AMD K6-III
The K6-III (code name: "Sharptooth") was an x86 microprocessor line manufactured by AMD that launched on February 22, 1999. The launch consisted of both 400 and 450 MHz models and was based on the preceding K6-2 architecture. Its improved 256 KB on-chip L2 cache gave it significant improvements in system performance over its predecessor the K6-2. The K6-III was the last processor officially released for desktop Socket 7 systems, however later mobile K6-III+ and K6-2+ processors could be run unofficially in certain socket 7 motherboards if an updated BIOS was made available for a given board.
 | |
| General information | |
|---|---|
| Launched | February 22, 1999 |
| Discontinued | end of 2003 [1] |
| Common manufacturer(s) | |
| Performance | |
| Max. CPU clock rate | 333 MHz to 550 MHz |
| FSB speeds | 66 MHz to 100 MHz |
| Architecture and classification | |
| Min. feature size | 0.25μm to 0.18μm |
| Microarchitecture | x86 |
| Instruction set | MMX, 3DNow!, Enhanced 3DNow! (K6-III+) |
| Physical specifications | |
| Cores |
|
| Socket(s) | |
| Products, models, variants | |
| Core name(s) |
|
| History | |
| Predecessor | K6-2 |
| Successor | Athlon |
At its release, the fastest available desktop processor from Intel was the Pentium II 450 MHz, and in integer application benchmarks a 400 MHz K6-III was able to beat it as the fastest processor available for business applications.[2] Just days later on February 26 Intel released the Pentium III "Katmai" line at speeds of 500 MHz, slightly faster than the K6-III 450 MHz. However a K6-III system when equipped with a 1MB L3 cache on the motherboard was found by Ars Technica to allow the 400 and 450 MHz K6-IIIs to often outperform[3] the more expensive Pentium III "Katmai" 450- and 500-MHz models, respectively.
It is important to note however that Intel retained the lead in 3D gaming performance. Many popular first person games at the time were specifically tuned to extract maximum performance from Intel's pipelined floating point unit in drawing their 3D environments. Since the K6-III inherits the same floating point unit as the K6-2 (low latency but not pipelined), unless the game was updated to use AMD's 3D-Now! SIMD instructions - performance could still remain significantly lower than when run on Intel.
Architecture
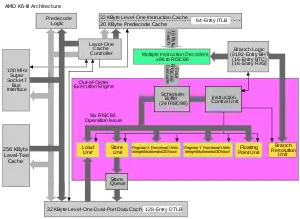
In conception, the design is simple: it was a K6-2 with on-die 256KiB L2 cache. In execution, however, the design was not simple, with 21.4 million transistors. The pipeline was short compared to that of the Pentium III and thus the design did not scale well past 500 MHz. Nevertheless, the K6-III 400 sold well, and the AMD K6-III 450 was clearly the fastest x86 chip on the market on introduction, comfortably outperforming AMD K6-2s and Intel Pentium IIs.[4]
3DNow!
3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). It added single instruction multiple data (SIMD) instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications. The first microprocessor to implement 3DNow was the AMD K6-2, which was introduced in 1998.
The K6-III+ had the "Enhanced 3DNow!"(Extended 3DNow! or 3DNow+) which added 5 new DSP instructions, but not the 19 new extended MMX instructions.
TriLevel Cache
The original K6-2 had a 64 KB primary cache and a much larger amount of motherboard-mounted cache (usually 512 KB or 1024 KB but varying depending on the choice of motherboard). The K6-III, with its 256 KB on-die secondary cache, re-purposed the variable-size external cache on the motherboard as the L3 cache. This scheme was termed "TriLevel Cache" by AMD. The L3 cache has a capacity of up to 2 MB.
%2540AMD-K6-III%252B_400ATZ%25401.6V_CORE_A_0336WPBW_1999_AMD_DSCx8_polysilicon%2540macrolens.jpg.webp) Die shot of an AMD K6-III+ 400ATZ processor
Die shot of an AMD K6-III+ 400ATZ processor_-_(cpuid591)%2540AMD-K6-III_450AHX%25402.4V_CORE_B_9931FPDW_1998_AMD_DSCx8_polysilicon%2540macrolens.jpg.webp) Die shot of an AMD-K6-III 450AHX processor
Die shot of an AMD-K6-III 450AHX processor
Market performance
Intel's Pentium II replacement was not yet available but, as a stop-gap, Intel introduced a modestly revised version of the Pentium II and re-badged it as the "Pentium III". The base design was unchanged (the addition of SSE instructions was at that time of no performance significance) but Intel's new production process allowed clockspeed improvements, and it became difficult to determine which company's part was the faster.
Both firms were keen to establish a clear lead, and both experienced manufacturing problems with their higher-frequency parts. AMD chose not to sell a 500 MHz or faster K6-III after the rare 500 MHz K6-III had been immediately recalled; it was found to be drawing enough current to damage some motherboards. AMD preferred to concentrate on their soon-to-be-released Athlon instead. Intel produced a 550 MHz Pentium III with some success but their 600 MHz version had reliability issues and was soon recalled.
With the release of the Athlon, the K6-III became something of an orphan. No longer a competitive CPU in its intended market segment, it nevertheless required substantial manufacturing resources to produce: in spite of its 21.4 million transistors, its 118 mm² die was considerably smaller than the 184 mm² of the 22-million-transistor Athlon (cache RAM taking much less area per-transistor than logic), but the K6-III was still significantly more costly to produce than the 81 mm² 9.3 million-transistor K6-2 CPUs. (roughly 2/3 the size of the K6-III) For a time, the K6-III was a low priority part for AMD—something to be made only when all orders for high-priced Athlons and cheap-to-produce K6-2s had been filled—and it became difficult to obtain in significant quantities.
The original K6-III went out of production when Intel released their "Coppermine" Pentium III (a much improved part that used an on-die cache) and, at the same time, switched to a new production process. The changeover was fraught with difficulties and Intel CPUs were in global short supply for 12 months or more. This, coupled with the better performance of the Athlon, resulted in even many former Intel-only manufacturers ordering Athlon parts, and stretched AMD's manufacturing facilities to the limit. In consequence, AMD stopped making the K6-III in order to leave more room to manufacture Athlons (and K6-2s).
K6-III+ and K6-2+
By the time the x86 CPU shortage was over, AMD had developed and released revised members of the K6 family. These K6-2+ and K6-III+ variants were specifically designed as low-power mobile (laptop) CPUs, and significantly marked the transition of the K6 architecture (and foretold of AMD's future K7 project) to the new 180 nm production process. Functionally, both parts were die shrunk K6-IIIs (the 2+ disabled 128 KiB of cache, the III+ had the full 256 KiB) and introduced AMD's new PowerNow! power saving technology. PowerNow! offered processor power savings for mobile applications by measuring computational load, and reduced processor operational voltage and frequency during idle periods in order to reduce overall system power consumption.
Although intended for notebook computers, both parts found an enthusiast following also in desktop systems as some motherboard companies (such as Gigabyte and FIC) provided BIOS updates for their desktop motherboards to allow usage of these processors. For other officially not supported mainboards, the enthusiast community created unofficial BIOS updates on their own.[5][6][7] These boards became firm favorites within the overclocking community. Both the K6-III+ and K6-2+ 450 MHz CPUs were routinely overclocked to over 600 MHz (112*5.5=616). Unfortunately, even with the 180 nm process shrink, the K6 architecture's short 6-stage pipeline while efficient, was difficult to scale with regards to clock speed. K6 III+ and 2+ were never offered higher than 570 MHz officially, and overclocking efforts using air cooling achieved a maximum around 800 MHz (133x6) at best - however this constraint was also exacerbated by a lack of Socket 7 motherboards supporting stable speeds over 112 MHz FSB.
As AMD's marketing resources at the time were focused on the launch of the upcoming Athlon K7 processor line, the 180 nm K6 series were relatively unknown outside of the industry.
Features
CPU features table
Models
K6-III ("Sharptooth", K6-3D+, 250 nm)

_400AHX_Stack-DSC08639-DSC08653_-_ZS-PMax_(22848898849).jpg.webp)
- CPU ID: AuthenticAMD Family 5 Model 9
- L1-Cache: 32 + 32 KiB (Data + Instructions)
- L2-Cache: 256 KiB, full speed
- MMX, 3DNow!
- Socket 7, Super7
- Front side bus: 66/100, 100 MHz
- VCore: 2.2 V, 2.4 V
- First release: February 22, 1999
- Manufacturing process: 0.25 μm
- Clockrate: 333, 400, 450 MHz
K6-III-P (250 nm, mobile)
- CPU ID: AuthenticAMD Family 5 Model 9
- L1-Cache: 32 + 32 KiB (Data + Instructions)
- L2-Cache: 256 KiB, full speed
- MMX, 3DNow!
- Socket 7, Super7
- Front side bus: 66, 95, 96.2, 66/100, 100 MHz
- VCore: 2.0 V, 2.2 V
- First release: May 31, 1999
- Manufacturing process: 0.25 μm
- Clockrate: 350, 366, 380, 400, 433, 450, 475 MHz
K6-2+ (180 nm, mobile)

- CPU ID: AuthenticAMD Family 5 Model 13
- L1-Cache: 32 + 32 KiB (Data + Instructions)
- L2-Cache: 128 KiB, full speed
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!, PowerNow!
- Super Socket 7
- Front side bus: 95, 97, 100 MHz
- VCore: 2.0 V
- First release: April 18, 2000
- Manufacturing process: 0.18 μm
- Clockrate: 450, 475, 500, 533, 550 MHz. (570 MHz, undocumented)
K6-III+ (180 nm, mobile)

- CPU ID: AuthenticAMD Family 5 Model 13
- L1-Cache: 32 + 32 KiB (Data + Instructions)
- L2-Cache: 256 KiB, full speed
- MMX, Extended 3DNow!, PowerNow!
- Super7
- Front side bus: 95, 100 MHz
- VCore: 2.0 V, (1.6 V, 1.8 V low voltage types)
- First release: April 18, 2000
- Manufacturing process: 0.18 μm
- Clockrate: 400, 450, 475, 500 MHz. (550 MHz, undocumented)
References
- AMD to kill K6, K6-II, K6-III
- https://www.theregister.co.uk/1999/02/24/intel_pentium_iii_vs_amd/
- "Ars Technica: Intel vs. AMD - (10/99)". arstechnica.com. Retrieved 2018-09-13.
- AMD K6-3 Review - Windows 98 Performance Comparison by Anand Lal Shimpi on anandtech.com
- M577 BIOS 03/06/1999 with K6-2+/III+ & HDD up to 128GB by Ondrej Zary on rainbow-software.org
- Award BIOS Modifications by Petr Soucek on ryston.cz
- K6plus by Jan Steunebrink on inter.nl.net
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to AMD K6-III. |
- AMD-K6-III Processor AMD (archived)
- AMD K6-III-P Mobile Product Brief AMD (archived)
- AMD K6-III+ Mobile Product Brief AMD (archived)
- Socket 7: Fit For Years To Come! at Tom's Hardware
- Recipe For Revival: K6-2+ at AcesHardware.Com (archived)
- K6-III+: Super-7 to the Limit at AcesHardware.Com (archived)