1] |
+/− from before this election[lower-alpha 2] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic Alliance | 1,012,568 | 51.46 | +24.35 | 22 | +10 | +11 | |
| ANC | 620,918 | 31.55 | −13.70 | 14 | −5 | −13 | |
| Congress of the People[lower-alpha 3] | 152,356 | 7.74 | +7.74 | 3 | +3 | +3 | |
| Independent Democrats | 92,116 | 4.68 | −3.16 | 2 | −1 | +1 | |
| ACDP | 28,995 | 1.47 | −1.97 | 1 | −1 | −1 | |
| UDM | 14,013 | 0.71 | −1.04 | 0 | −1 | 0 | |
| Al Jama-ah[lower-alpha 3] | 9,039 | 0.46 | +0.46 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Freedom Front Plus | 8,384 | 0.43 | −0.19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pan Africanist Congress | 4,467 | 0.23 | −0.19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Africa Muslim Party | 4,333 | 0.22 | −0.48 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Christian Democratic Alliance[lower-alpha 9] | 3,987 | 0.20 | −0.47 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| National Party[lower-alpha 3] | 3,378 | 0.17 | +0.17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Cape Party[lower-alpha 3] | 2,552 | 0.13 | +0.13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| National Alliance[lower-alpha 4] | 1,996 | 0.10 | +0.10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| African People's Convention[lower-alpha 4] | 1,778 | 0.09 | +0.09 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| United Christian Democratic Party | 1,552 | 0.08 | −0.15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Azanian People's Organisation | 1,291 | 0.07 | −0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| United Independent Front[lower-alpha 6] | 1,178 | 0.06 | +0.06 | 0 | 0 | −1 | |
| IFP | 1,158 | 0.06 | −0.08 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Peace and Justice Congress | 630 | 0.03 | −0.18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Universal Party | 599 | 0.03 | −0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| National Democratic Convention[lower-alpha 6] | 463 | 0.02 | +0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 1,967,751 | 100.00 | 42 | ||||
| Spoilt votes | 20,026 | ||||||
NCOP seats
The National Council of Provinces (NCOP) consists of 90 members, ten elected by each provincial legislature. The Members of NCOP have to be elected in proportion to the party membership of the provincial legislature.
| Party | Delegate type | Province | Total | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC | FS | G | KZN | L | M | NW | NC | WC | |||||
| ANC | Permanent | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 35 | 62 | |
| Special | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 27 | |||
| Democratic Alliance | Permanent | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 10 | 13 | ||
| Special | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||||||||
| Congress of the People | Permanent | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 | 8 | |||
| Special | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Independent Democrats | Permanent | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||
| Special | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||
| IFP | Permanent | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||
| Special | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Freedom Front Plus | Special | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| United Christian Democratic Party | Special | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| UDM | Special | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Total | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 90 | |||
Aftermath
The ANC received widespread congratulations for its decisive national victory, both from international and domestic sources. This included the opposition, with DA leader Helen Zille acknowledging that the people had given it a strong mandate to rule. "We trust that the ANC will not abuse this confidence, and will govern well and in the interests of all South Africans."[32] However, with 65.9% of the vote and 264 seats in the National Assembly (down from 74.3% and 297 seats), the ANC no longer had the two-thirds majority it needed to change the Constitution unilaterally. The governing party had lost considerable support in 8 of the 9 provinces, partially compensated for by a big increase in KwaZulu-Natal at the expense of the IFP.
Thanking supporters the following week,[33] DA leader Helen Zille related proudly that her party had achieved all three of its primary objectives: it had kept the ANC below a two-thirds majority (albeit only just), won an outright majority in the Western Cape and significantly improved its standing in parliament.[34] Zille saw the results as a vindication of the party's statement at the beginning of its campaign that the only two genuine political forces in South Africa were the DA and the ANC, with the latter losing support while the former consistently gained it, and voters refusing to waste their ballots on small, insignificant parties.
Notes to the tables
- Change in seats compared to the composition of the legislature after the election of 14 April 2004.
- Change in seats compared to the composition of the legislature after the second floor-crossing period that ended on 15 September 2007.
- Party did not contest the previous election to this legislature.
- Party did not contest the previous election to this legislature, having been created during the floor-crossing period of 2007.
- Successor to the Christian Democratic Party, the Federation of Democrats and the New Labour Party in this legislature.
- Party did not contest the previous election to this legislature, having been created during the floor-crossing period of 2005.
- No members of this legislature crossed the floor during the 2005 or 2007 floor-crossing periods.
- Successor to the Christian Democratic Party in this legislature.
- Successor to the New Labour Party in this legislature.
See also
References
- Motlanthe sets election date IOL.co.za, 10 February 2009
- "Court backs S Africa expat vote". BBC News. 9 February 2009. Retrieved 23 May 2010.
- South African registered overseas voters can vote - People's Daily Online
- (Press Statement: Results for the Election of ANC Officials, 19 December 2007) Archived 29 June 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- http://www.anc.org.za/show.php?doc=./ancdocs/pr/2008/pr0108.html Archived 24 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine (Statement of the ANC National Executive Committee, 8 January 2008.) The ANC National Executive Committee confirmed that "the ANC President will lead the ANC election campaign as the organisation's candidate for president of South Africa in the 2009 election."
- Winnie set for shock comeback to ANC politics
- Perry, Alex. "South African Election: Why It Matters." TIME. 21 April 2009. . Retrieved 21 April 2009.
- "DA election launch in Soweto". News24. 15 January 2009.
- "Minorities become important as polls loom". IOL. 7 September 2008. Retrieved 2 July 2009.
- "DA: Helen Zille, leader of the Democratic Alliance, on the party's victory in the Western Cape by-elections". Archived from the original on 4 June 2009.
- "DA sets its sights on governing Western Cape". SABC. 12 November 2008. Archived from the original on 29 June 2011. Retrieved 13 April 2016.
- "DA plans to rule SA from 2014". IOL. 11 November 2008.
- "Lekota open to DA Alliance". IOL. 19 November 2008.
- "Zille backs Lekota's views". IOL. 19 November 2008.
- "Zille slams COPE as a ploy to resurrect political careers". 10 January 2009.
-
- "60 landless people arrested". The Sowetan.
- "Protesters refuse to vote". IOL.
- "'One house, one vote' for South Africans". BBC. 21 April 2009. Retrieved 4 January 2010.
- "'No land, no home, no vote'". Weekend Argus.
- "Feeling of change in the West Coast air". Cape Argus.
-
- "Tutu: Why I Won't Vote". TheTimes. Archived from the original on 8 October 2008. Retrieved 24 April 2009.
- "Tutu decides to vote". IOL.
-
- "Elections: A Dangerous Time for Poor People's Movements in South Africa". SACSIS. Archived from the original on 28 April 2011. Retrieved 21 April 2009.
- ""No Vote" Campaigns are not a Rejection of Democracy". Mail and Guardian.
- "Farm Workers Announce Election Boycott". AllAfrica.
- "Why we refuse to vote". Cape Argus. Archived from the original on 24 April 2009. Retrieved 21 April 2009.
- "NOPE our dreams don't fit on your ballots". Archived from the original on 26 March 2009.
- "Grassroots movements plan to boycott South African poll". ekklesia.
- "Tutu: Why Steve Biko wouldn't vote". Pambazuka.
- "Nope your vote doesn't make a difference". Polity. Archived from the original on 27 April 2009. Retrieved 24 April 2009.
- "Farm workers threaten boycott elections". Polity.
- "IEC Election Report 2009". IEC. Retrieved 21 April 2014.
- "Building a base for a credible opposition". SundayTribune. 3 May 2009.
- Independent Electoral Commission
- "April 22, 2009 General Election Results - Republic of South Africa Totals". Election Resources on the Internet. Retrieved 24 December 2010.
- "April 22, 2009 General Election Results - Eastern Cape". Election Resources on the Internet. Retrieved 24 December 2010.
- "April 22, 2009 General Election Results - Free State". Election Resources on the Internet. Retrieved 24 December 2010.
- "April 22, 2009 General Election Results - Gauteng". Election Resources on the Internet. Retrieved 24 December 2010.
- "April 22, 2009 General Election Results - KwaZulu-Natal". Election Resources on the Internet. Retrieved 24 December 2010.
- "April 22, 2009 General Election Results - Limpopo". Election Resources on the Internet. Retrieved 24 December 2010.
- "April 22, 2009 General Election Results - Mpumalanga". Election Resources on the Internet. Retrieved 24 December 2010.
- "April 22, 2009 General Election Results - North West". Election Resources on the Internet. Retrieved 24 December 2010.
- "April 22, 2009 General Election Results - Northern Cape". Election Resources on the Internet. Retrieved 24 December 2010.
- "April 22, 2009 General Election Results - Western Cape". Election Resources on the Internet. Retrieved 24 December 2010.
- https://www.da.org.za/archive/sa-today-thank-you-for-voting-for-change/
- http://www.politicsweb.co.za/news-and-analysis/we-fulfilled-our-key-objectives--helen-zille
- http://www.politicsweb.co.za/news-and-analysis/we-fulfilled-our-key-objectives--helen-zille

.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)

